L15 Applied Microbiology
一、Controlling Food Spoilage
Methods of preservation 保存
- Filtration
- Low Temperature
- High Temperature
- Pasteurization
- Dehydration
- Radiation
- Others
1. High Hydrostatic Pressure (HHP)
Applies pressures from 100-800 milliPascals (MPs)
- highly detrimental to cell membranes
- effective at eliminating eukaryotic microbes
- not as effective at elimination of Gram-positive microbes
2. Packaging
Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP)
- shrink wrap materials and vacuum technology control atmosphere
- impermeable to gasses
- high CO2 content packaging
- high O2 content packaging produces superoxide radicals that inhibit microbial growth
Chemical-Based Preservation
Microbial Product-Based Inhibition
Bacteriocins 细菌素
Bacteriocins are proteinaceous toxins produced by bacteria to inhibit the growth of similar or closely related bacterial strain(s).
Bacteriophages
- sprayed onto ready-to-eat meats prior to packaging
二、Water Purification and Sanitary Analysis
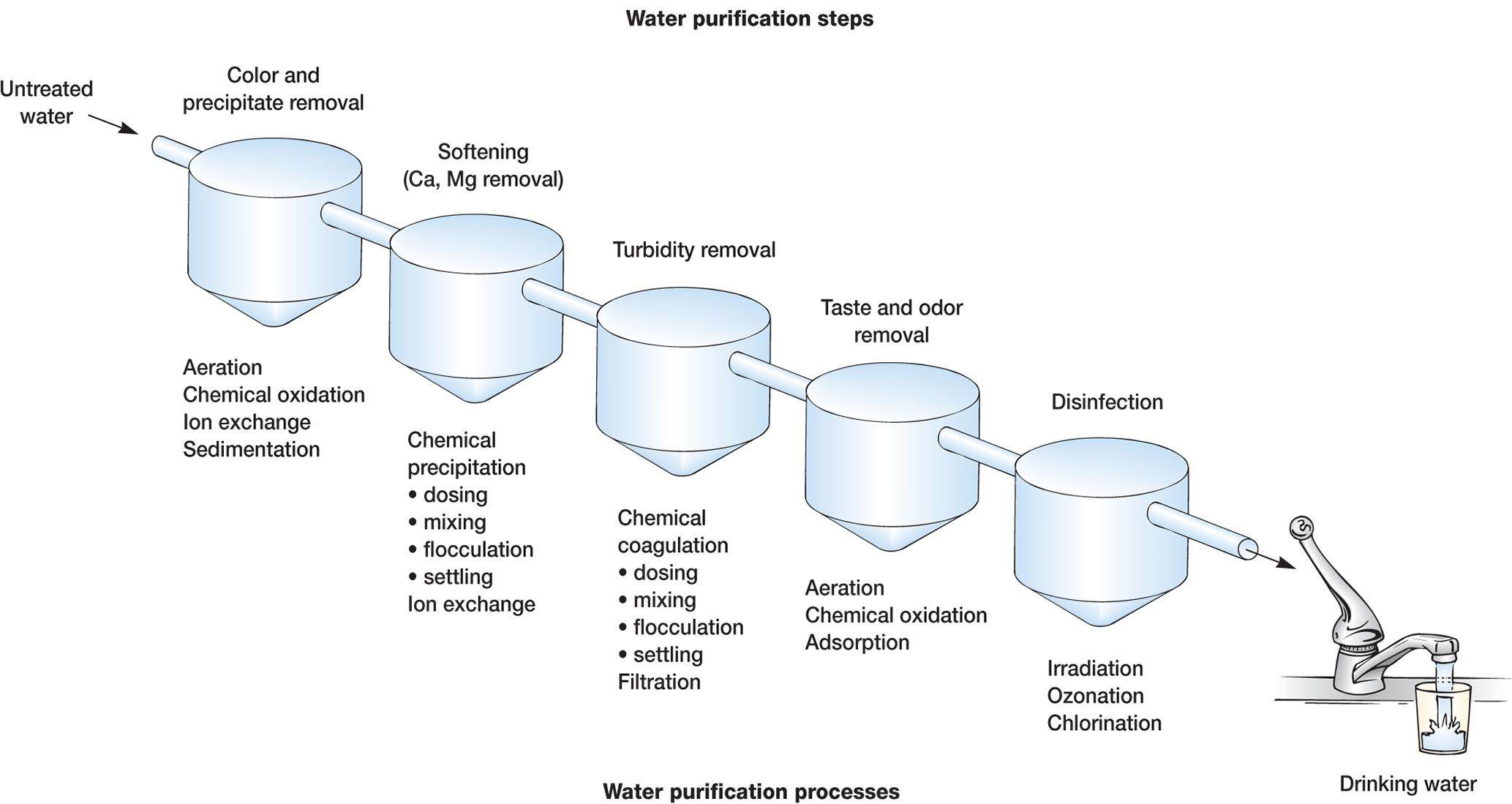
Sanitary Analysis of Waters 水质卫生分析
Based on detecting indicator organisms
- indicate fecal contamination of water supplies
- indicate possible contamination by human pathogens
1. “Ideal” Indicator Organism
Suitable for analysis of all types of water
Present whenever enteric pathogens are present
Survives longer than hardiest enteric pathogen
Does not reproduce in contaminated water
Detected by highly specific test
- test easy to do and sensitive
Harmless to humans
Its level in water reflects degree of fecal pollution
Two Commonly Used Indicators
Conforms (Escherichia, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, etc.)
Fecal Streptococci
- increasingly used to test brackish and marine water
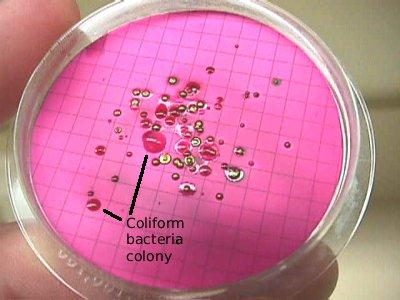
2. Multiple-tube Fermentation Test
MPN: most probable number
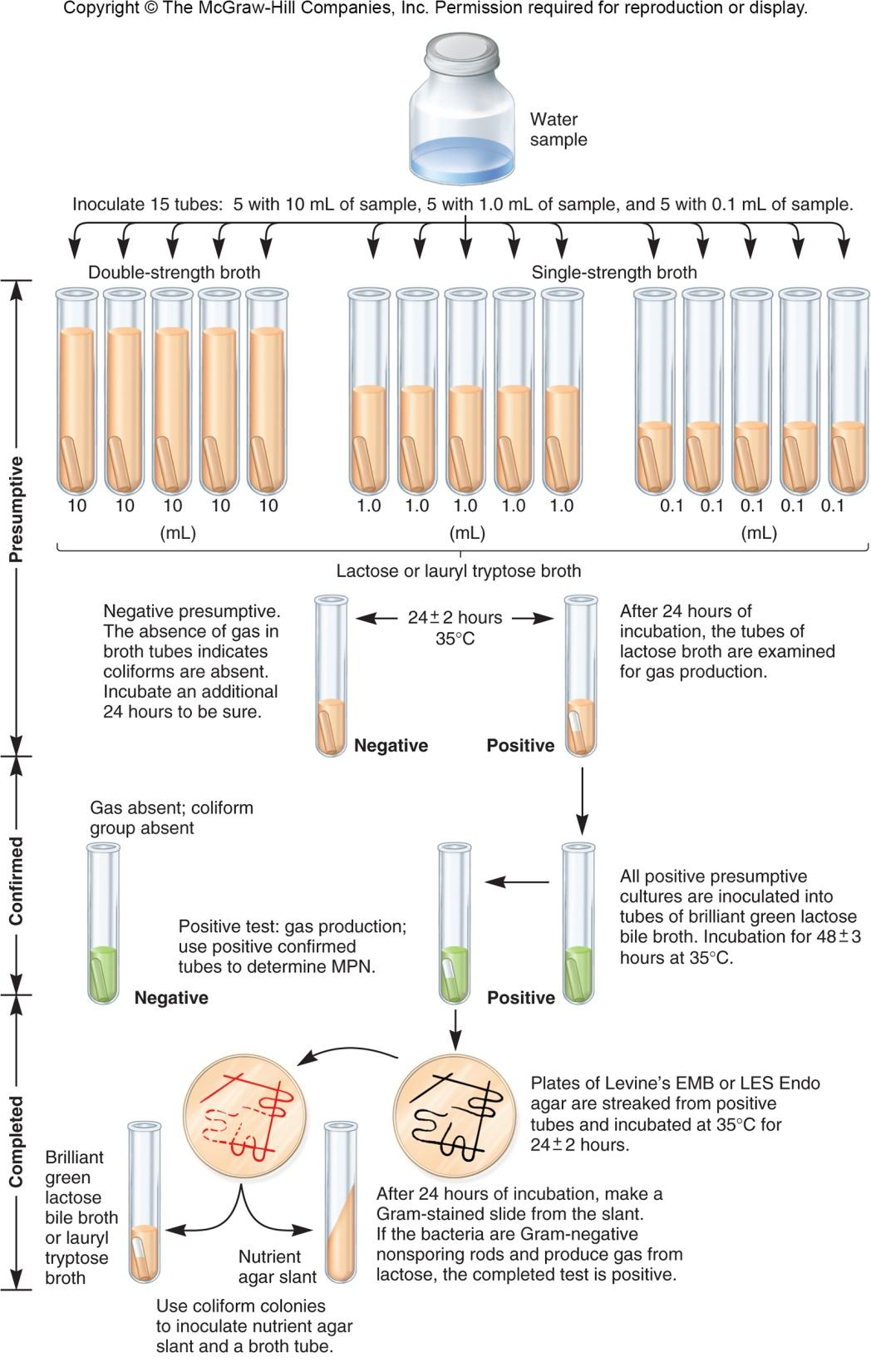
3. Other Tests for Indicator Organisms
- Membrane filtration technique
- Presence-absence (P-A) test
- Defined substrate tests 定义基板测试
- Molecular analysis
- flow cytometry
- FISH
- quantitative PCRs
- microarrays
Wastewater Treatment
Decreases organic matter and number of microorganisms
Has lead to major reduction in spread of pathogens

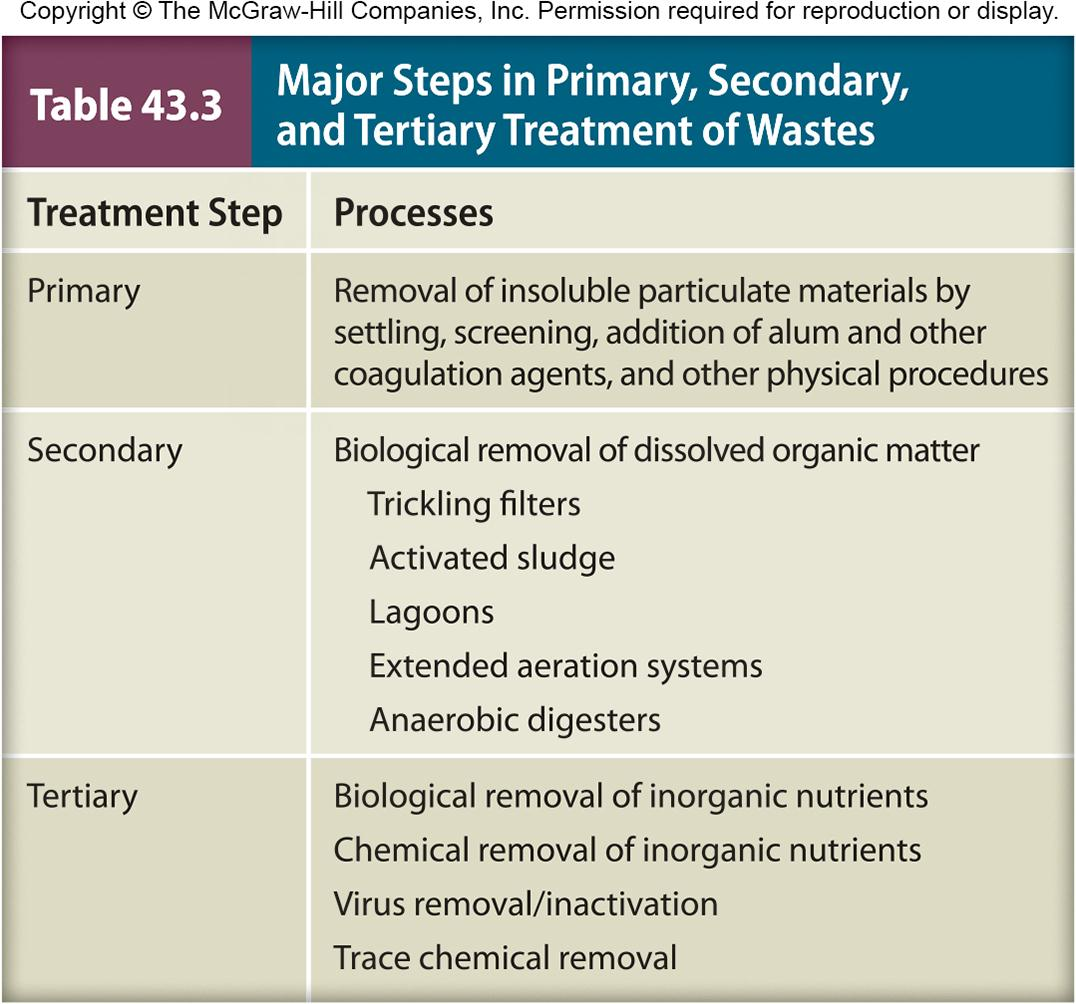
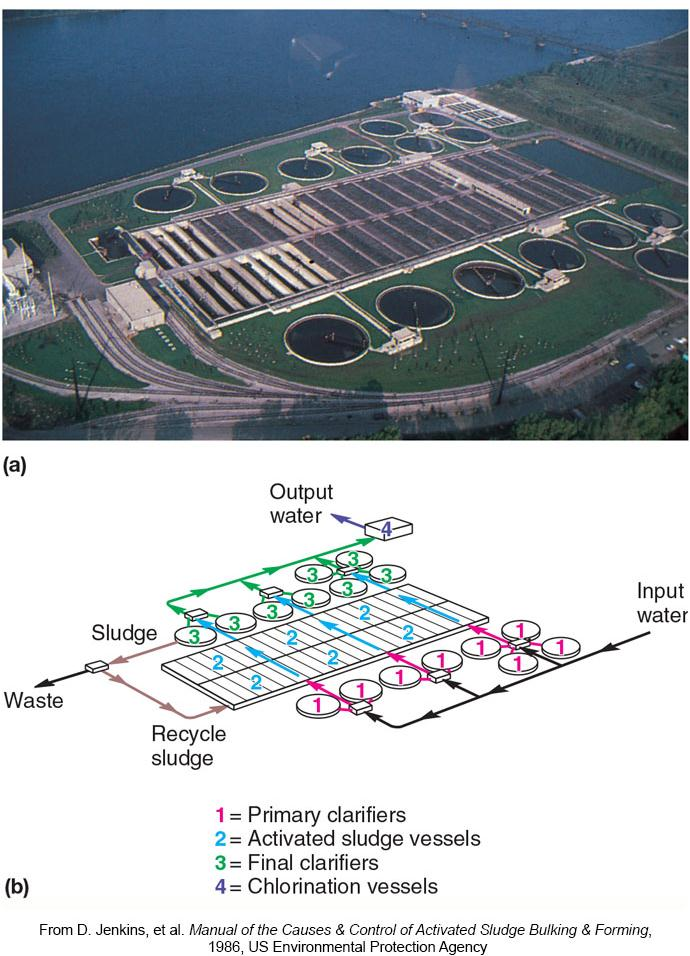
1. Wastewater Treatment Processes
Primary treatment
- removes solid material and forms sludge
Secondary treatment
- dissolved organic matter transformed into microbial biomass and carbon dioxide
Tertiary treatment
- removal of nitrogen and phosphorus that may promote eutrophication
- removes heavy metals, biodegradable organics, and remaining microbes, including microbes
Measuring Water Quality
Testing for water quality is often a measurement of carbon (organic matter) removal
total organic carbon (TOC) levels
- oxidation of carbon to CO2, then measuring by infrared methods
chemical oxygen demand (COD) test
- similar to TOC testing, but will not measure lignin levels
biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) test
- measures carbon oxidized by microbes in 5 days at 20° C