L12 Introduction of the Transposable Elements
Transposition: An Overview
Transposition involves the integration of small segments of DNA into the chromosome
- This can occur at many different locations within the genome
These small, mobile DNA segments are termed transposable elements (TEs)
- Sometimes referred to as “jumping genes”
TEs were first identified by Barbara McClintock in the early 1950s from her classical studies in corn
- Since then, many different types of TEs have been found in species as diverse as bacteria, fungi, plants and animals
Transposition Pathways
Many transposable elements have been found in bacteria, fungi, plant and animal cells
Three general types of transposition pathways have been identified
Simple or conservative transposition (cut-and-paste transposition)
Replicative transposition
Retrotransposition
一、Simple Transposition
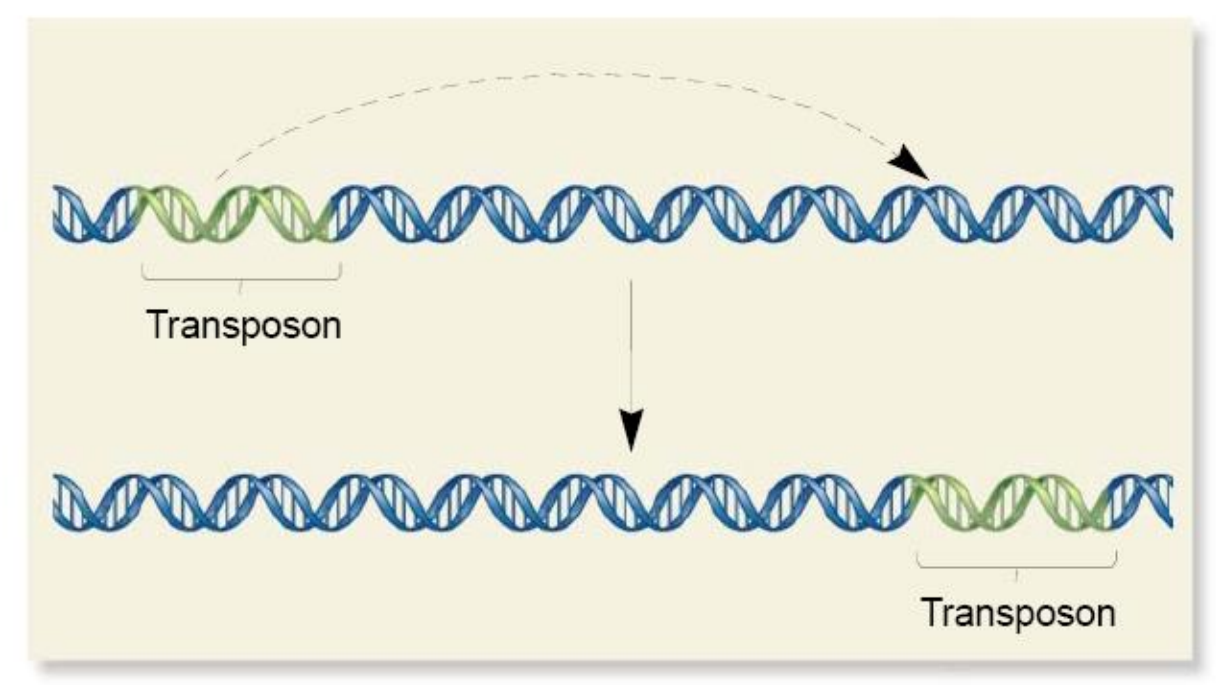
This mechanism is also called “cut-and-paste”
It is widely found in bacteria and eukaryotes
Insertion Sequence
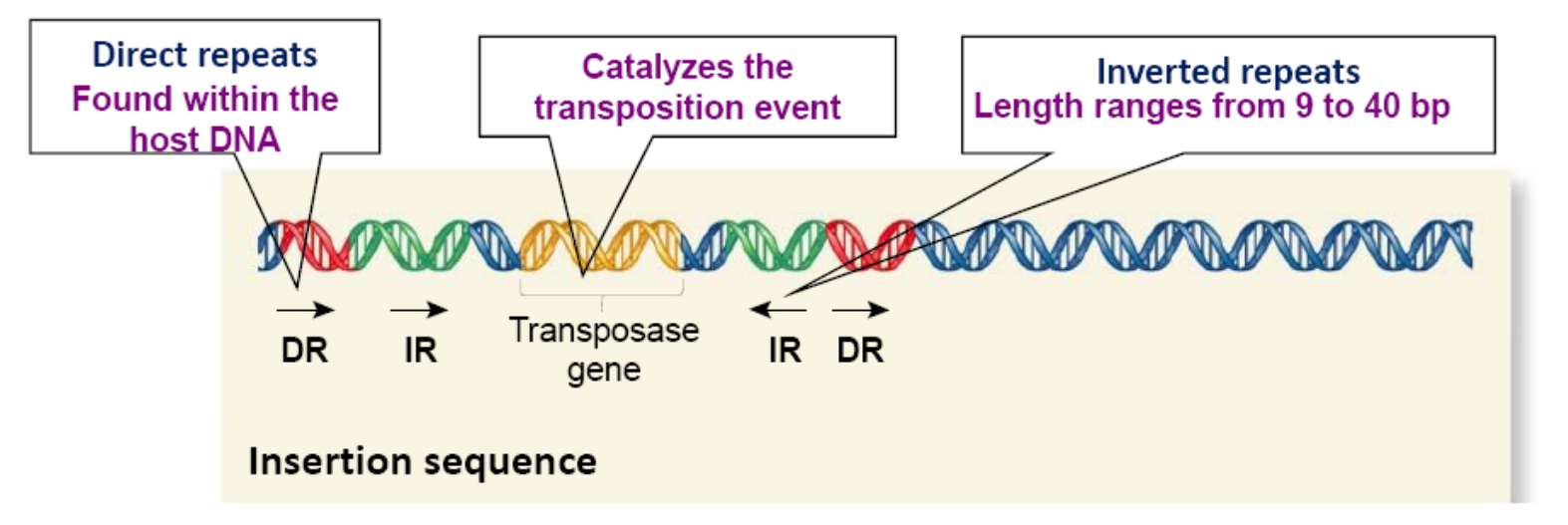
Inverted repeats (IR) are DNA sequences that are identical (or very similar) but run in opposite directions, such as

Composite Transposon
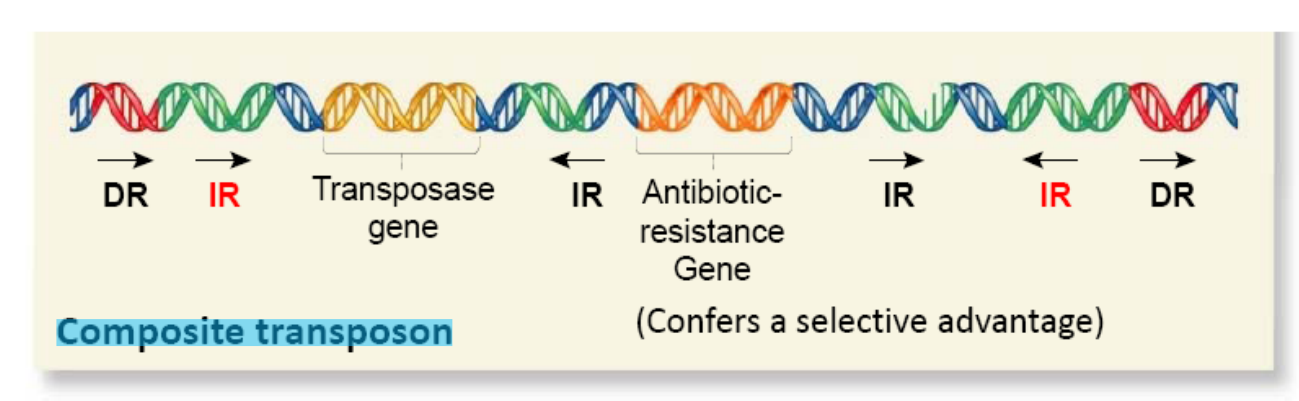
Contain additional genes that are not necessary for transposition per se
Only the two inverted repeats at the end of the transposon are involved in the transposition event
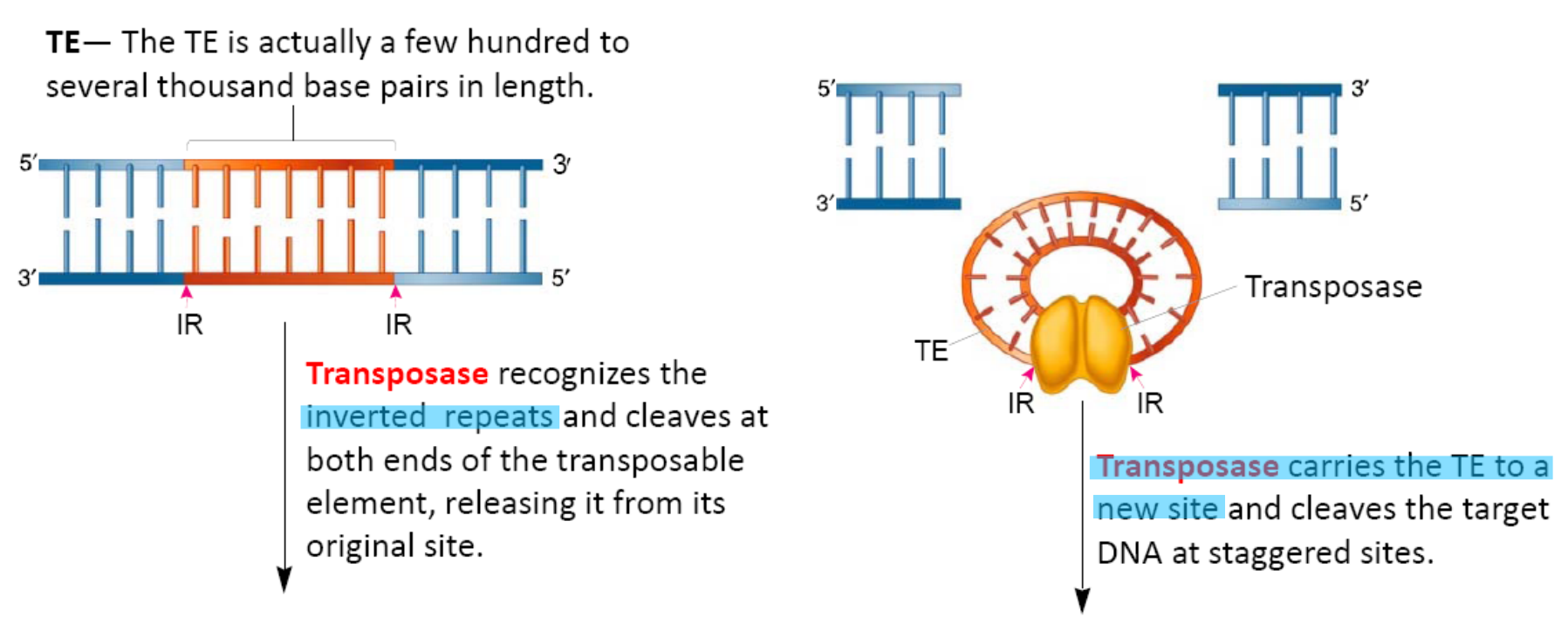
Transposase
The enzyme transposase catalyzes the removal of a TE and the its reinsertion at another location
Transposase recognizes the inverted repeats at the ends of a TE and brings them close together
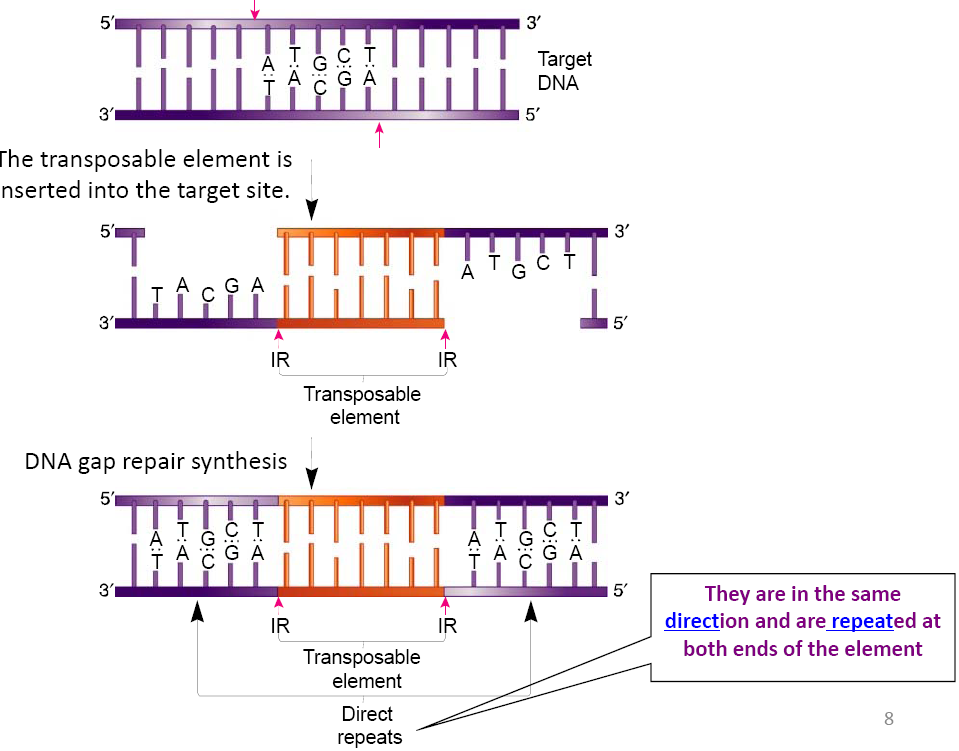
形成了新的directed repeat
Increase Copy Number
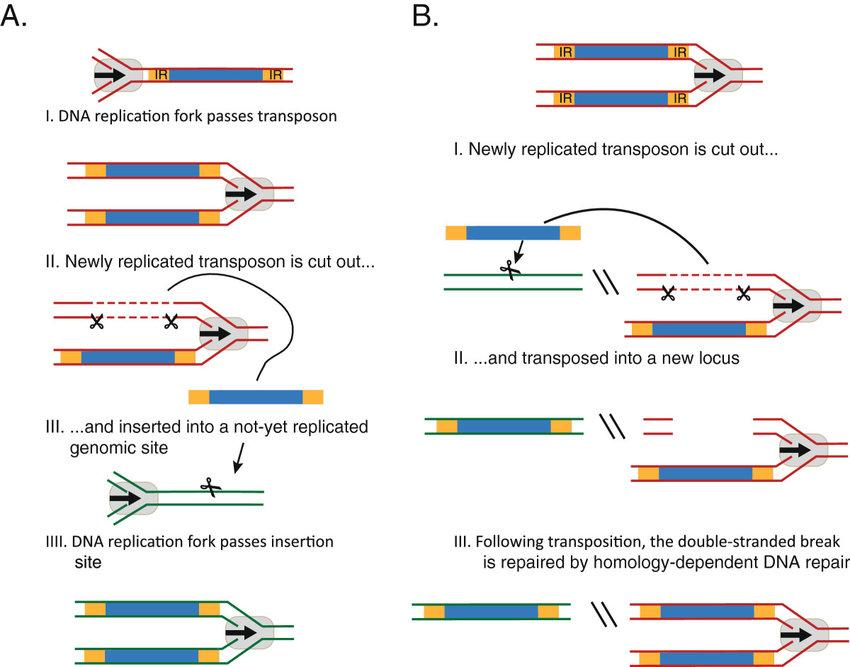
二、Replicative Transposition
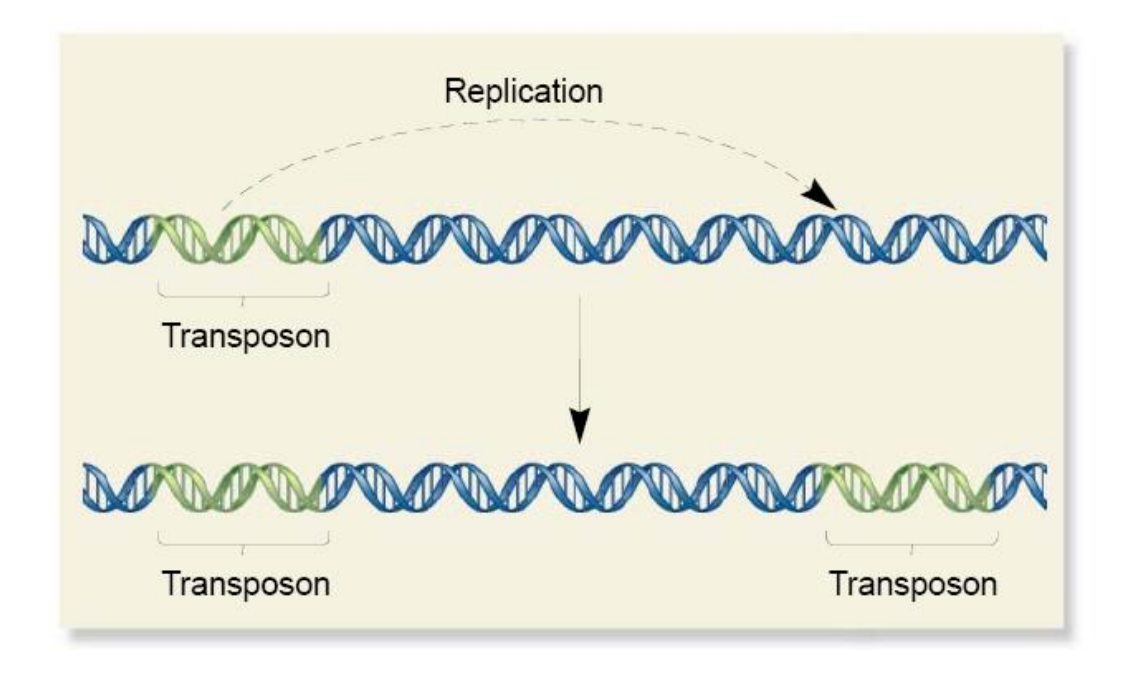
This mechanism involves reolicntion of the TE and insertion of the codv into another chromosomal location
It is relatively uncommon and only found in bacteria
Replicative Transposition: Requires Both Transposase and Resolvase
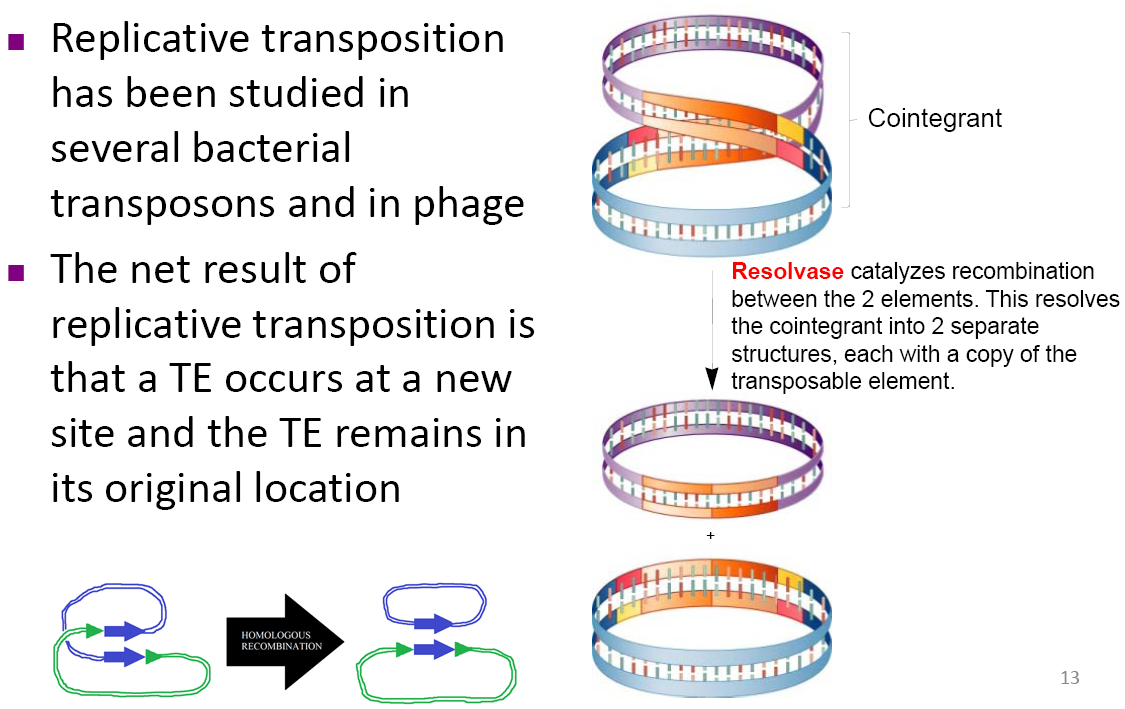
Replicative transposition has been studied in several bacterial transposons and in phage
The net result of replicative transposition is that a TE occurs at a new site and the TE remains in its original location
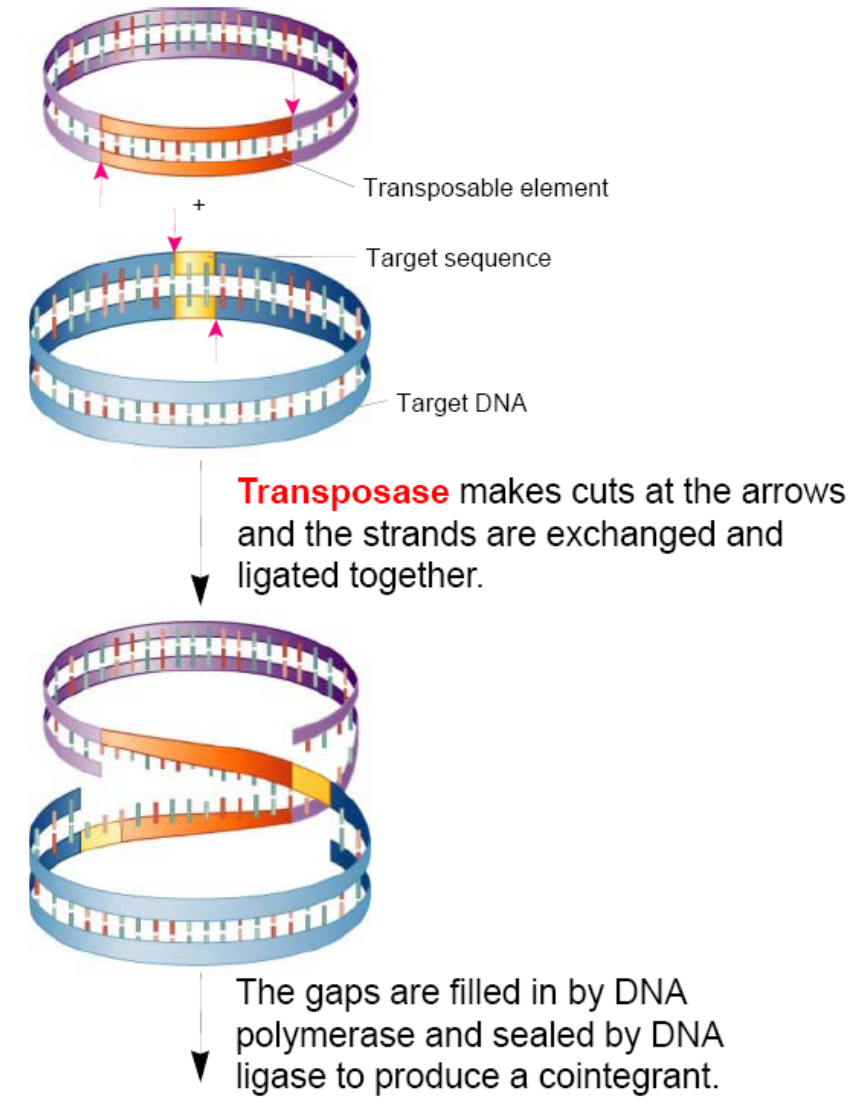
Transposase makes cuts at the arrows and the strands are exchanged and ligated together.
The gaps are filled in by DNA polymerase and sealed by DNA ligase to produce a cointegrant.
Resolvase catalyzes recombination between the 2 elements. This resolves the cointegrant into 2 separate structures, each with a copy of the transposable element.
- Replicative transposition has been studied in several bacterial transposons and in phage
- The net result of replicative transposition is that a TE occurs at a new site and the TE remains in its original location
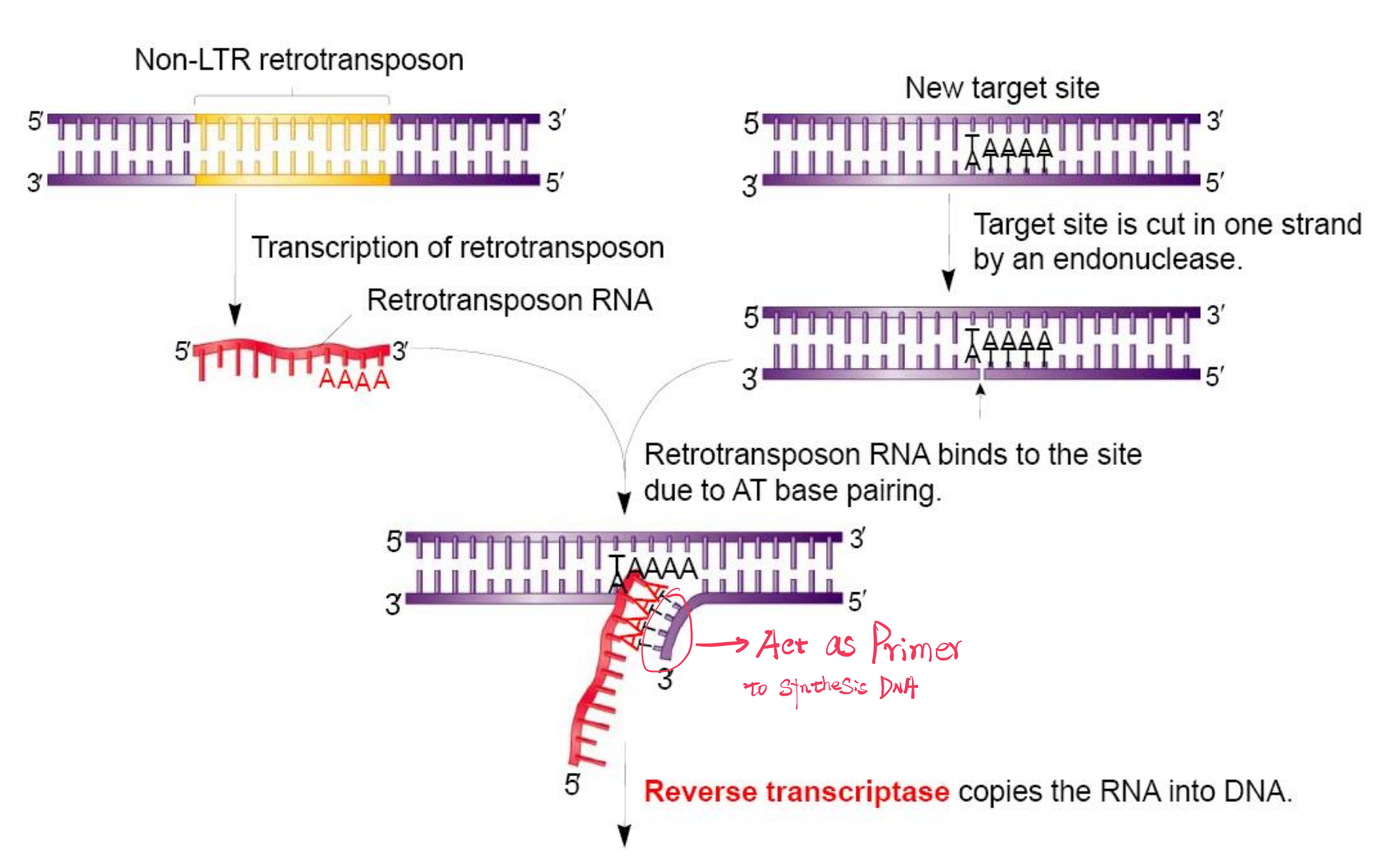
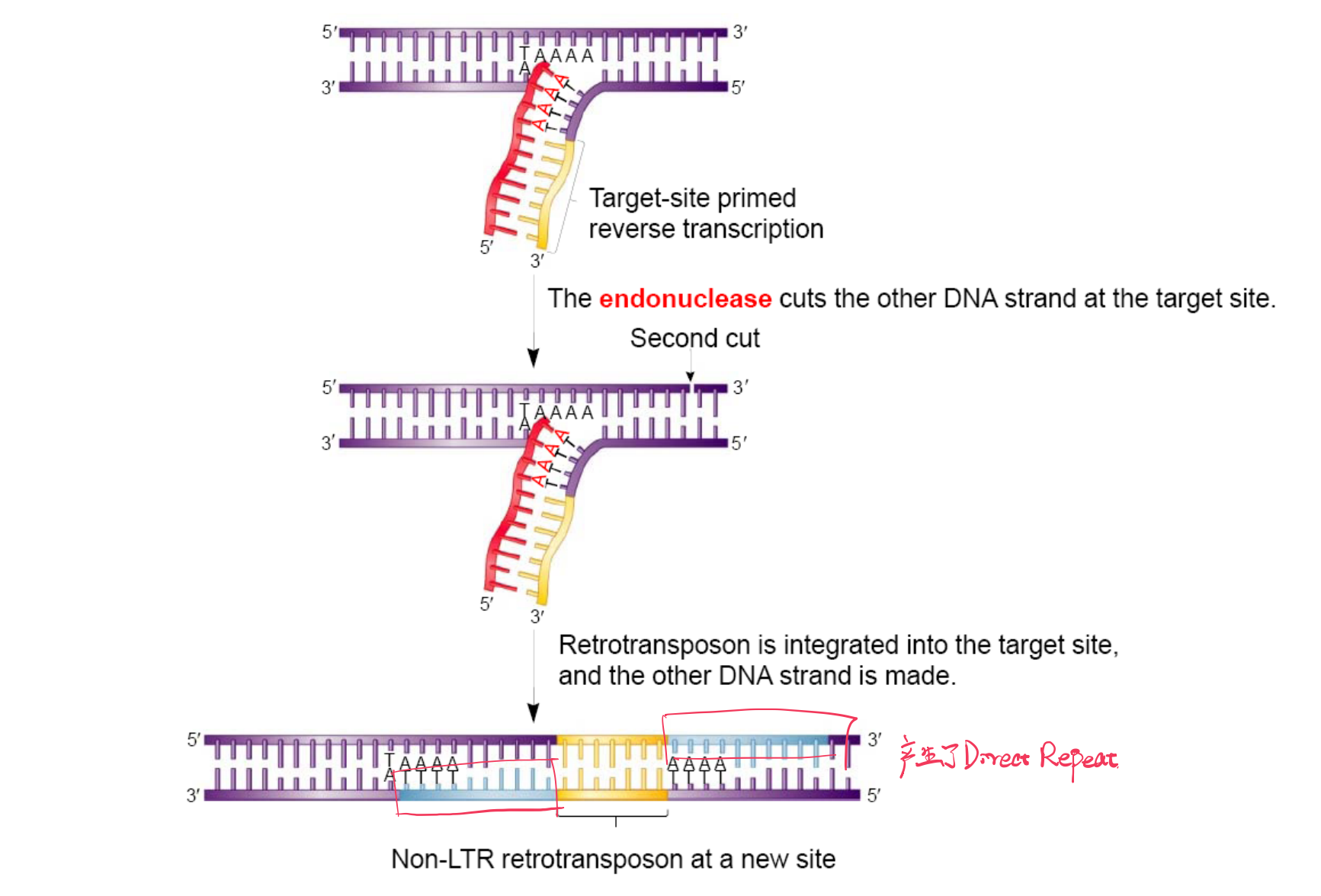
三、Retrotransposition (RNA Transposon)
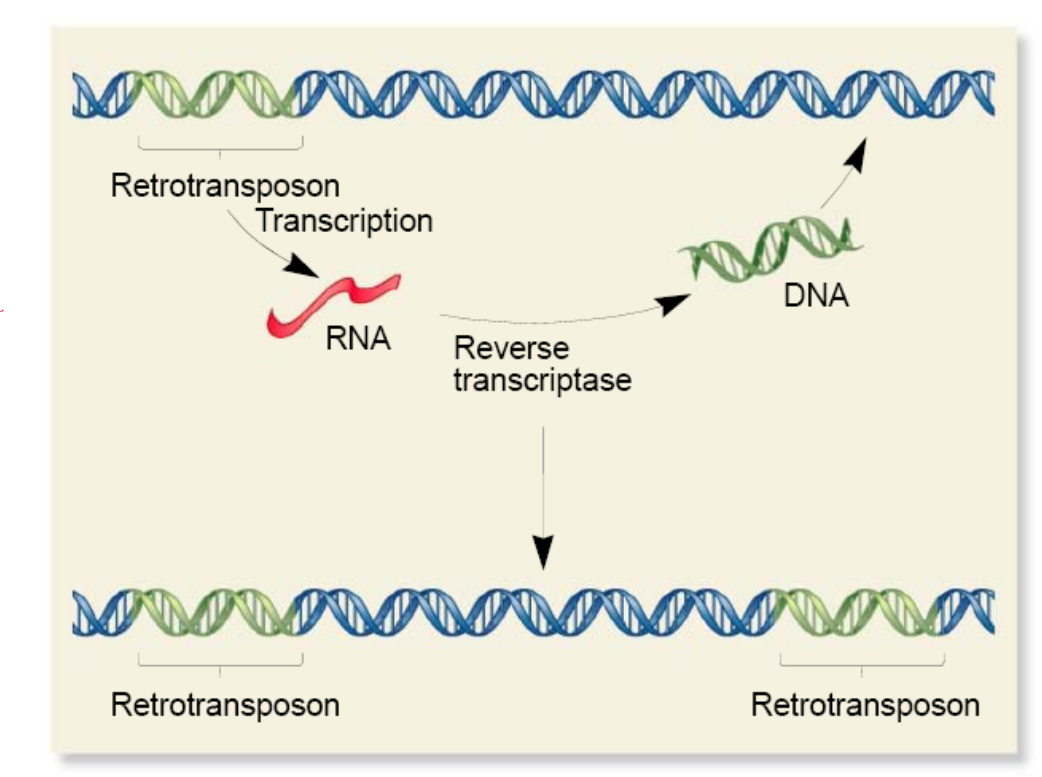
Transcription → Retrotranscription → Integration
This mechanism is very common but only found in eukaryotes
TE moves via an RNA intermediate.
These types of elements are termed retroelements, retrotransposons, or retroposons
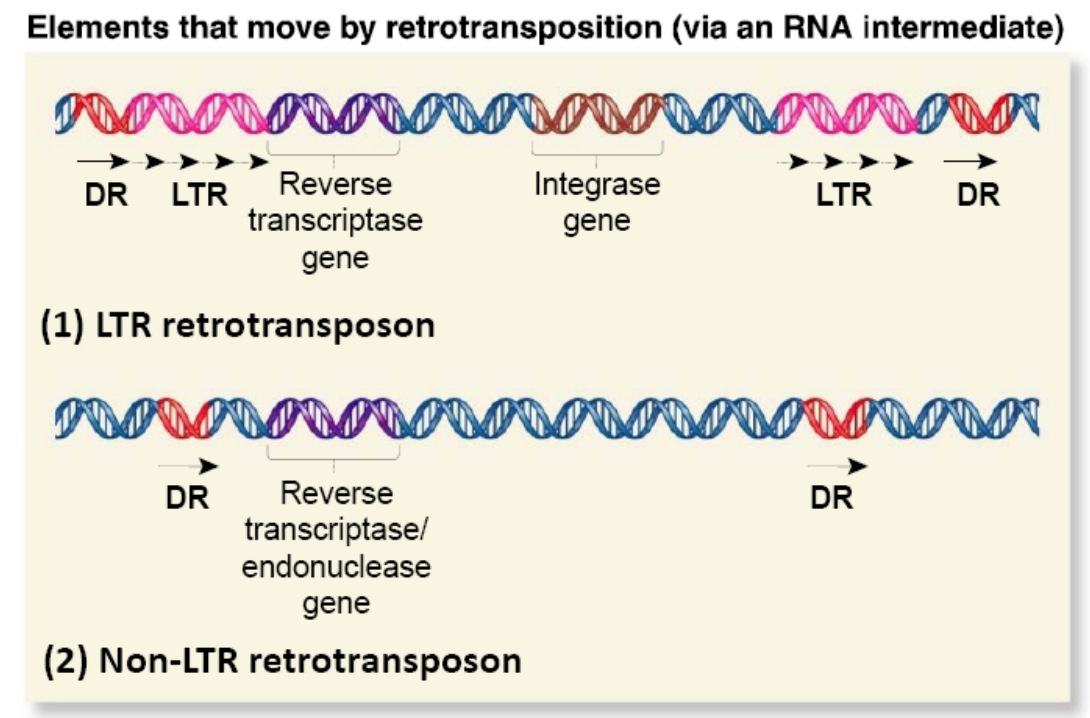
The organization of retroelements can be quite variable
They are categorized based on their evolutionary relationship to retroviral sequences
- Retroviruses are RNA viruses that make a DNA copy that integrates into the host’s genome
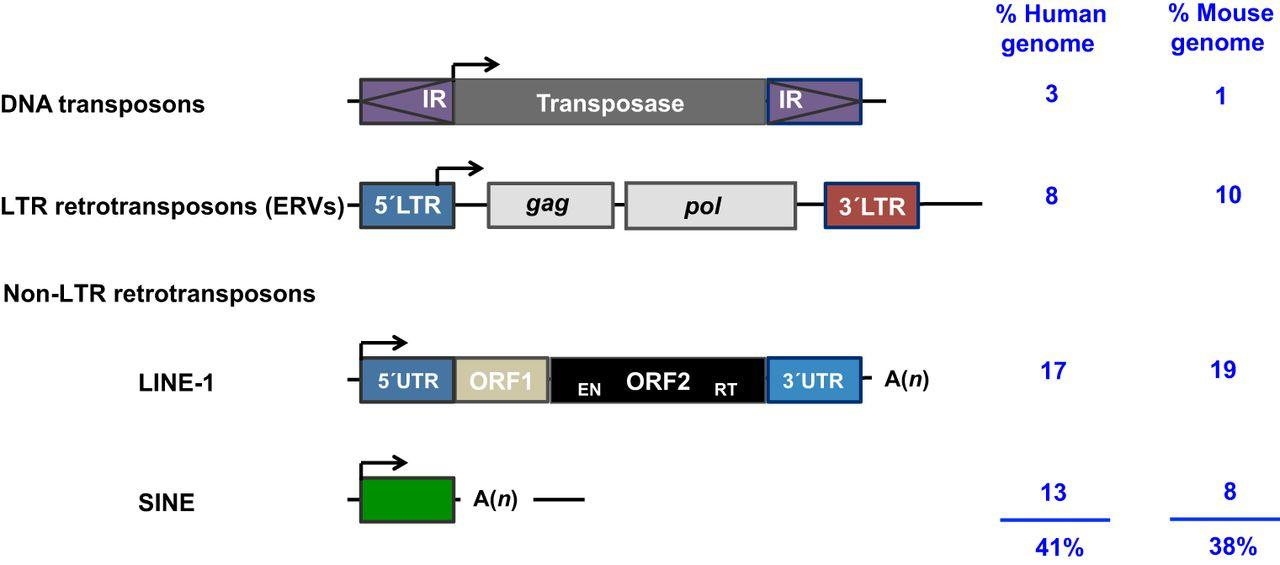
LTR Retrotranspson
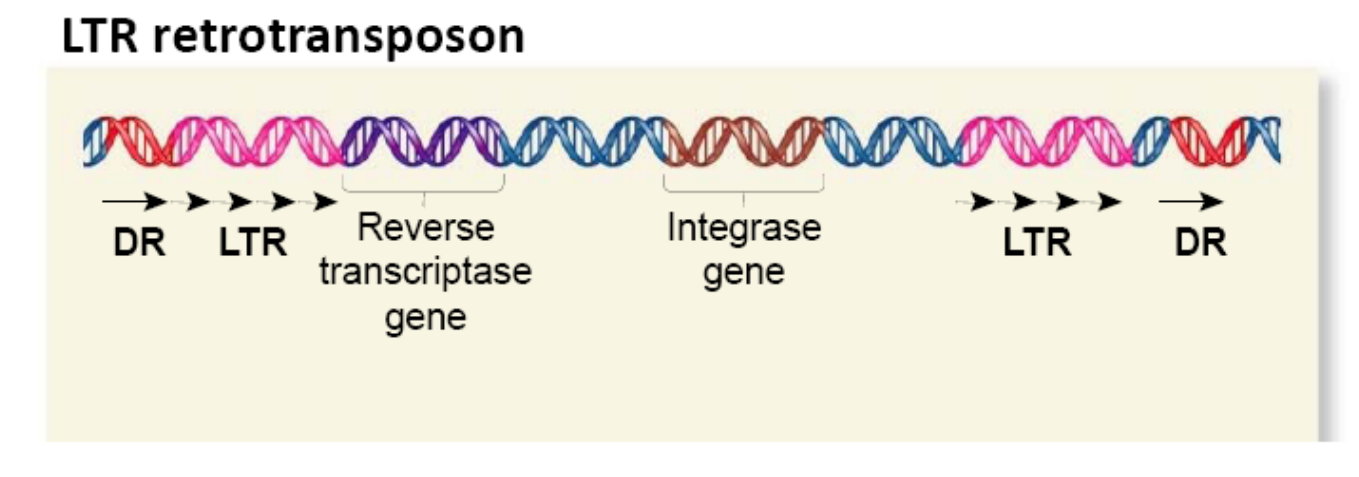
Long terminal repeats (LTR) are typically a few hundred nucleotides long
Evolutionarily related to known retroviruses
Like their viral counterparts, they encode virally related proteins that are needed for the transposition process
Non-LTR Retrotranspson
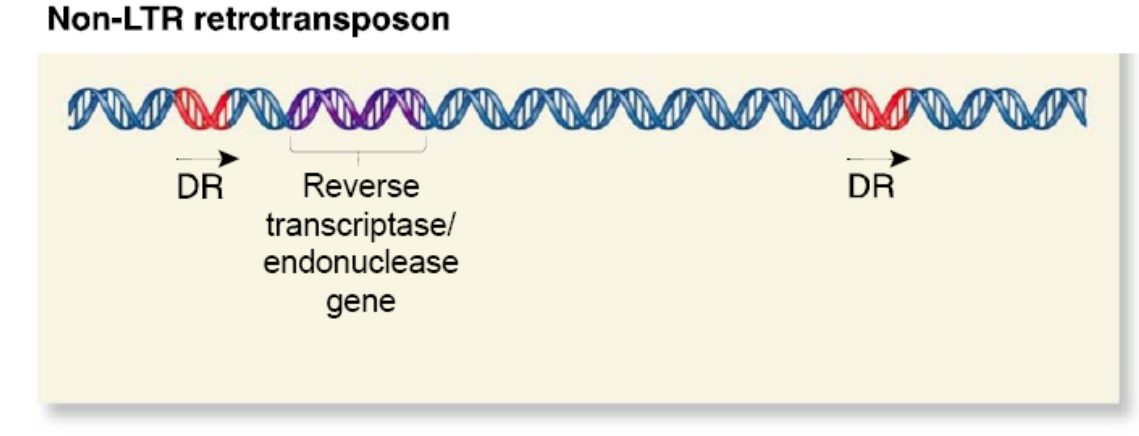
Appear less like retroviruses
- May contain a gene encoding a protein with both reverse transcriptase and endonuclease function
- Some are evolutionarily derived from normal eukaryotic genes
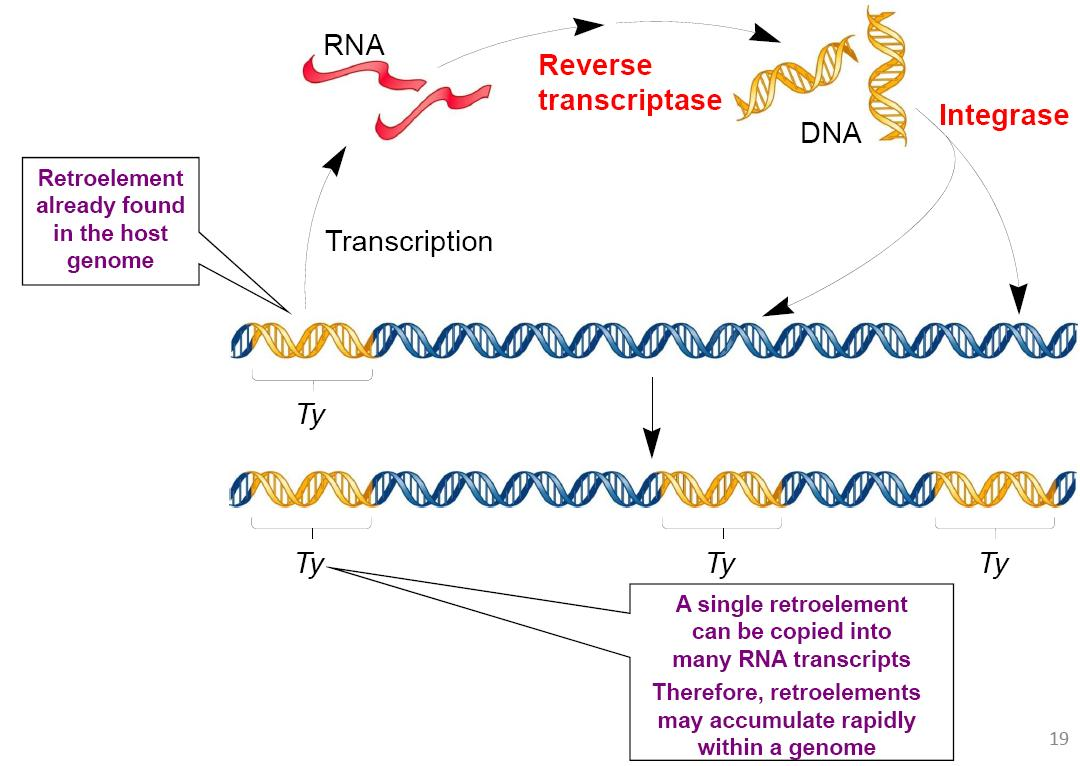
Retroelements Use Reverse Transcriptase and Integrase
Retroelements use an RNA intermediate in their transposition mechanism
The movement of retroelements also requires two key
enzymes:
- Reverse transcriptase
- Integrase
Increase Copy Number
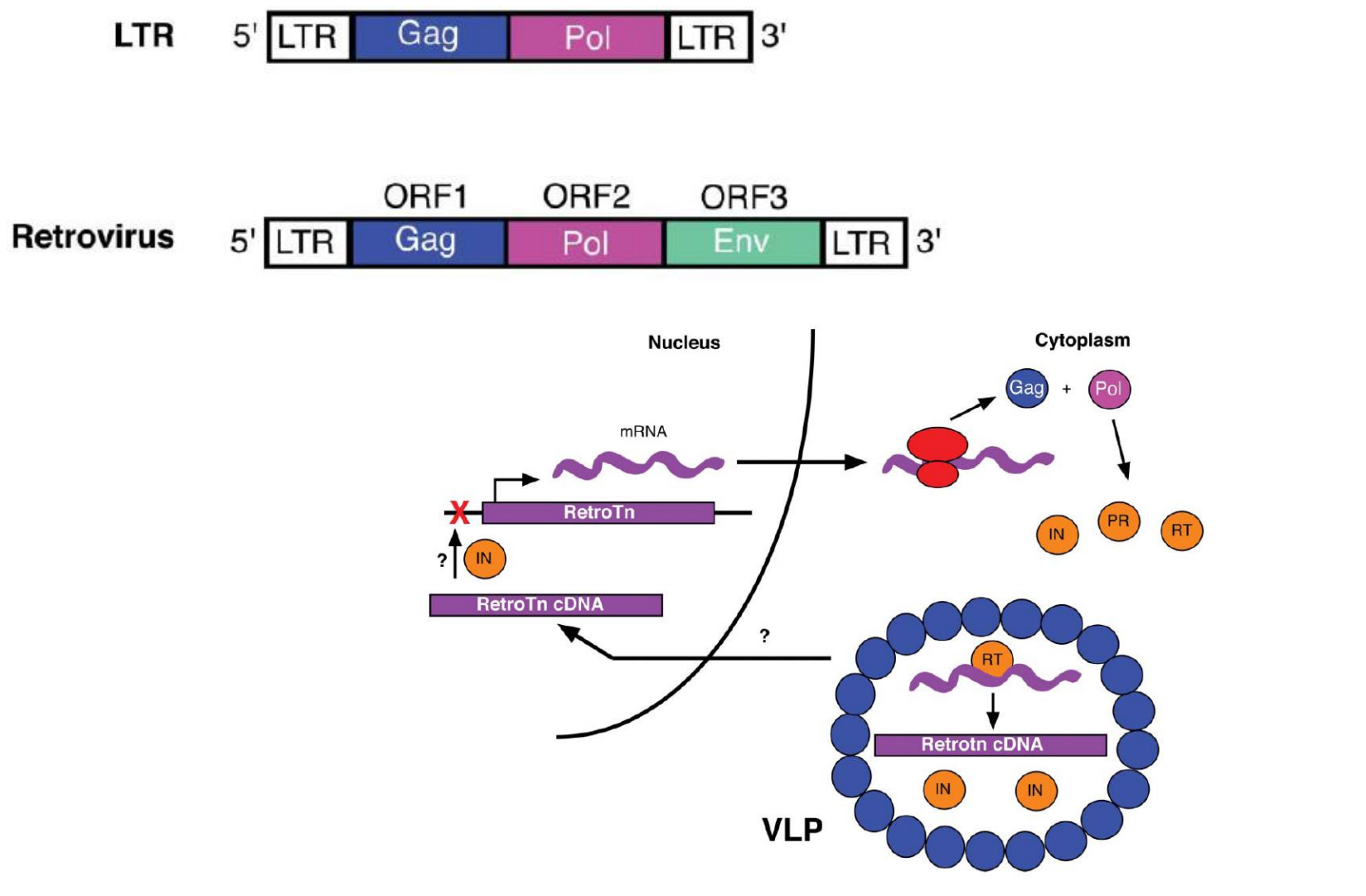
Target‐Site primed Reverse Transcription
Summary
四、Influences of Transposons
Transposable Elements Influences on Mutation and Evolution
Over the past few decades, researchers have found that transposable elements probably occur in the genomes of all species