L09 Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Antimicrobial
General Characteristics of Antimicrobial Drugs
- Selective toxicity 选择性毒性: ability of drug to kill or inhibit pathogen while damaging host as little as possible
- Therapeutic dose 治疗剂量:drug level required for clinical treatment
- Toxic dose 有毒剂量:drug level at which drug becomes too toxic for patient (i.e., produces side effects)
- Therapeutic index 治疗指数: ratio of toxic dose to therapeutic dose
- Side effects : undesirable effects of drugs on host cells
- Narrow-spectrum drugs: attack only a few different pathogens
- Broad-spectrum drugs: attack many different pathogens
- Cidal agent 杀灭剂: kills microbes
- Static agent: inhibits growth of microbes
Determining the Level of Antimicrobial Activity
Effectiveness expressed in two ways:
- minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) :In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible growth of a bacterium or bacteria. MIC depends on the microorganism, the affected human being (in vivo only), and the antibiotic itself.
- minimal lethal concentration (MLC):minimal lethal concentration (MLC) the lowest concentration of antimicrobial that kills a particular bacterium; usually in reference to an antimicrobial sensitivity test.
Antimicrobial Sensitivity Test
1. Dilution Susceptibility Tests
Dilution susceptibility tests. A dilution test is carried out by adding dilutions of an antimicrobial to a broth or agar medium. A standardized inoculum of the test organism is then added. After overnight incubation, the MIC is reported as the lowest concentration of antimicrobial required to prevent visible growth.
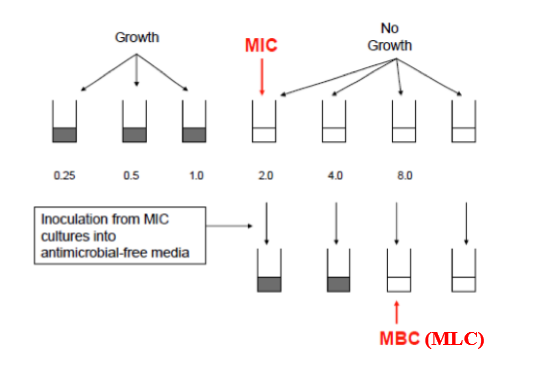
if broth used, tubes showing no growth can be subcultured into drug-free medium
- broth from which microbe can’t be recovered is MLC
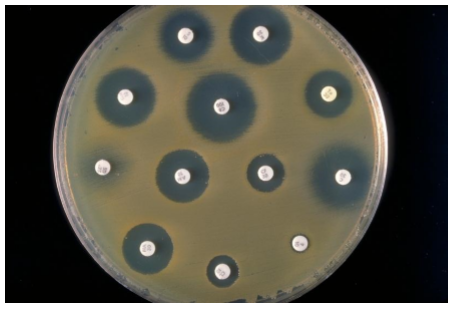
2. Disk Diffusion Tests
Disks impregnated with specific drugs are placed on agar plates inoculated with test microbe
Drug diffuses from disk into agar, establishing concentration gradient
Observe clear zones (no growth) around disks
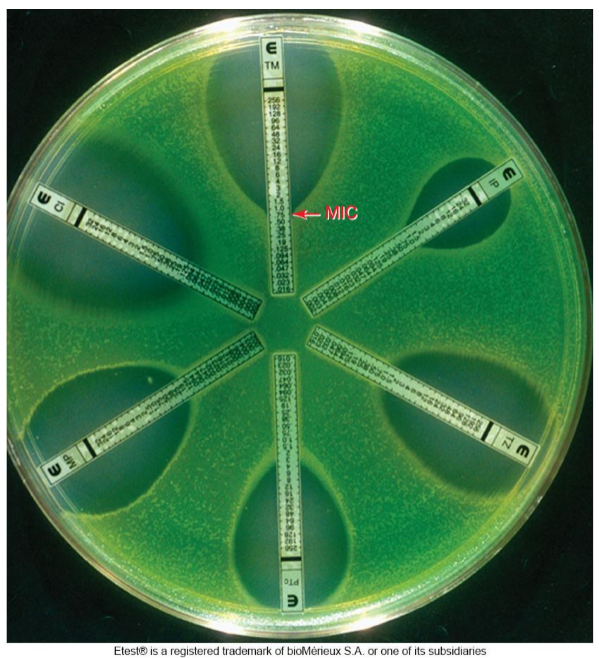
3. The E Test
Similar to disk diffusion method, but uses strip rather than disk
E-test strips contain a gradient of an antibiotic
Intersection of elliptical zone of inhibition with strip indicates MIC
Factors Influencing Antimicrobial Drugs
- Susceptibility of pathogen to drug
- Ability of drug to reach site of infection (oral, topical, etc.)
- Ability of drug to reach concentrations in body that exceed MIC of pathogen (amount, route, speed of uptake, rate of clearance, etc.)
Overcoming Drug Resistance
Use drugs only when necessary
Give drug in appropriate concentrations to destroy susceptible
Give two or more drugs at same time
Possible future solutions
- continued development of new drugs
- bacteriophages
Antibacterial Drugs
1. Inhibitors of cell wall synthesis
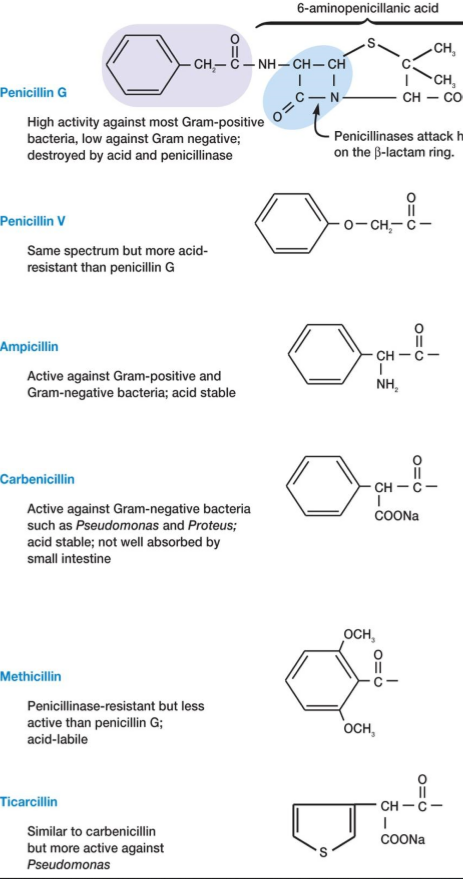
Penicillins 青霉素,盘尼西林
Mode of action:
blocks the enzyme that catalyzes transpeptidation (formation of cross-links in peptidoglycan)
prevents the synthesis of complete cell walls leading to lysis of cell
acts only on growing bacteria that are synthesizing new peptidoglycan
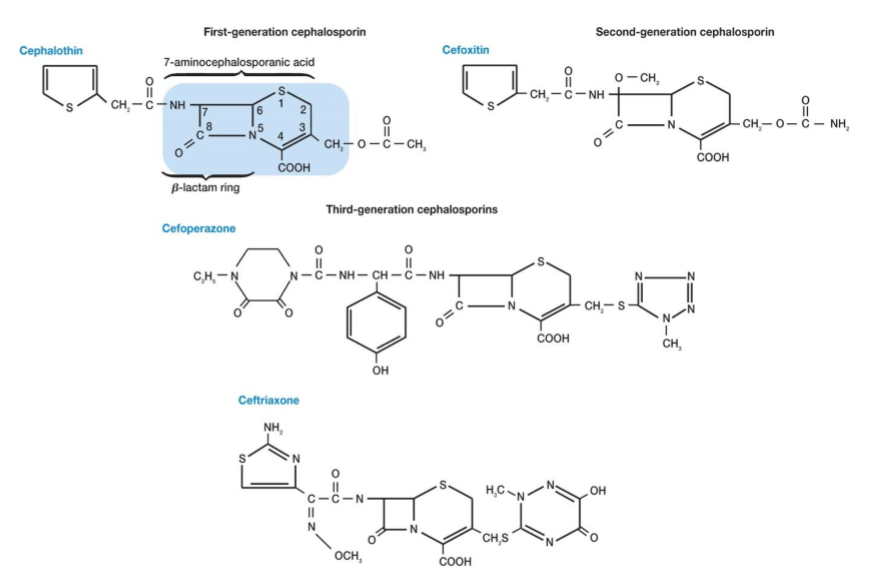
Cephalosporins 头孢菌素类
Structurally and functionally similar to penicillins
• Broad-spectrum antibiotics that can be used by most patients that are allergic(过敏的) to penicillin
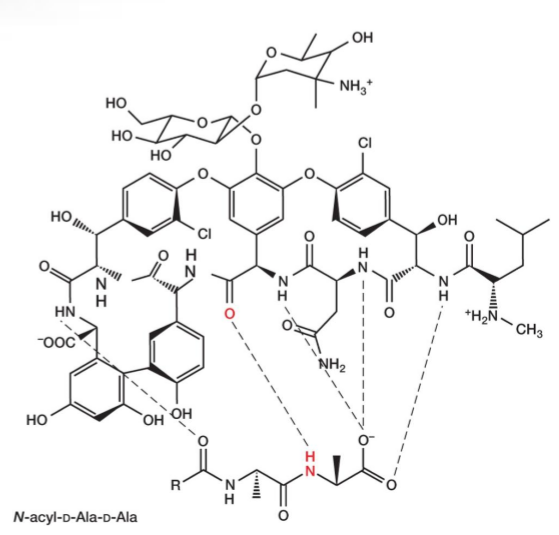
Vancomycin(万古霉素) and Teicoplanin(替考拉宁)
Glycopeptide antibiotics
• Inhibit cell wall synthesis
• Vancomycin - important for treatment of antibiotic-resistant staphylococcal and enterococcal infections
– previously considered “drug of last resort” so rise in resistance to vancomycin is of great concern
2. Protein synthesis inhibitors
Many antibiotics bind specifically to the bacterial ribosome
- binding can be to 30S (small) or 50S (large) ribosomal subunit
- Other antibiotics inhibit a step in protein synthesis
- aminoacyl-tRNA binding
- peptide bond formation
- mRNA reading – translocation
Aminoglycoside Antibiotics 氨基糖苷类抗生素
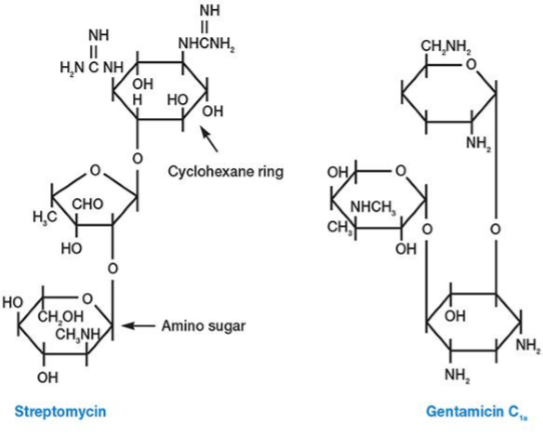
Large group, all with a cyclohexane ring, amino sugars
Bind to 30S ribosomal subunit, interfere with protein synthesis by directly inhibiting the process and by causing misreading of the mRNA
Tetracyclines 四环素
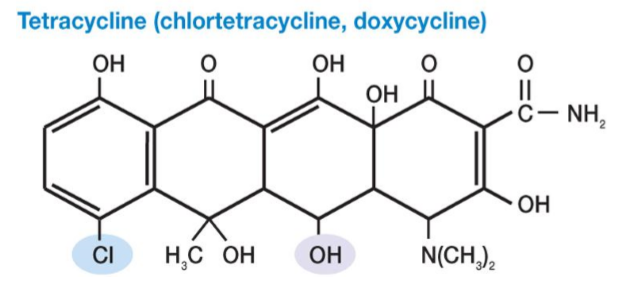
All have a four-ring structure to which a variety of side chains are attached
Are broad spectrum, bacteriostatic
Combine with 30S ribosomal subunit
inhibits bind of aminoacyl-tRNA molecules to the A site of the ribosome
Macrolides 大环内酯类
Contain 12- to 22-carbon lactone rings linked to one or more sugars • e.g., erythromycin
broad spectrum, usually bacteriostatic
binds to 23S rRNA of 50S ribosomal subunit
inhibits peptide chain elongation
Used for patients allergic to penicillin
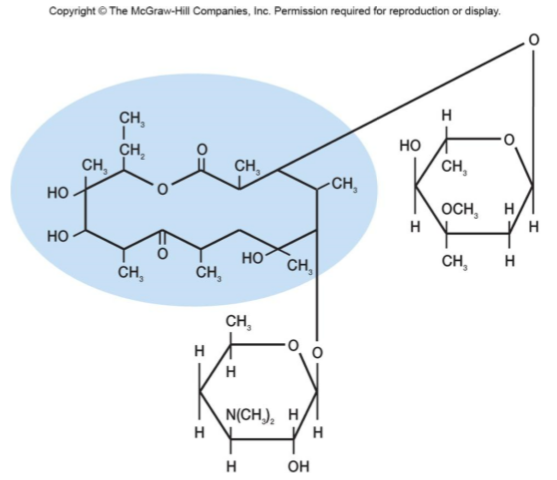
Chloramphenicol 氯霉素
Now is chemically synthesized
Binds to 23s rRNA on 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyl transferase reaction
Toxic with numerous side effects so only used in life-threatening situations
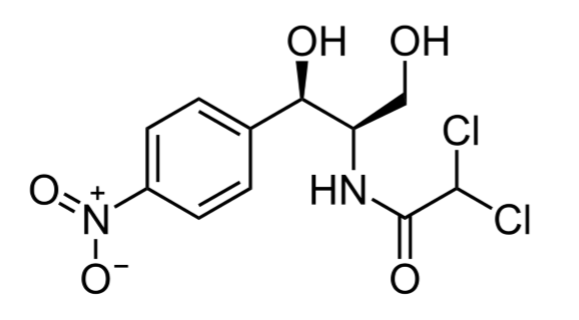
3. Metabolic antagonists
Act as antimetabolites :
antagonize(对…起反作用) or block functioning of metabolic pathways by competitively inhibiting the use of metabolites by key enzymes
Are structural analogs(类似物) :
molecules that are structurally similar to, and compete with, naturally occurring metabolic intermediates $\rarr$ block normal cellular metabolism
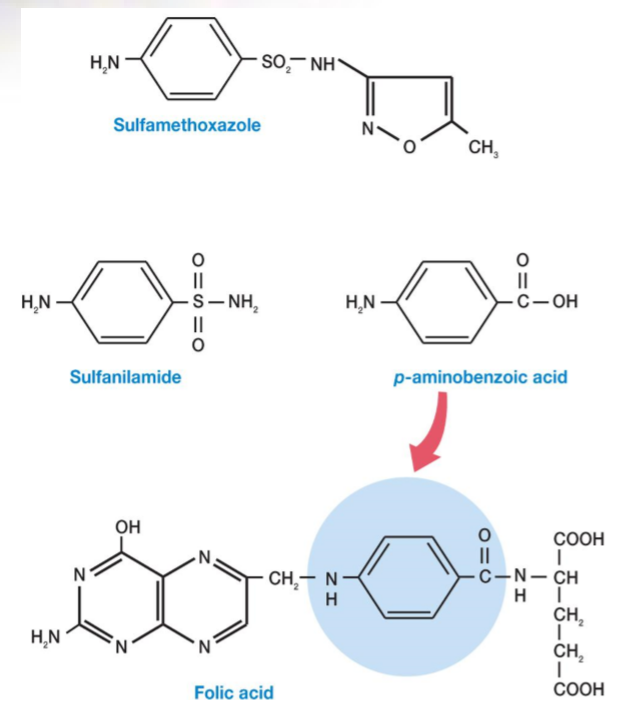
Sulfonamides or Sulfa Drugs 磺胺类药;磺酰胺类
Structurally related to sulfanilamide, a paminobenzoic acid (PABA, 对氨基苯甲酸, Para-Aminobenzoic Acid) analog
PABA used for the synthesis of folic acid(叶酸,维生素B类) and is made by many pathogens
sulfa drugs are selectively toxic due to competitive inhibition of folic acid synthesis enzymes
磺胺类药物抗菌谱较广,对大部分革兰氏阴性菌和革兰氏阳性菌均有杀伤作用。目前临床上使用的磺胺类药物均是对氨基苯甲酸(PABA)的类似物。PABA是细菌叶酸从头合成途径必经的中间产物。磺胺类药物通过与对氨基苯甲酸竞争二氢叶酸合酶的反应位点,达到竞争性抑制细菌叶酸合成、使细菌死亡的目的。磺胺类药物一般来说是通过口服给药的,但亦有磺胺类药物(比如磺胺嘧啶银)是外用药
4. Nucleic acid synthesis inhibition
A variety of mechanisms :
block DNA replication :
inhibition of DNA polymerase
inhibition of DNA helicase(解旋酶)
block transcription
- inhibition of RNA polymerase
Drugs not as selectively toxic as other antibiotics because bacteria and eukaryotes do not differ greatly in the way they synthesize nucleic acids
Quinolones 喹诺酮类
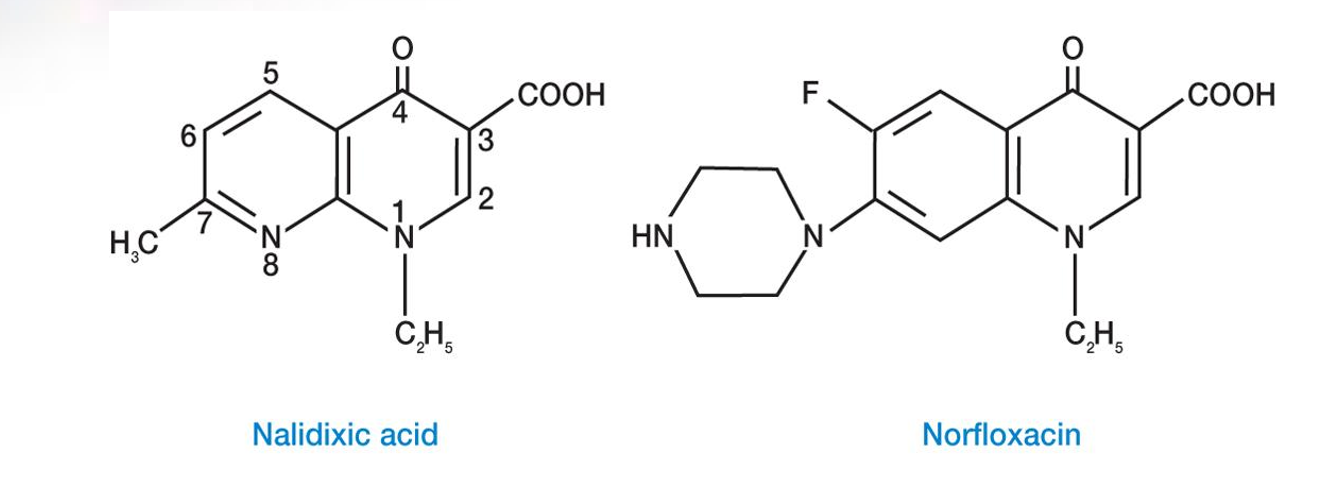
Synthetic drugs containing the 4-quinolone ring
Act by inhibiting bacterial DNA-gyrase and topoisomerase II (回旋酶,促旋酶[大肠杆菌的II类拓扑异构酶,可在DNA中引入负超螺旋])
Broad spectrum, bactericidal, wide range of infections
Antifungal Drugs
Fewer effective agents because of similarity of eukaryotic fungal cells and human cells so many have low therapeutic index and are toxic
• Easier to treat superficial mycoses(皮肤真菌病) than systemic infections
Treating Systemic Mycoses
Three common drugs :
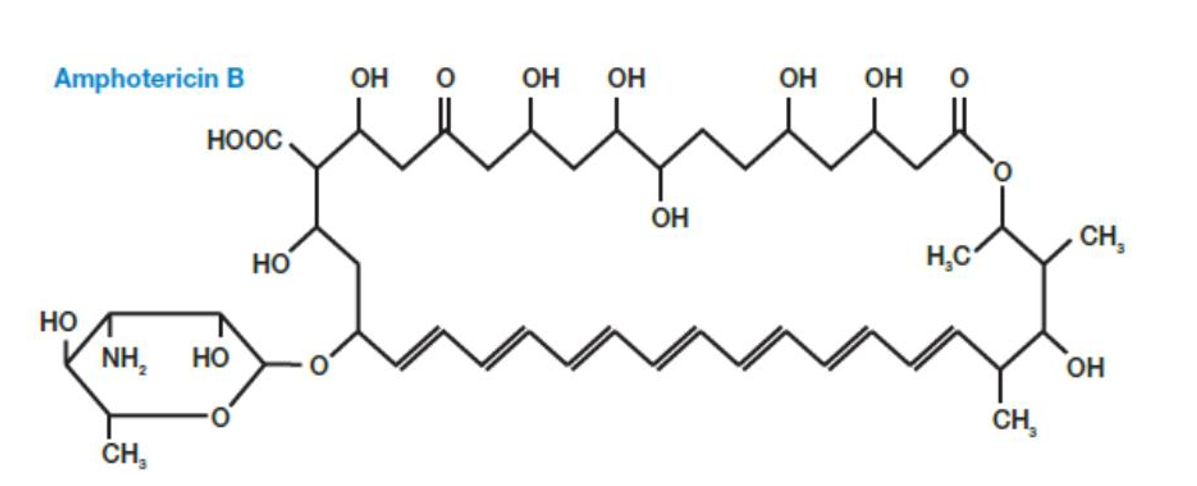
amphotericin B - binds sterols in membranes
5-flucytosine – disrupts RNA function
Fluconazole – inhibit sterol synthesis
Antiviral Drugs
Drug development has been slow because it is difficult to specifically target viral replication
Drugs currently used inhibit virus-specific enzymes and life cycle processes
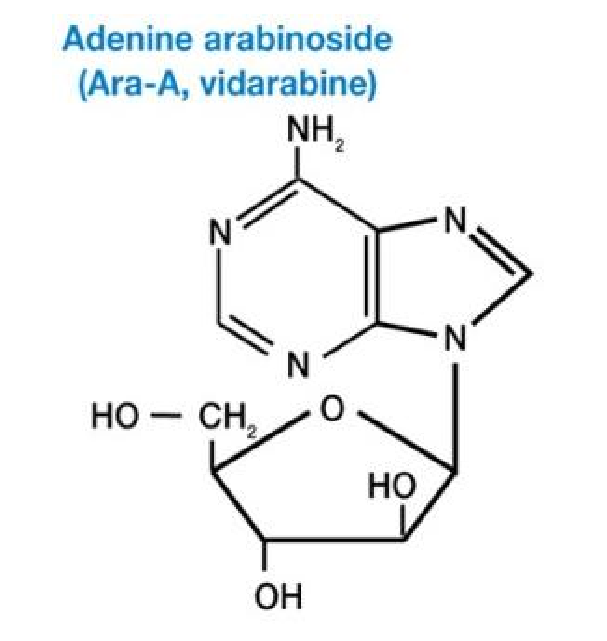
Adenine arabinoside (vidarabine) 腺嘌呤阿拉伯糖苷
inhibits herpes(疱疹) virus enzymes involved in DNA and RNA synthesis and function
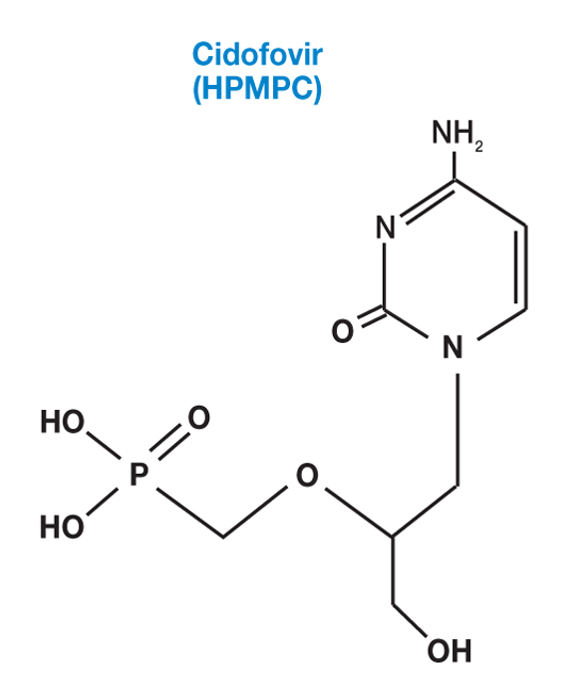
HPMPC (cidofovir)
inhibits viral DNA polymerase papovaviruses, adenoviruses, herpesviruses, iridoviruses, and poxviruses
Tamiflu(奥司他韦 Oseltamivir)
是一种作用于神经氨酸酶的特异性抑制剂,其抑制神经氨酸酶(neuraminidase)的作用,可以抑制成熟的流感病毒脱离宿主细胞,从而抑制流感病毒在人体内的传播以起到治疗流行性感冒的作用。
商品名Tamiflu,中国大陆称达菲,港译特敏福,台湾译为克流感
Though not a cure for influenza, has been shown to shorten course of illness
Antiprotozoal Drugs
Examples of available drugs :
some antibiotics that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis are used against protozoa
chloroquine
chloroquine(氯喹(疟疾的特效药的一种)) – malaria