L07 Linkage, Crossing Over, and Chromosome Mapping
Linkage
Genetic Linkage is the phenomenon that genes close together on a chromosome tend to be transmitted as a unit, which influences inheritance patterns
Chromosomes are called linkage groups. They contain a group of genes that are linked together
The number of linkage groups is the number of types of chromosomes of the species
对人来说,女性有23个linkage group(22+X),男性有24个linkage group(22+XY)
- 22 autosomal linkage groups
- An X chromosome linkage group
- A Y chromosome linkage group
For linkage group, crossing-over should be in consideration
Crossing Over
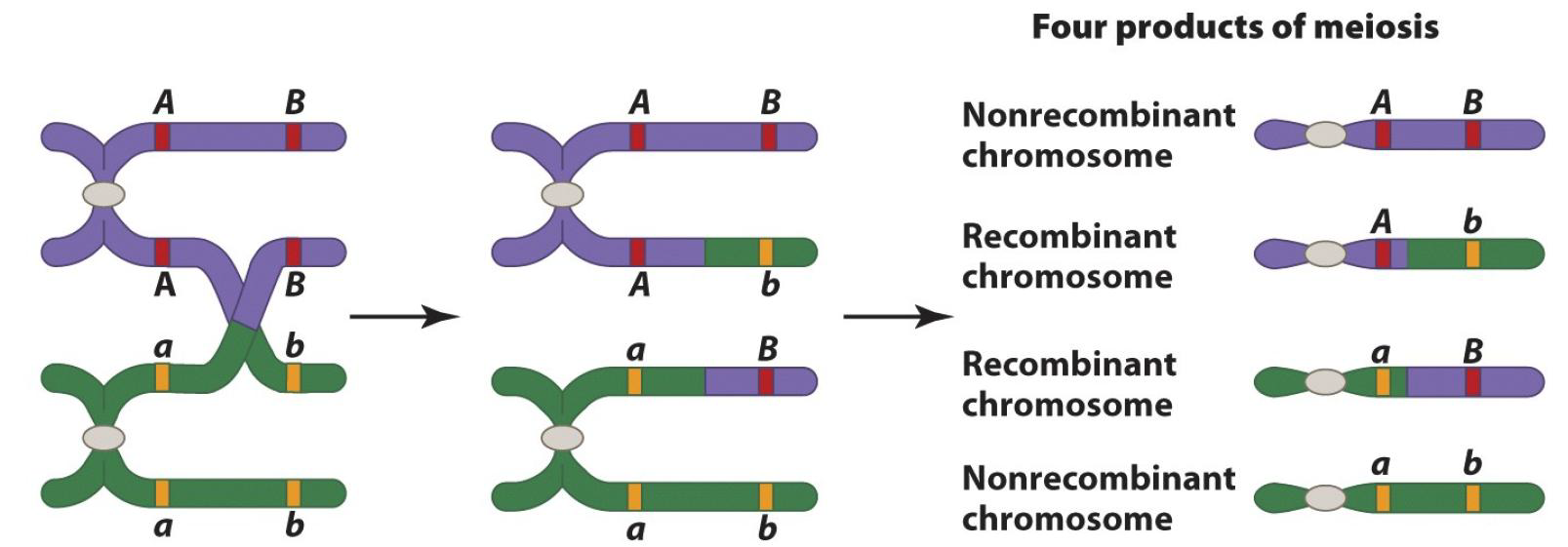
The term linked or linkage means that two or more genes do not independently assort and tend to be transmitted together
Genes that are far apart on the same chromosome may independently assort from each other because of the crossing-over
- A dihybrid cross studies linkage between two genes
- A trihybrid cross studies linkage between three genes
Multiple Crossovers
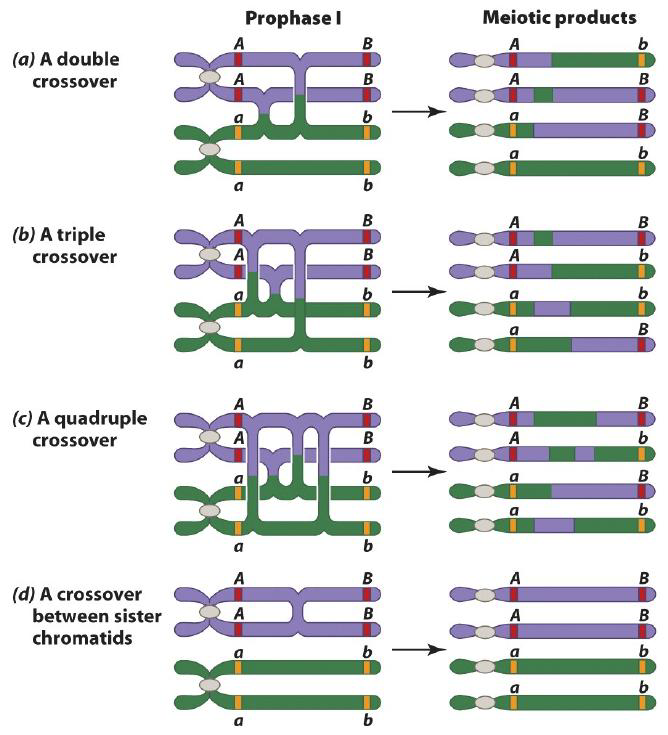
Meiosis Prophase I: Diplonema 双线期
The synaptonemal complex degrades and paired chromosomes separate slightly but are in contact as chiasmata(染色体交叉)
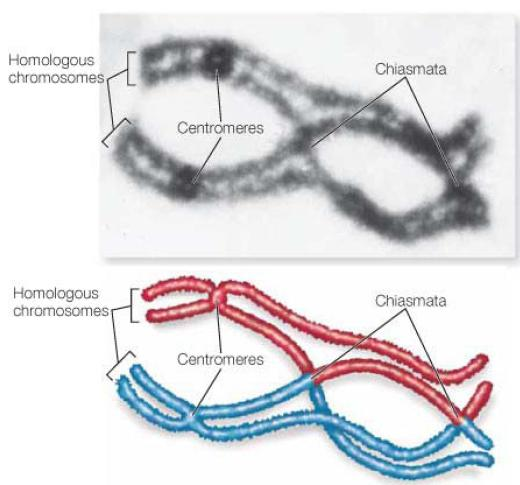
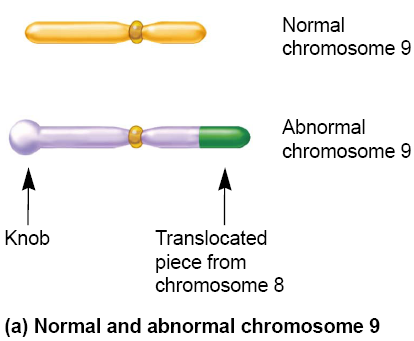
Direct Evidence That Crossing Over Results In Recombination
Harriet Creighton and Barbara McClintock worked with corn
In previous cytological examinations of corn, they found a chromosome number 9 that had two abnormalities (异常情况)

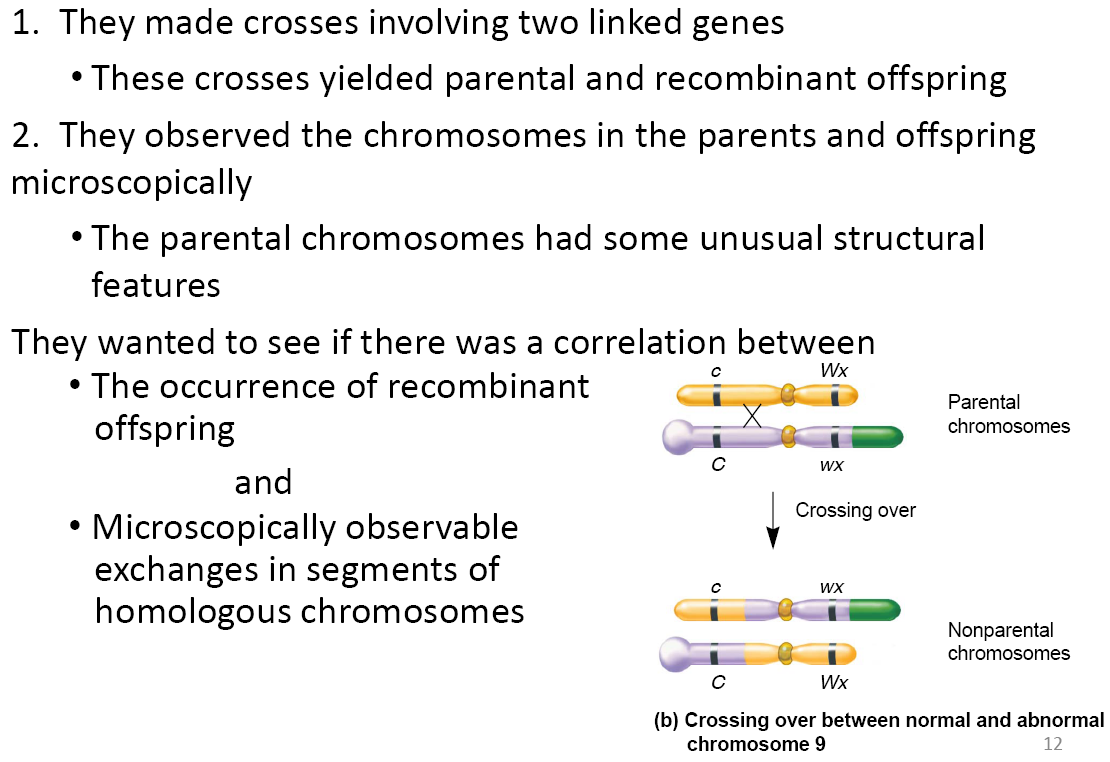
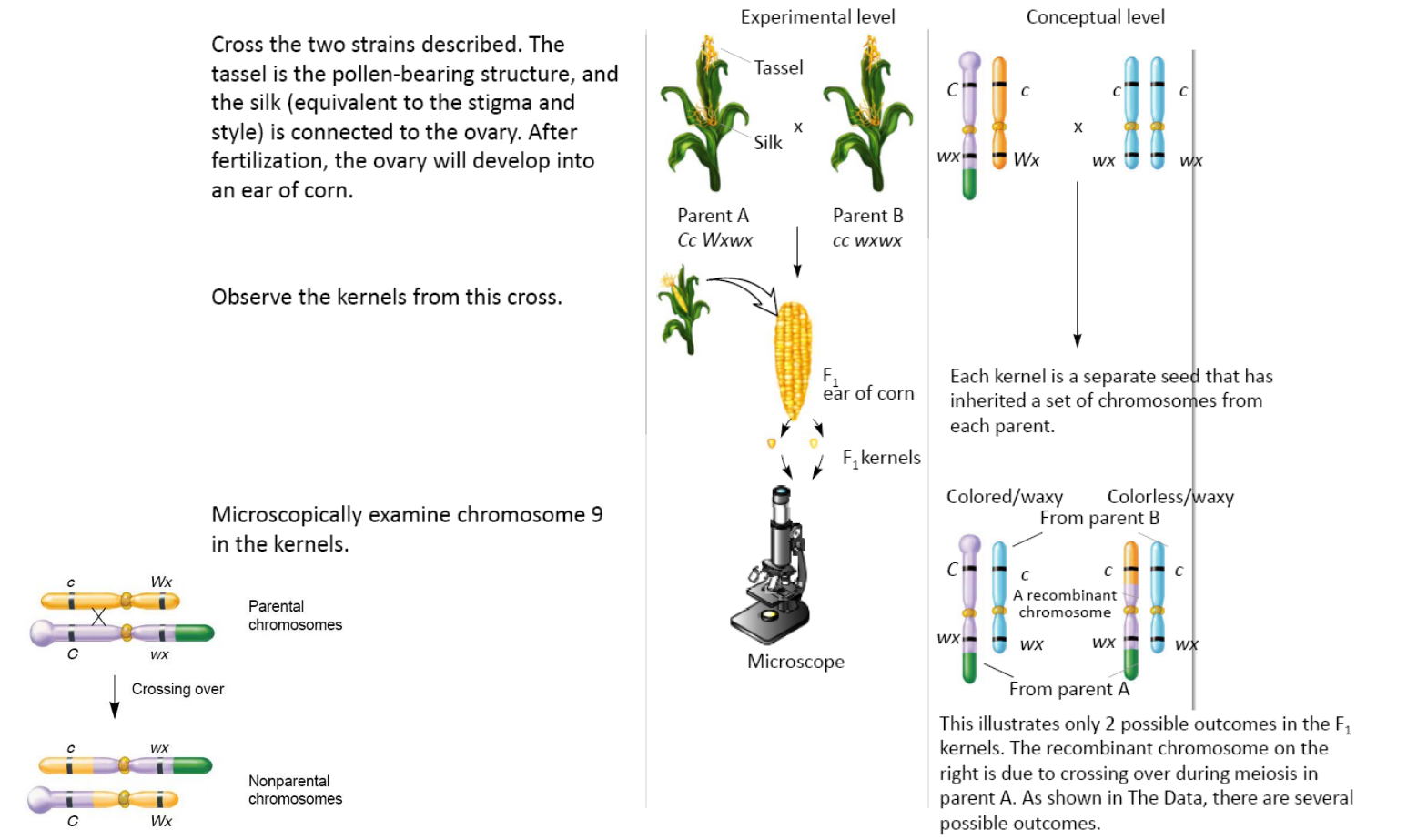
Chromosome Mapping
Genetic mapping is also known as gene mapping or chromosome mapping
Its purpose is to determine the linear order of linked genes along the same chromosome
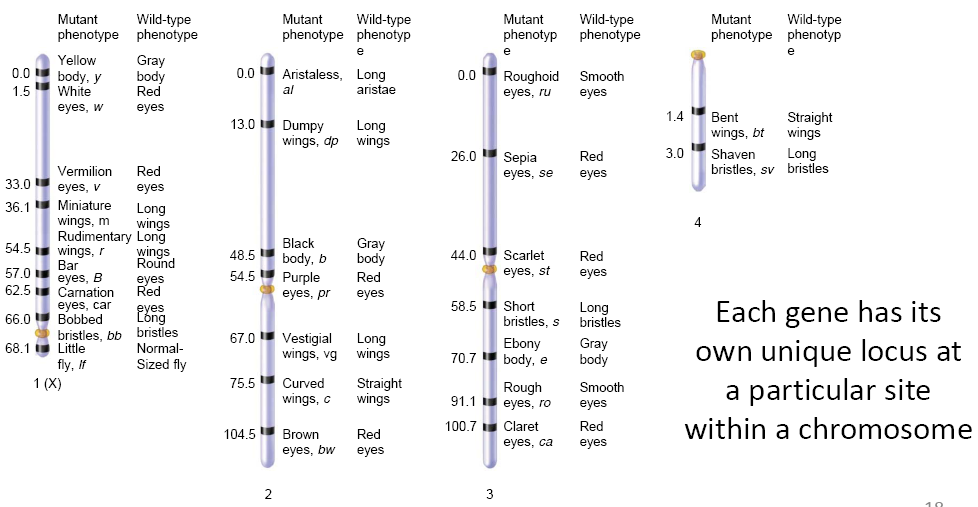
Genetic maps are useful in many ways including
Aiding in diagnosis of human disease
Aiding in cloning of disease genes
Predict likelihood of offspring having traits
Genetic maps can be made by
- Recombination analysis → Genetic map
- Molecular approaches including sequencing
recombination analysis
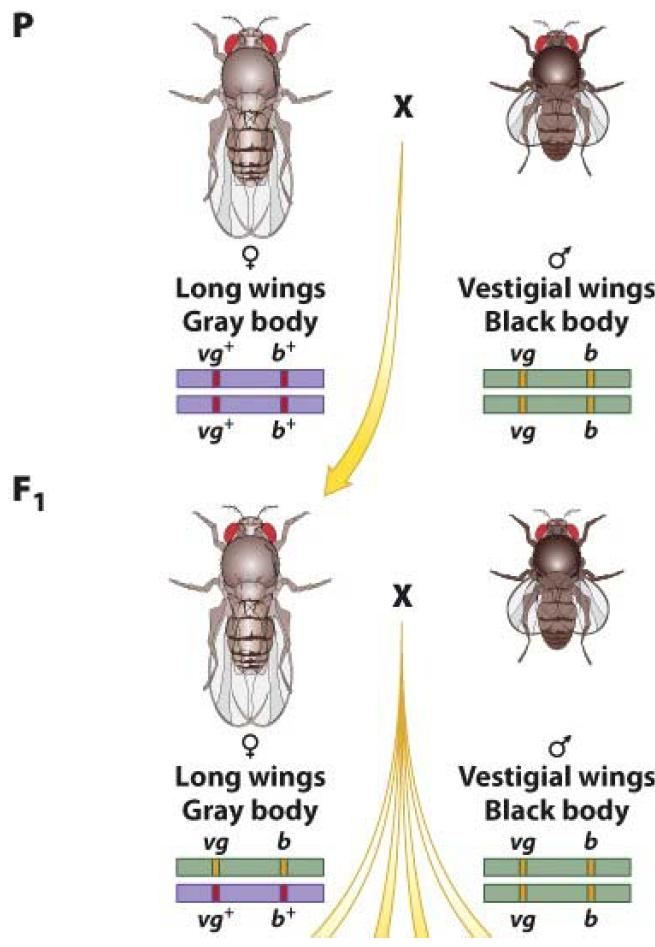
Genetic map created by recombination analysis estimates the relative distances between linked genes.
The percentage of recombinant offspring is correlated with the distance between the two genes:
- If the genes are far apart, would be many recombinant offspring.
- If the genes are close, would be very few recombinant offspring
Measure the recombination frequency by testcross(测交):
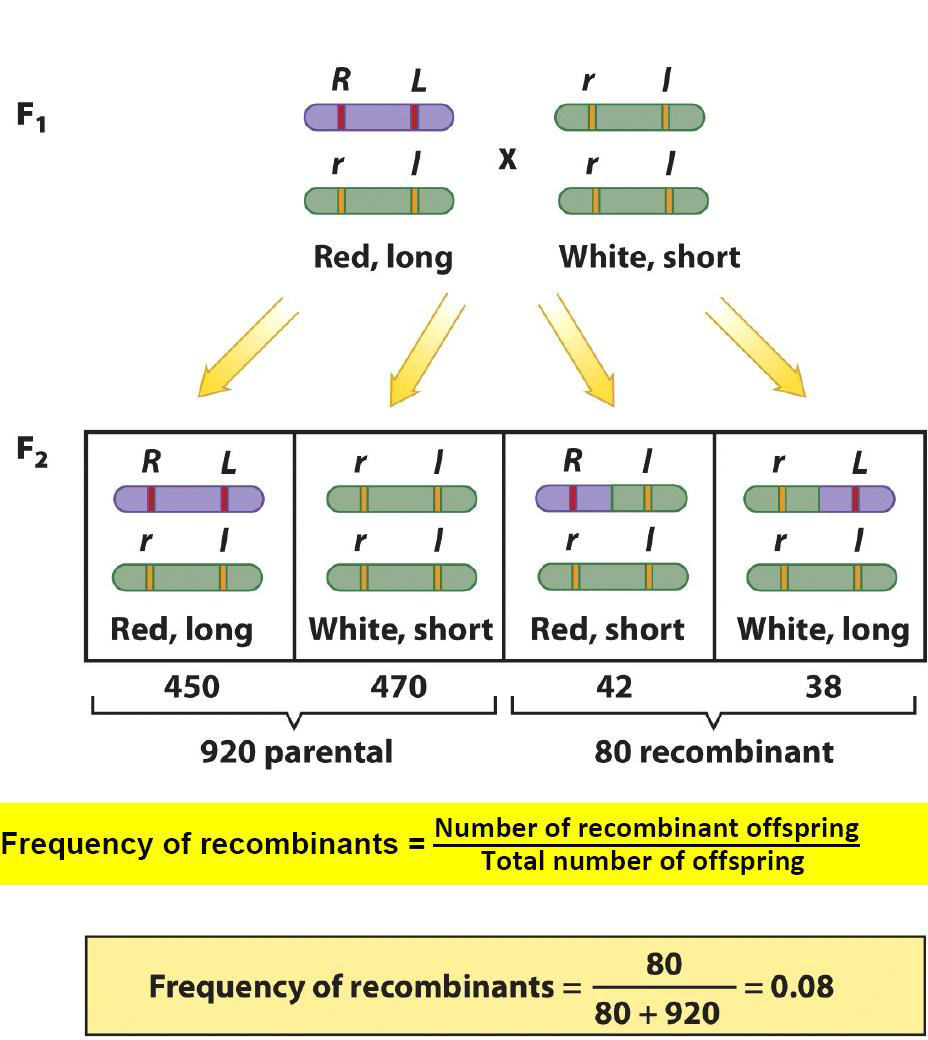
Recombination frequency represent the intensity of linkage between genes
• Recombination frequency never exceeds 50% (for 2 genes)
$$
\ \ \ \ \ \ Heterozygote\ for\ two\ or\ more\ genes\
\X\
\ Homozygote\ recessive\ for\ the\ same\ genes
$$
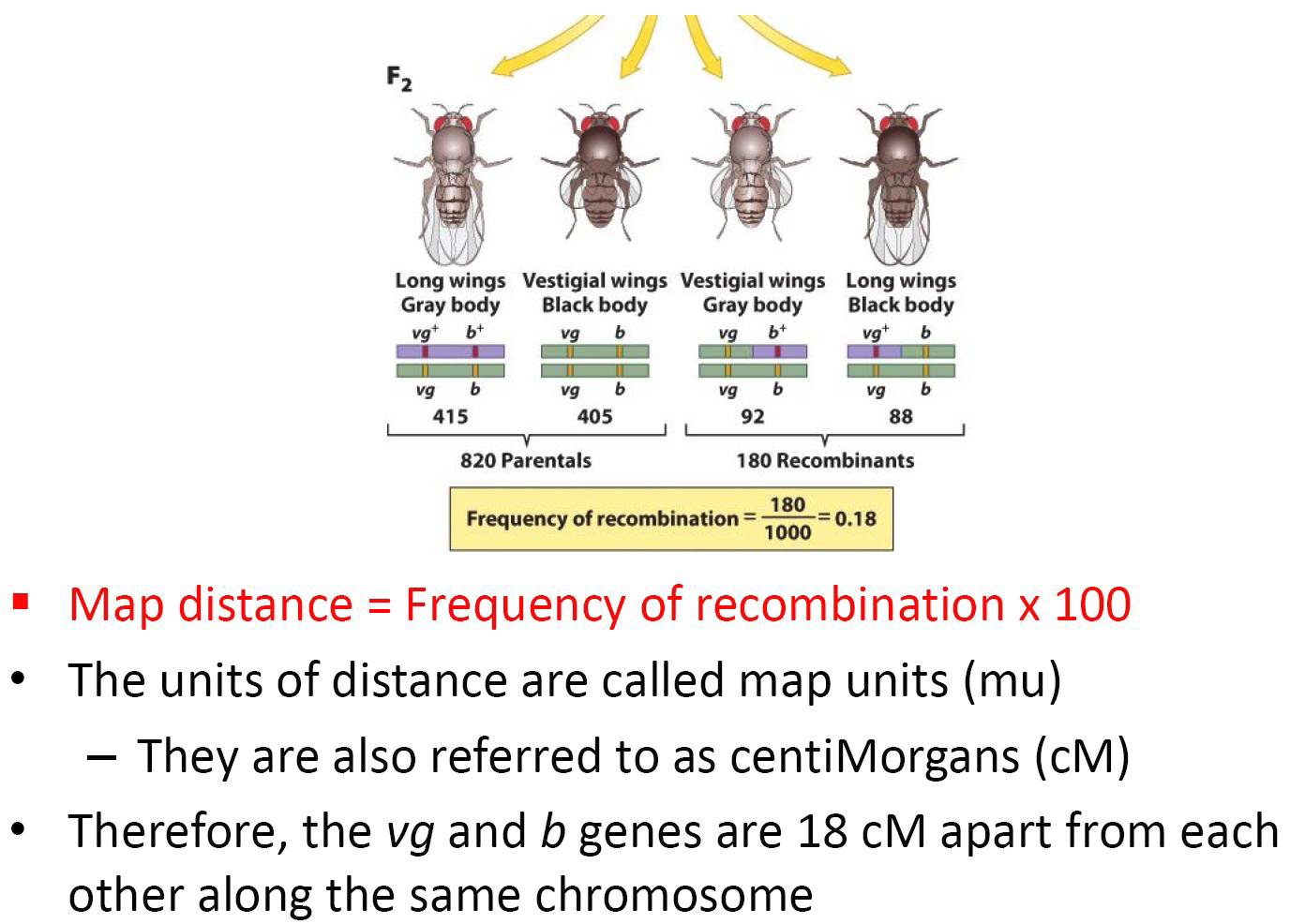
Construction of Genetic Map
By calculating recombination frequencies between each pair of adjacent genes, we are able to construct a map of a large segment of the chromosome
Interference
This lower-than-expected value is due to a common genetic phenomenon, termed interference
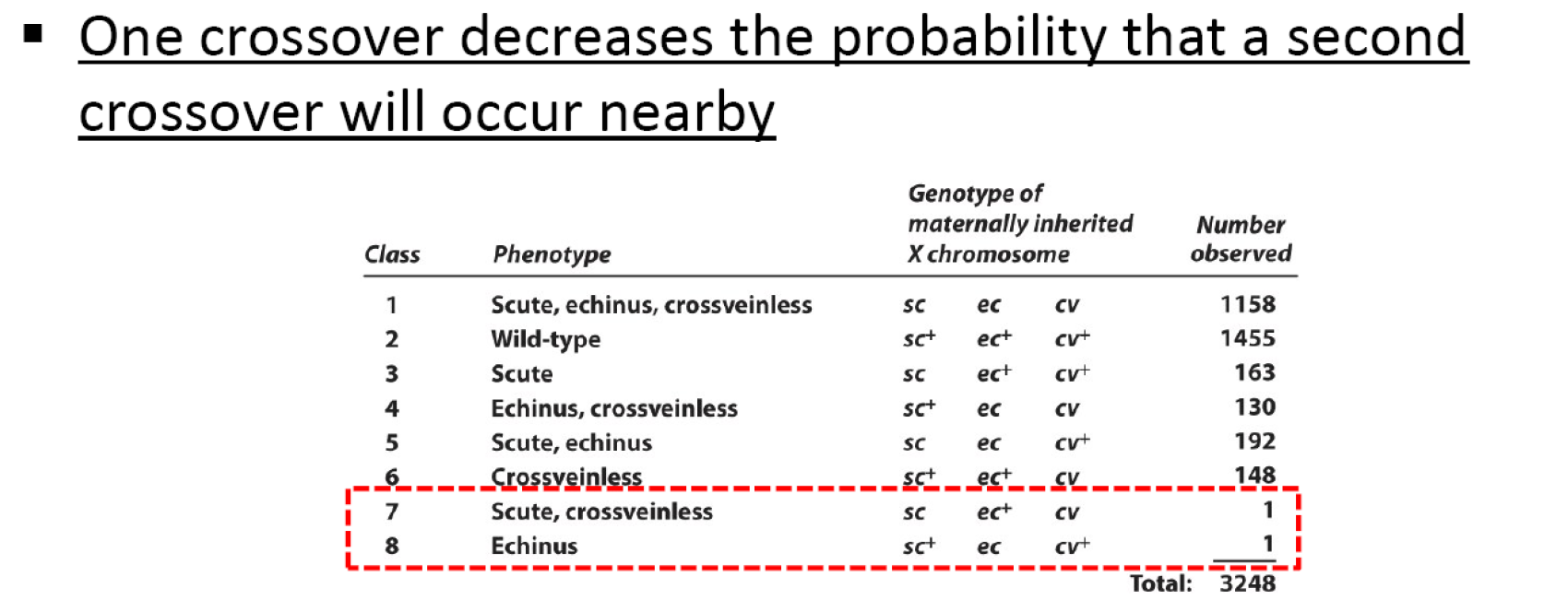
The extent of the interference is measured by the coefficient of coincidence.
The interference(I) is expressed as:
$$
I = 1-C
$$
C is the coefficient of coincidence:
$$
C = \frac{Observed\ number\ of\ double\ crossovers}{Expected\ nuber\ of\ double\ crossovers}
$$
The $I$ means $(I \cdot 100%)$ of the expected number of crossovers did not occur
The genetic map distance may be much greater than the observed recombination frequency
Multiple crossovers occur between widely separated genes, but some of these crossover do not produce genetically recombinant chromosomes.
Recombination Frequency Vs. Genetic Map Distance
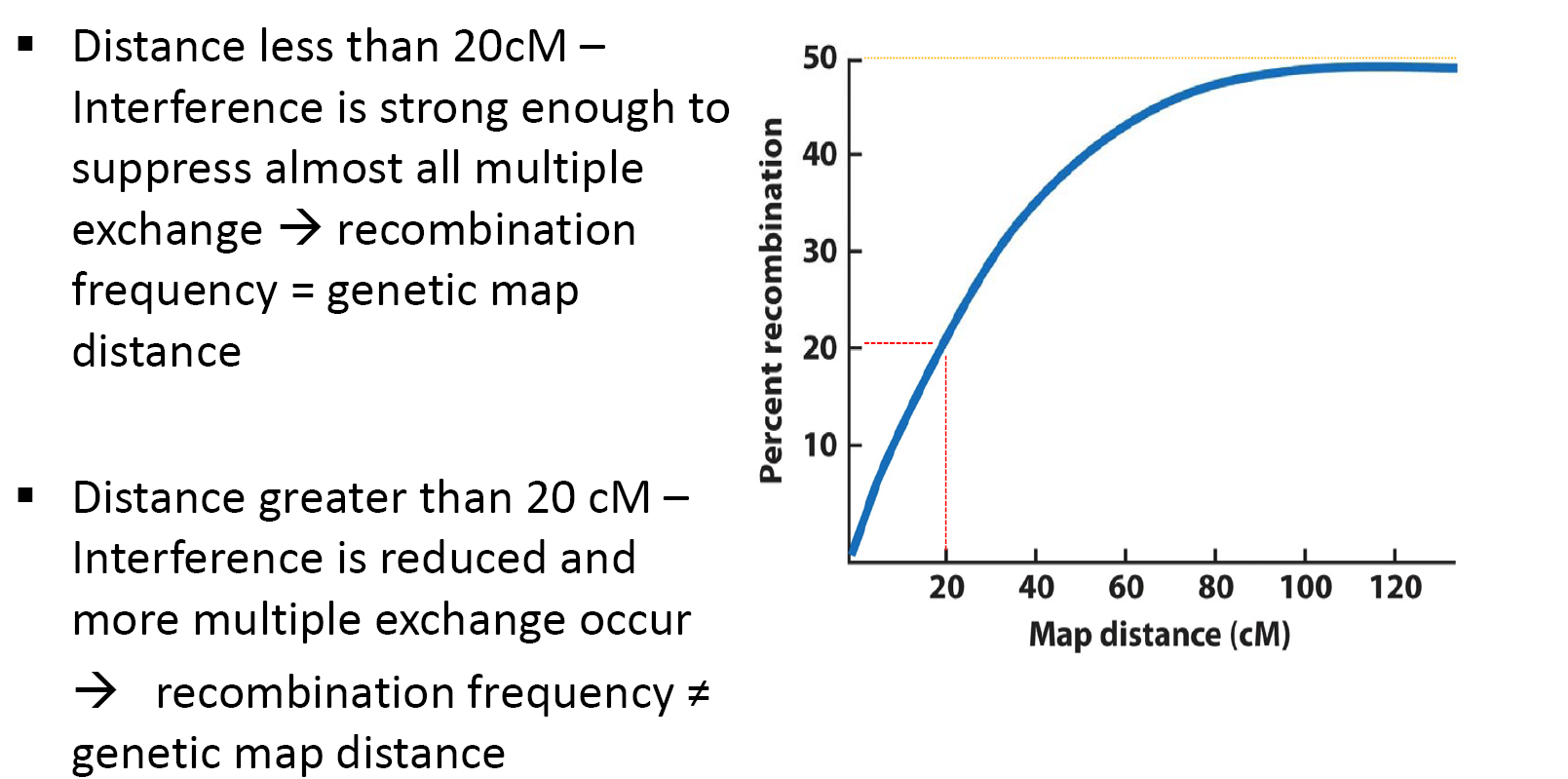
用重组频率来表示基因之间的相对距离具有一定的局限性
Example: Recombination near the centromere (in heterochromatin)
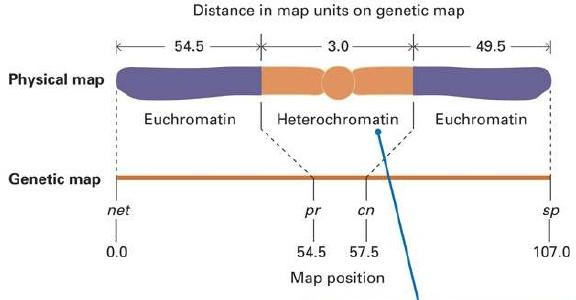
Very little recombination takes place in heterochromatin; a small distance in the genetic map corresponds to a large distance on the chromosome.
- Map distances based on recombination frequencies are not a direct measurement of physical distance along a chromosome
- Recombination “hot spots” overestimate physical length
- Low rates in heterochromatin and centromeres underestimate (估计不足) actual physical length