L11 Viruses
一、Virus Taxonomy and Phylogeny
Lack of information on origin and evolutionary history makes viral classification difficult
A uniform classification system developed in 1971 by the International Committee for Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)

Virus Classification
Classification based on numerous characteristics
nucleic acid type
presence or absence of envelope
capsid symmetry
dimensions of virion and capsid(病毒粒子和衣壳的尺寸)

Alternative Classification Scheme
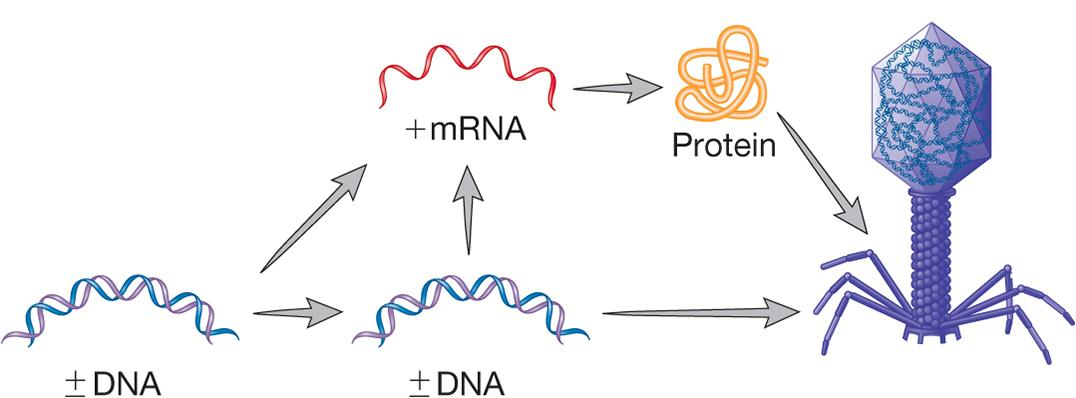
David Baltimore
- focuses on viral genome and process used to synthesize viral mRNA
| Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Double-stranded (ds) DNA viruses | Genome replication: dsDNA -> dsDNA mRNA synthesis: dsDNA -> mRNA |
| Single-stranded (ss) DNA viruses | Genome replication: ssDNA -> dsDNA -> ssDNA mRNA synthesis: ssDNA -> dsDNA -> mRNA |
| Double-stranded RNA viruses | Genome replication: dsRNA -> ssRNA -> dsRNA mRNA synthesis: dsRNA -> mRNA |
| Plus-strand RNA (+RNA) viruses | Genome replication: +RNA -> –RNA -> +RNA mRNA synthesis: +RNA = mRNA -> –RNA -> mRNA |
| Negative-strand RNA (–RNA) viruses | Genome replication: –RNA -> +RNA -> –RNA mRNA synthesis: –RNA -> mRNA |
| Retroviruses | Genome replication: ssRNA -> dsDNA -> ssRNA mRNA synthesis: ssRNA -> dsDNA -> mRNA |
| Reverse transcribing DNA viruses | Genome replication: dsDNA -> ssRNA -> dsDNA mRNA synthesis: dsDNA -> mRNA |
二、Different Virus Types
Double-stranded DNA Viruses
Largest group of known viruses
- most bacteriophages (噬菌体), herpesviruses(疱疹病毒), poxviruses(痘病毒), insect viruses
Some rely on host’s DNA/RNA polymerases
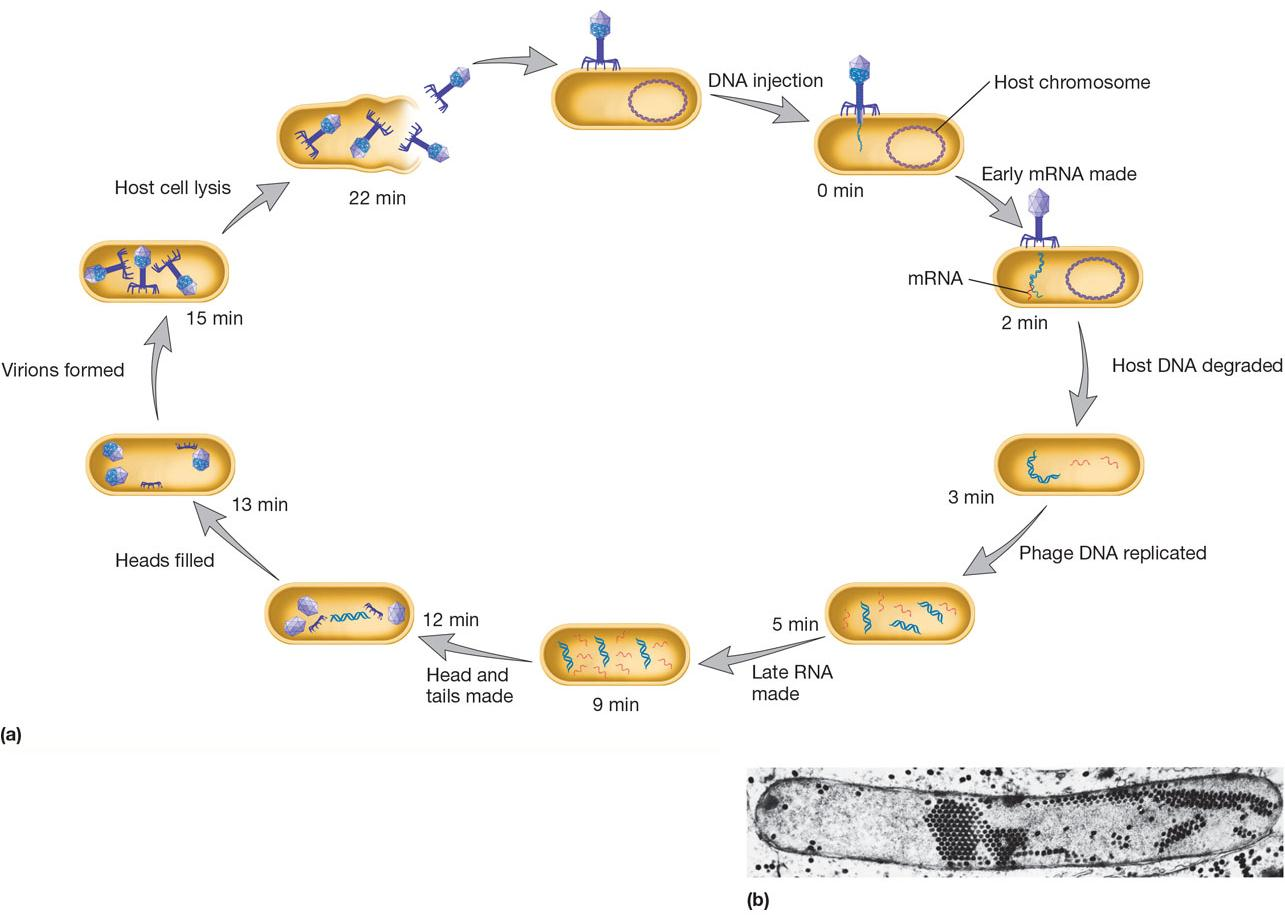
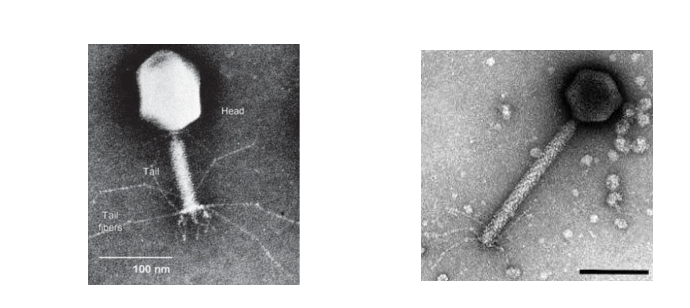
1. Bacteriophage T4: A Virulent Bacteriophage
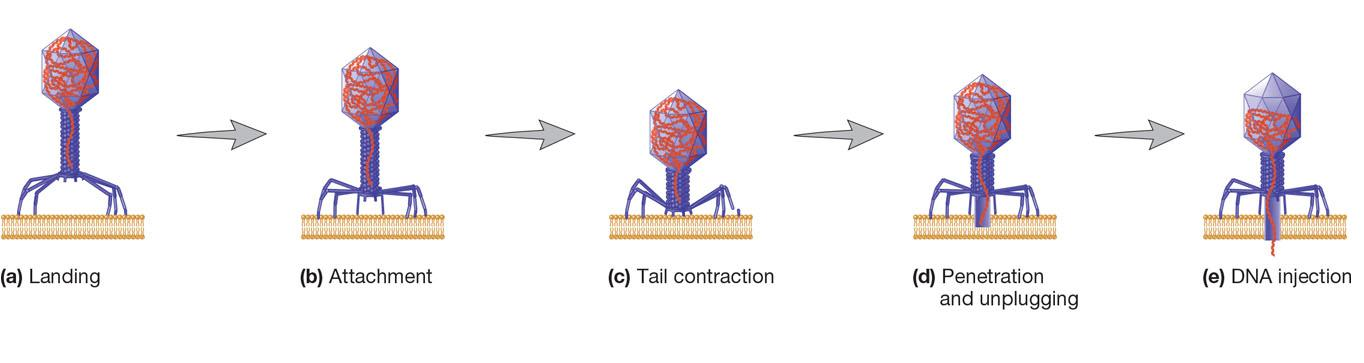
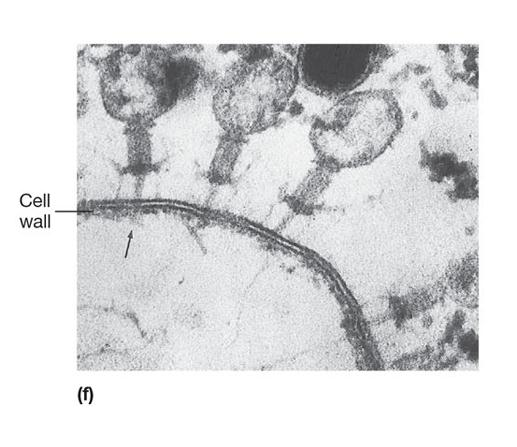
Lifecycle of T4
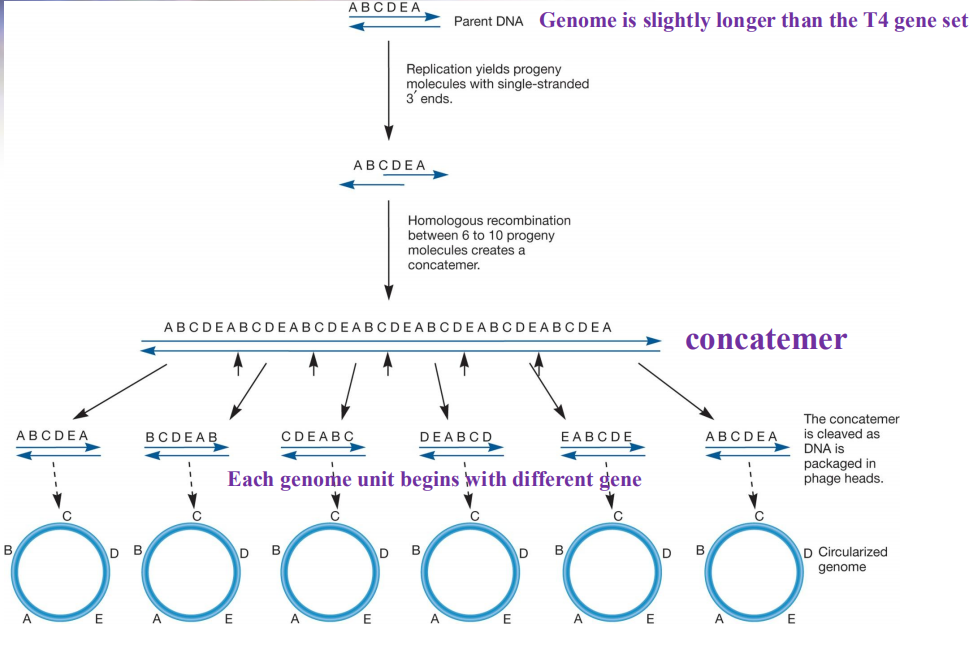
The T4 Genome
Codes for replication-related products including
protein subunits of its replisome
enzymes needed for DNA synthesis
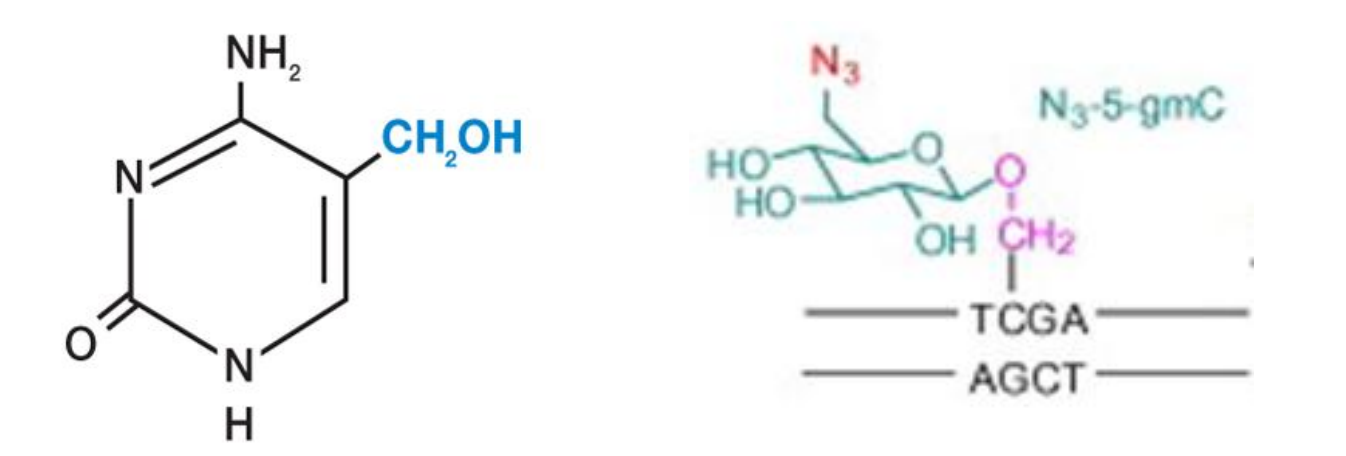
synthesis of hydroxymethylcytosine (HMC), a modified nucleotide replacing cytosine in T4 DNA
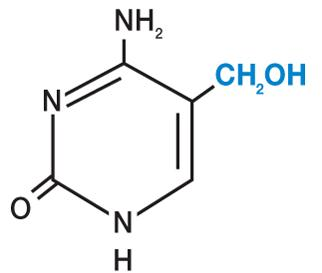
T4 DNA
HMC is then chemically modified by glucosylation
protects T4 phage DNA from E. coli restriction enzymes
restriction is a bacterial defense mechanism used against bacteriophage infection
Release of Phage Particles
In T4 - E. coli system, ~150 viral particles are released
two proteins are involved in process
T4 lysozyme attacks the E. coli cell wall
Holin creates holes in the E. coli plasma membrane
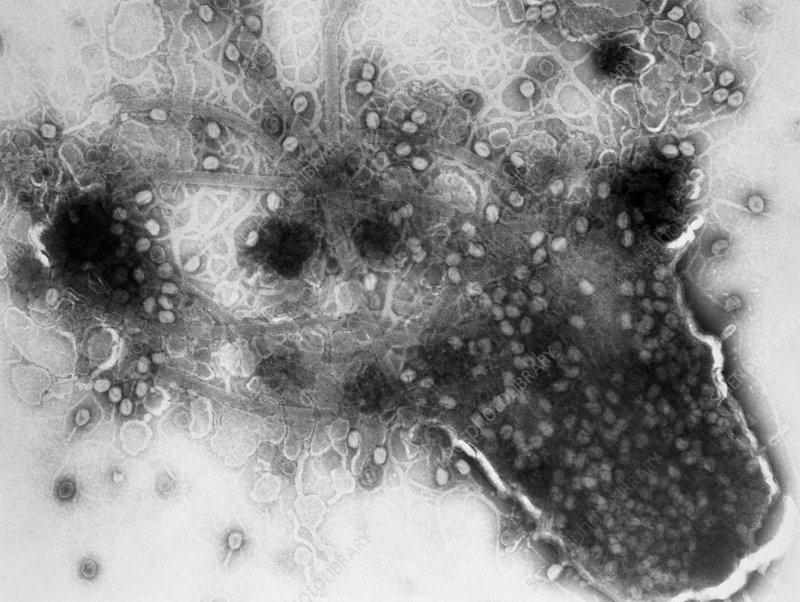
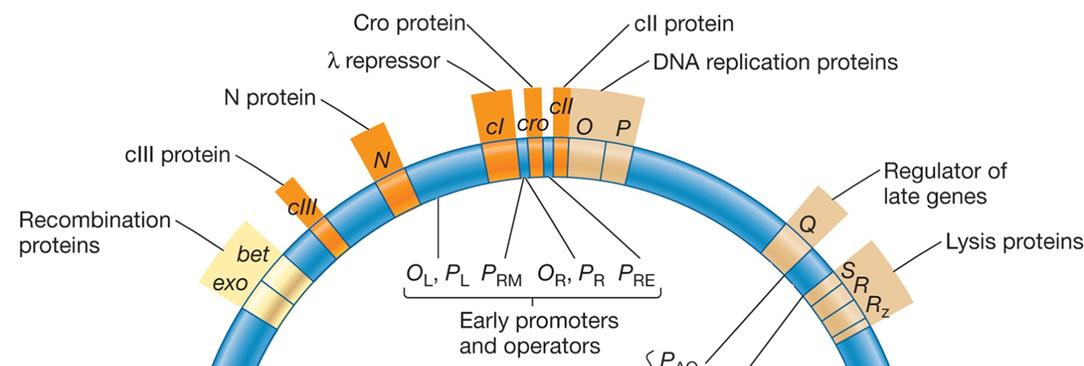
2. Bacteriophage Lambda: A Temperate Bacteriophage
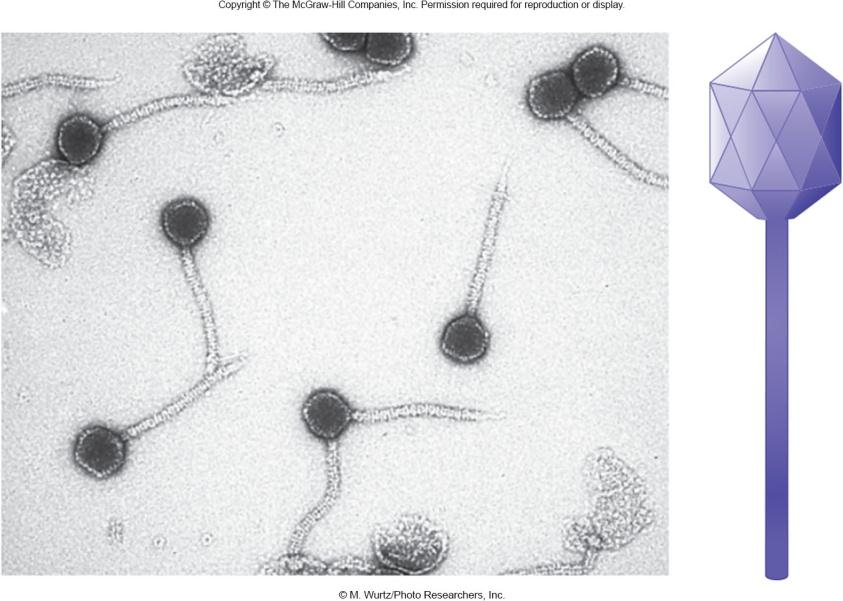
Phage lambda (λ) can enter either the lytic or lysogenic cycle upon infection of E. coli
Lambda Phage
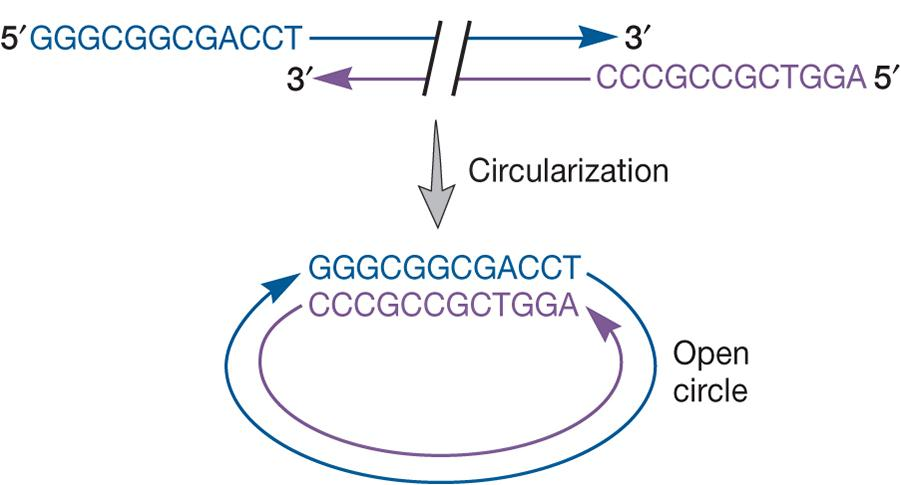
Linear ds DNA genome with cohesive ends
circularizes upon injection into host cytoplasm
40 genes, genes clustered together by function
transcription from different promoters determine if lytic cycle or lysogeny occurs
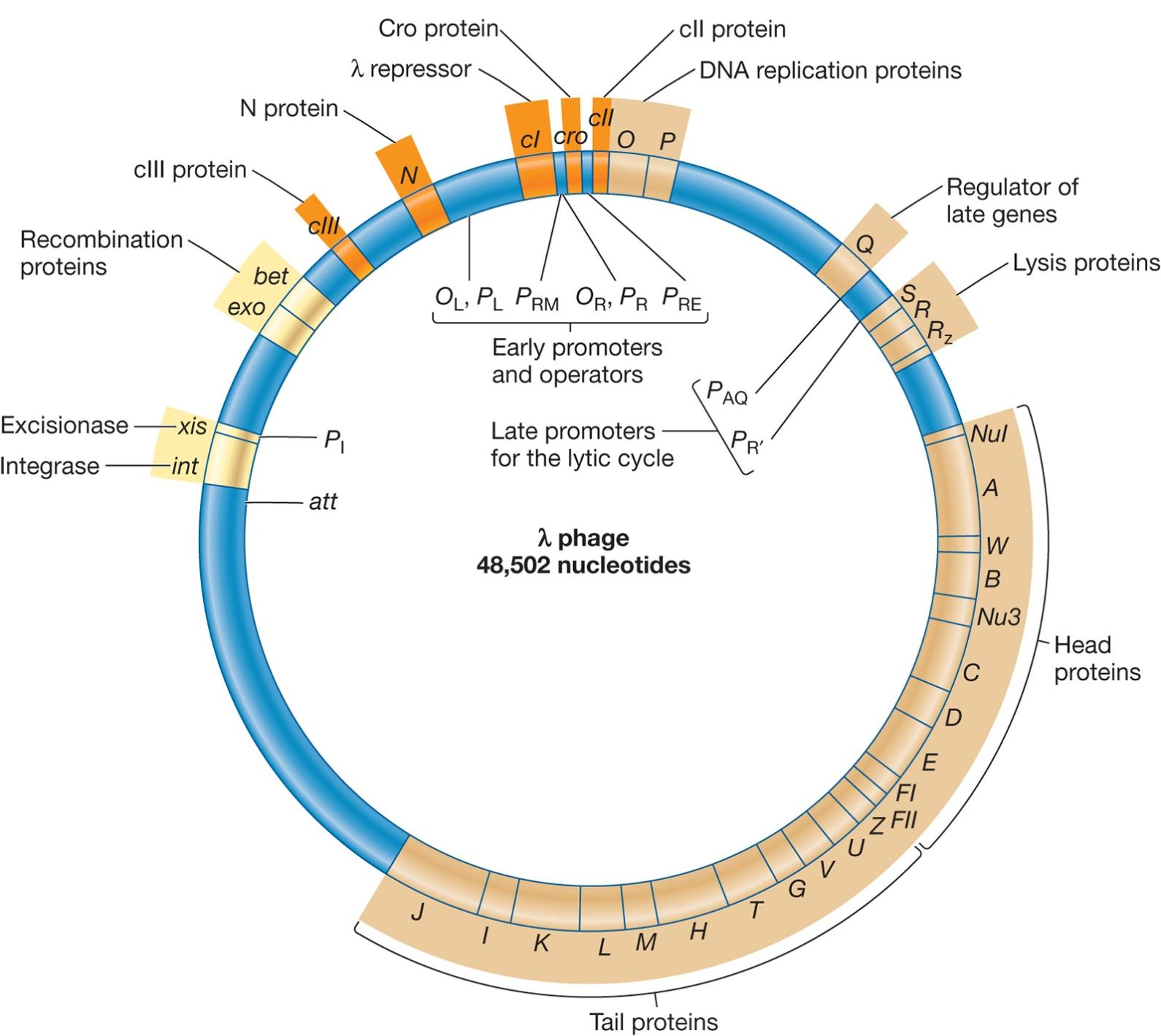
Regulatory Proteins Determine Lysogeny or the Lytic Cycle
Function as repressors, activators, or both
- cII activator
- cII levels high early in infection – lysogeny
- cII levels not high early in infection – lytic cycle
(1) The Decision Making Process
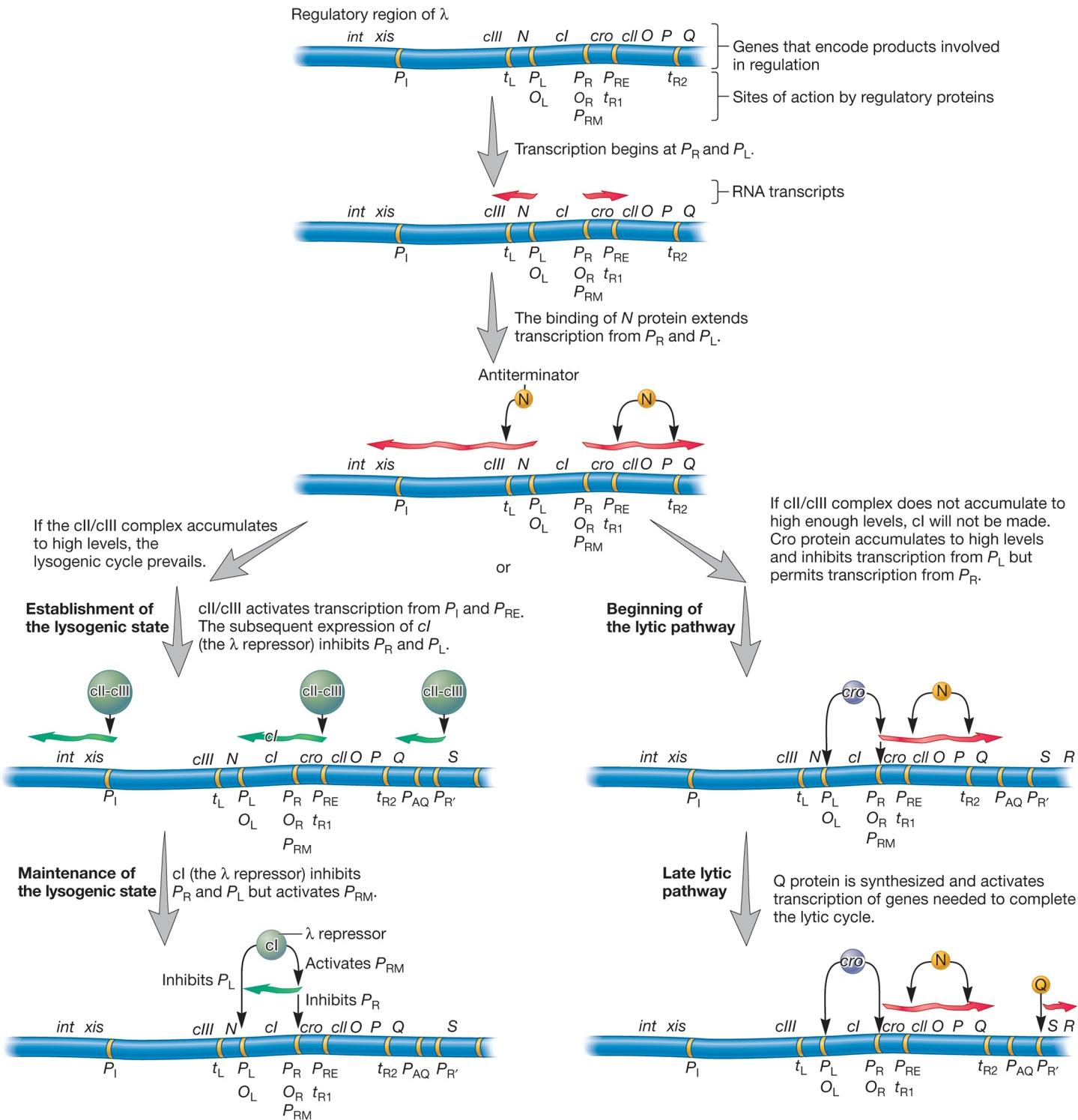
cI gene is the λ repressor.
How Does Induction Reverse Lysogeny?
Triggered by drop in λ repressor levels
- due to UV light, mutagenic chemicals
- DNA damage alters host cell RecA protein interacting with λ repressor, causing repressor to cleave itself
Transcription increases
xis gene, excisionase increases and binds integrase
- reverse integration
Cro protein levels increase
- synthesis of λ repressor blocked
- protein Q increases, lytic cycle proceeds
3. Other Temperate Phages
Bacteriophage Mu
E. coli phage P1
- lysogenic cycle occurs in absence of integration; P1 and E. coli replicate together
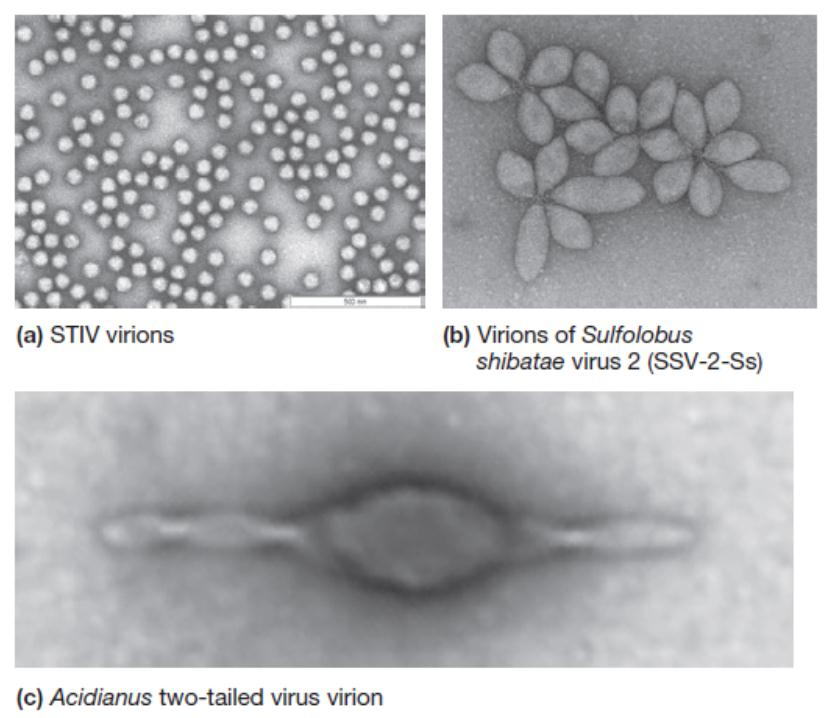
4. Archaeal Viruses
All known archaeal viruses have dsDNA genomes (1 exception with ssDNA genome)
5. Herpesviruses 孢疹病毒
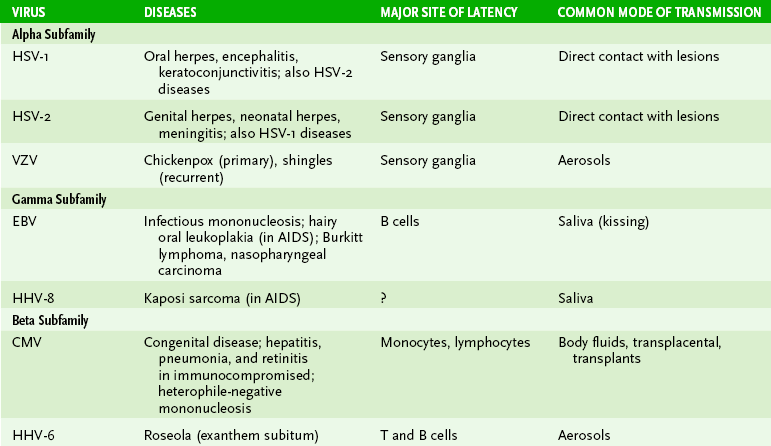
Herpesvirus Virons
Icosahedral(二十面的), 120–200 nm, enveloped, surface spikes
Linear dsDNA genomes, 50–100 genes
50,000–200,000 virions produced/cell
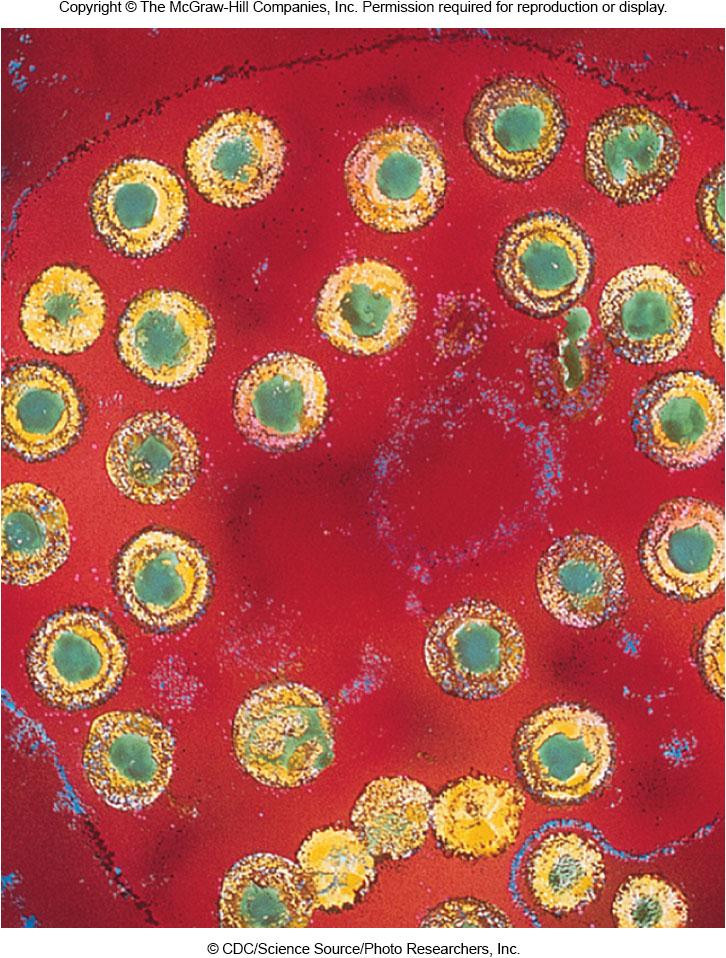
The Life Cycle of HSV-1
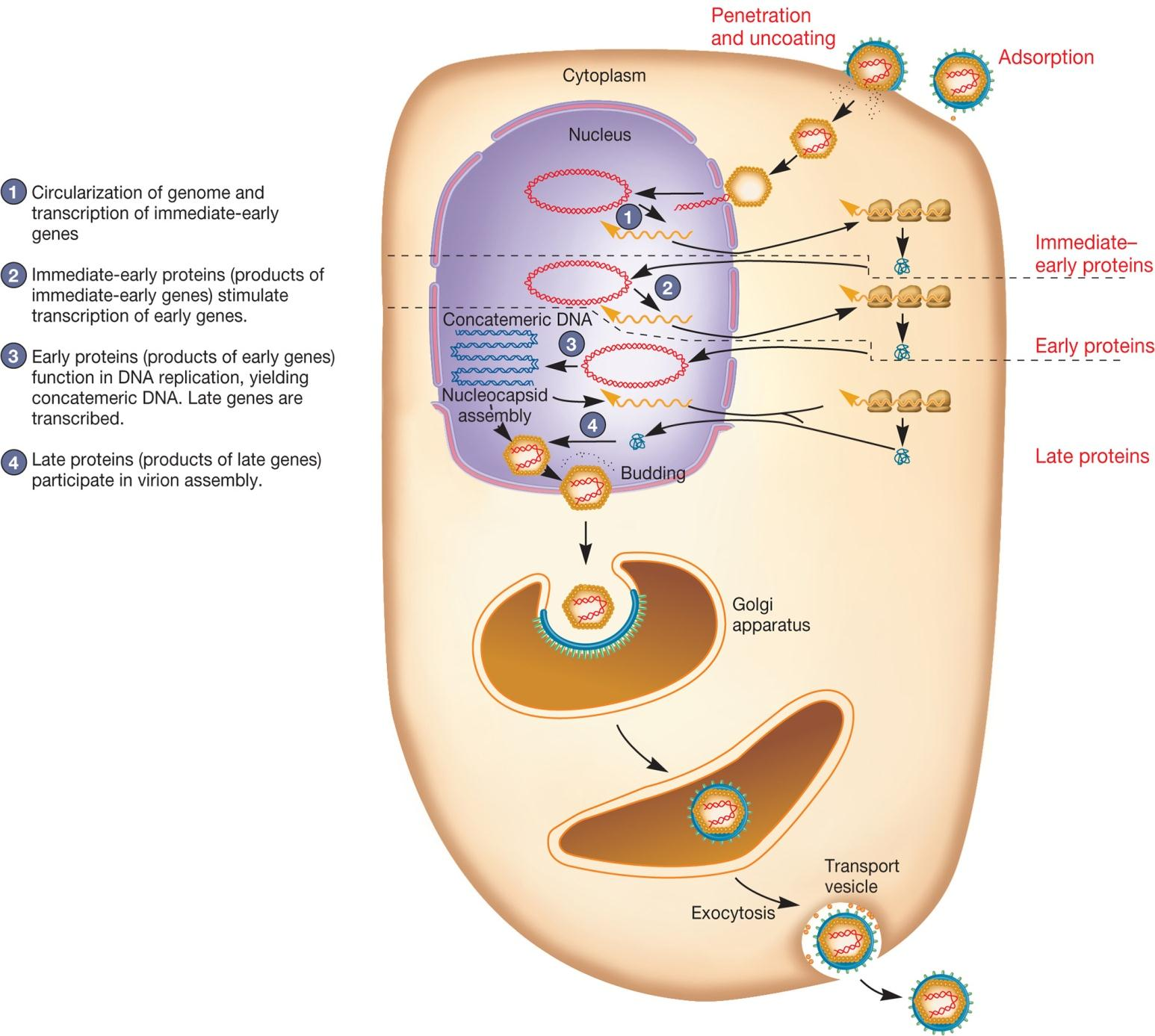
Single-Stranded DNA Viruses
1. Bacteriophage φX174
Double-Stranded RNA Viruses
1. Reproduction of RNA Phages
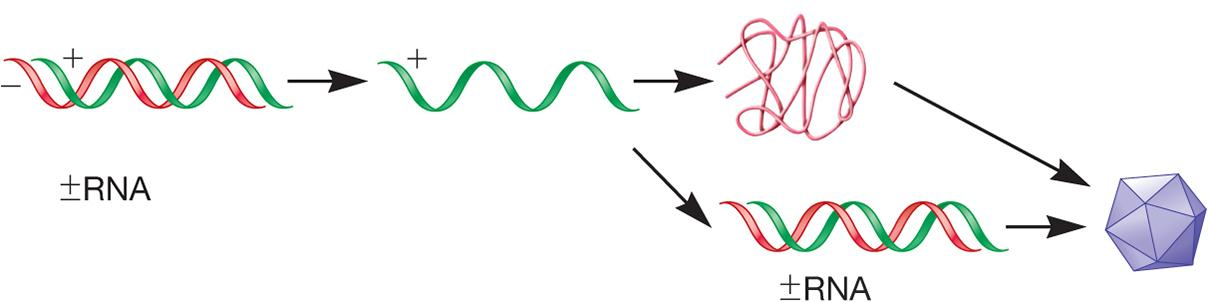
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase completes life cycles
- replicase and transcriptase activities
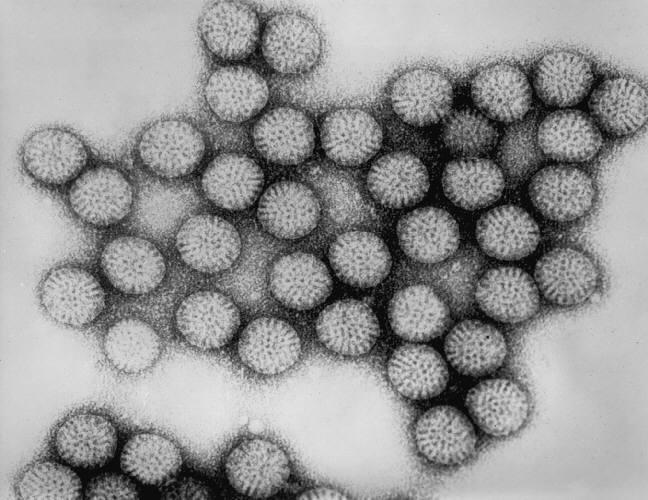
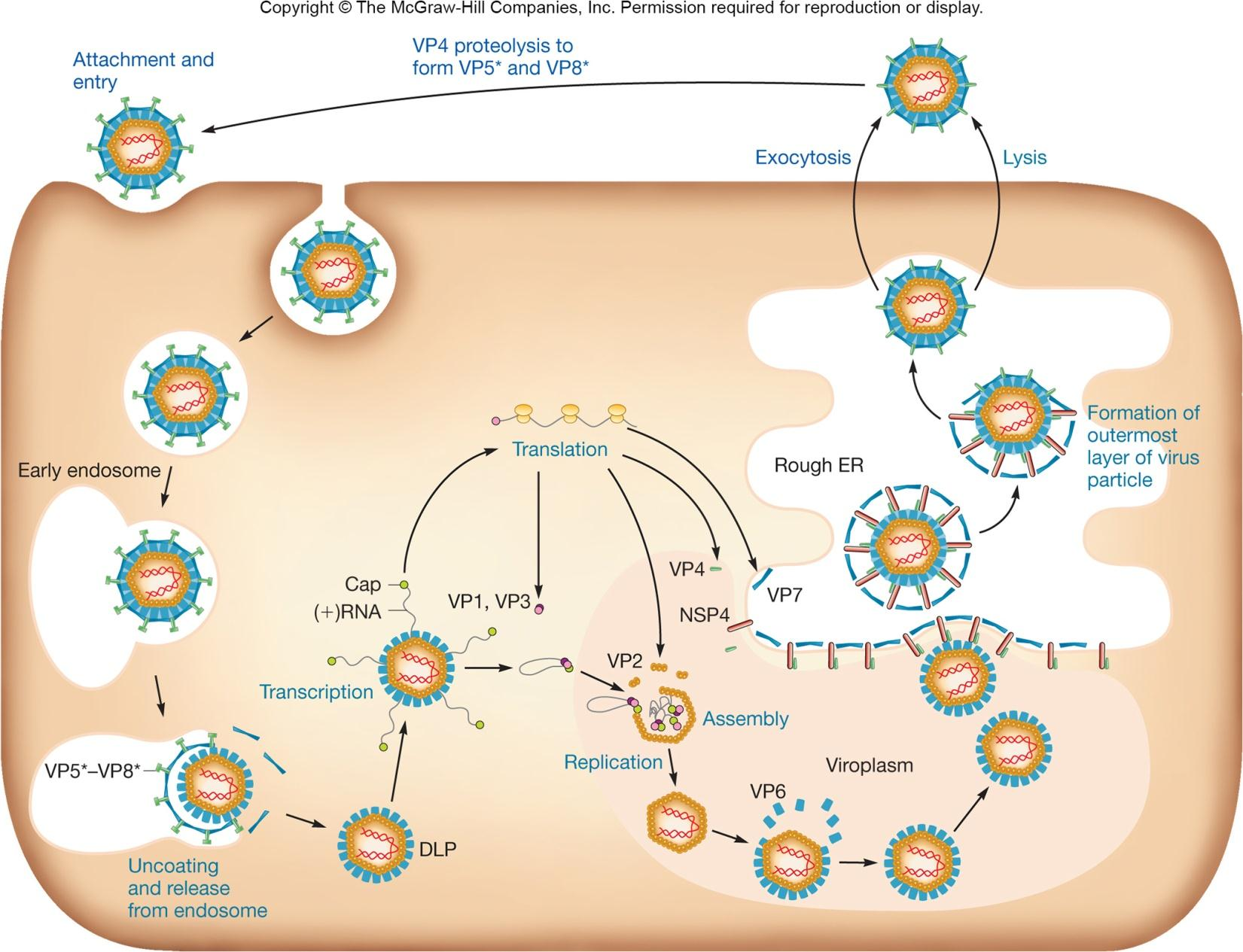
2. Rotavirus 轮状病毒
轮状病毒是一种致婴儿或新生畜胃肠炎的病毒
Human rotavirus kills >600,000 children worldwide each year
- transmitted by fecal material
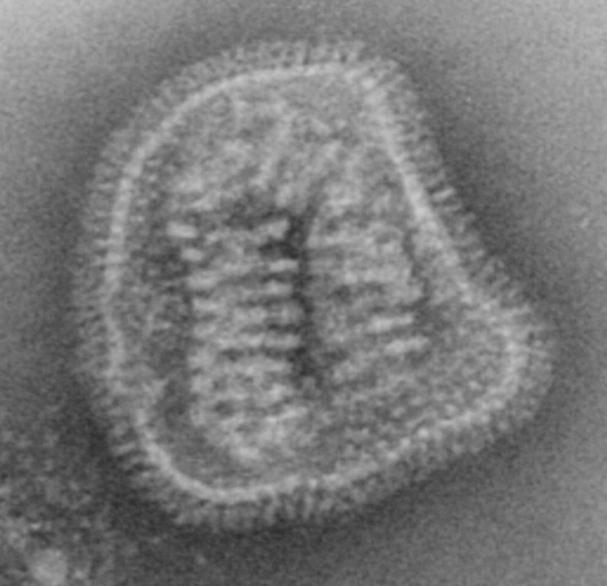
Virion
wheel-like appearance, non-enveloped, segmented genome, dsRNA
Life-cycle of Rotavirus
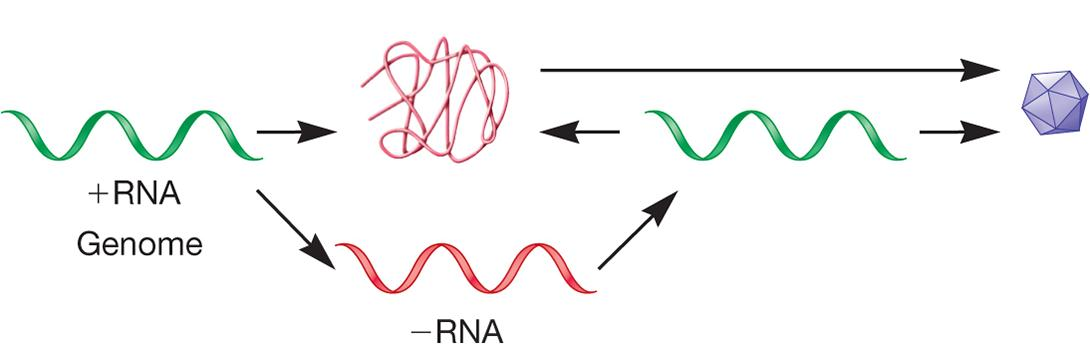
Plus-Strand RNA Viruses
Replicate in cytoplasm and synthesize RNA dependent RNA polymerase
- synthesizes negative strand RNA
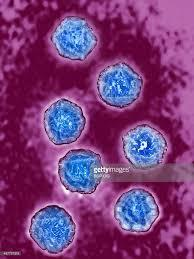
1. Poliovirus 脊髓灰质炎病毒;小儿麻痹病毒
Causative agent of poliomyelitis (脊髓灰质炎,小儿麻痹症)
transmitted by ingestion
may cripple and paralyze
vaccine is eradicating the disease
Virion
- nonenveloped
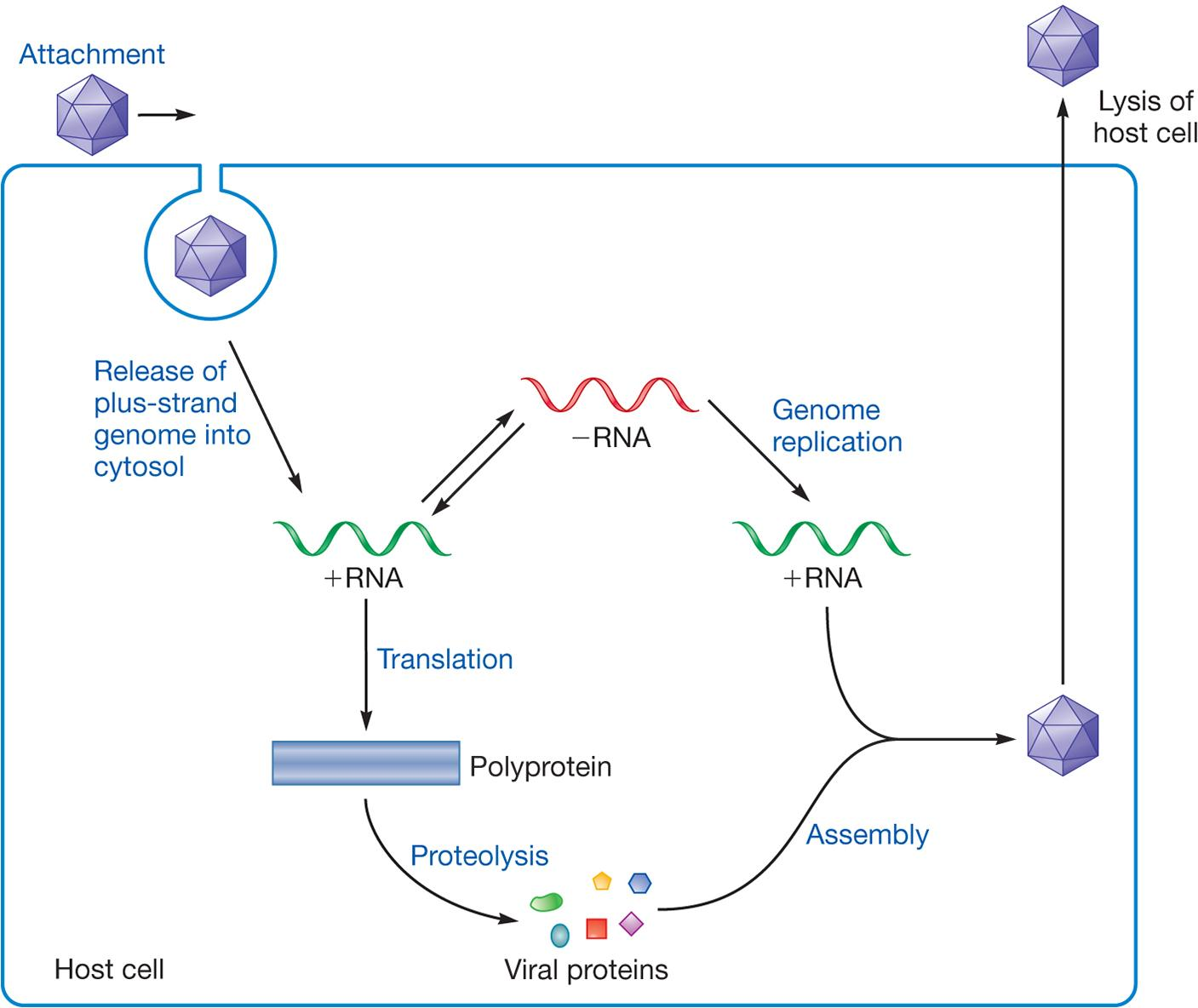
Poliovirus Life Cycle
2. Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)
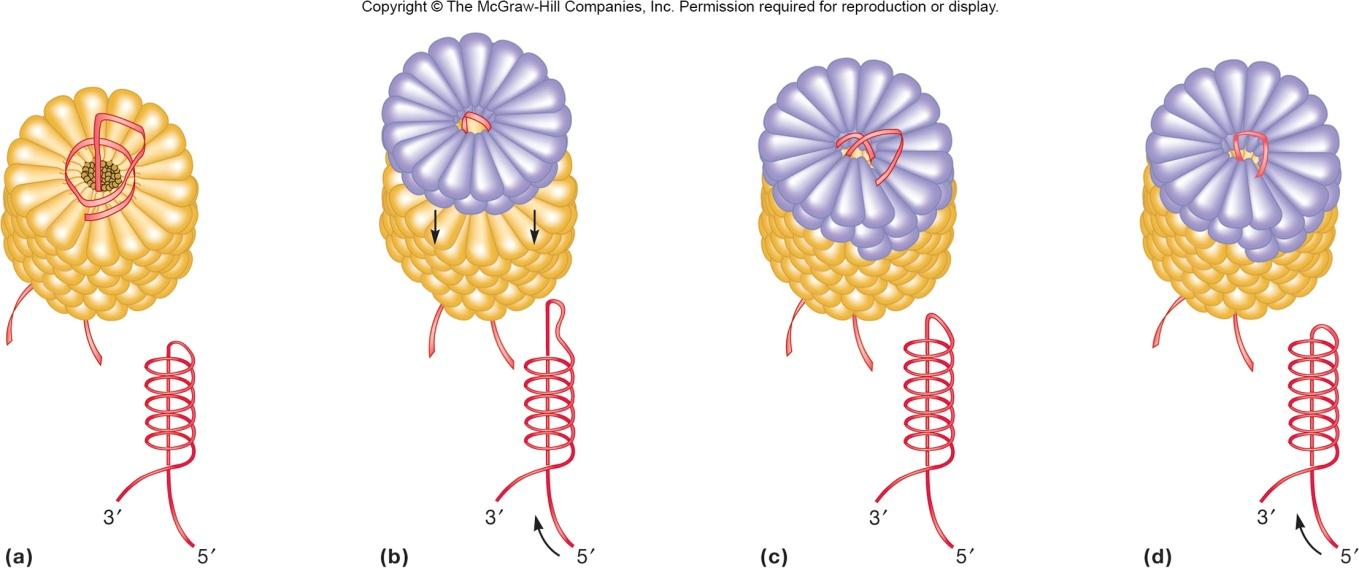
Most plant viruses are plus stranded RNA
TMV
filamentous, helical virion
TMV genome translated into 2 proteins, one with replicase and transcriptase activities
coat protein
Minus-Sense RNA Viruses
Enveloped virions, pleomorphic shape
Segmented and nonsegmented genomes
- Rhabdoviridae 弹状病毒科 – rabies virus (狂犬病;恐水症)
- Filoviridae 丝状病毒科 – Ebola (埃博拉病毒) and Marburg (青猴病;马尔堡病) viruses
- Paramyxoviridae 副粘病毒科 – measles (麻疹;风疹) virus
- Bunyaviridae 本雅病毒科 – segmented (种族隔离的) , hantaviruses (汉坦病毒)
- Orthomyxoviridae 正粘病毒科 – segmented, influenza (流行性感冒) virus
1. Negative-Strand Viruses
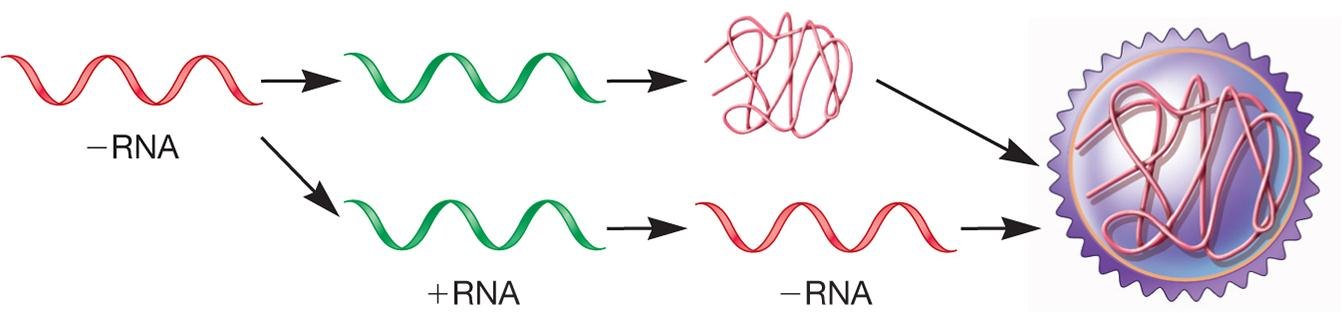
Cannot serve as mRNA to form viral proteins
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
2. Influenza Virus
Causative (成为原因的) agent of the flu
- transmitted by inhalation or ingestion
Three types of viruses – A, B, and C
Seven to eight segments of linear RNA
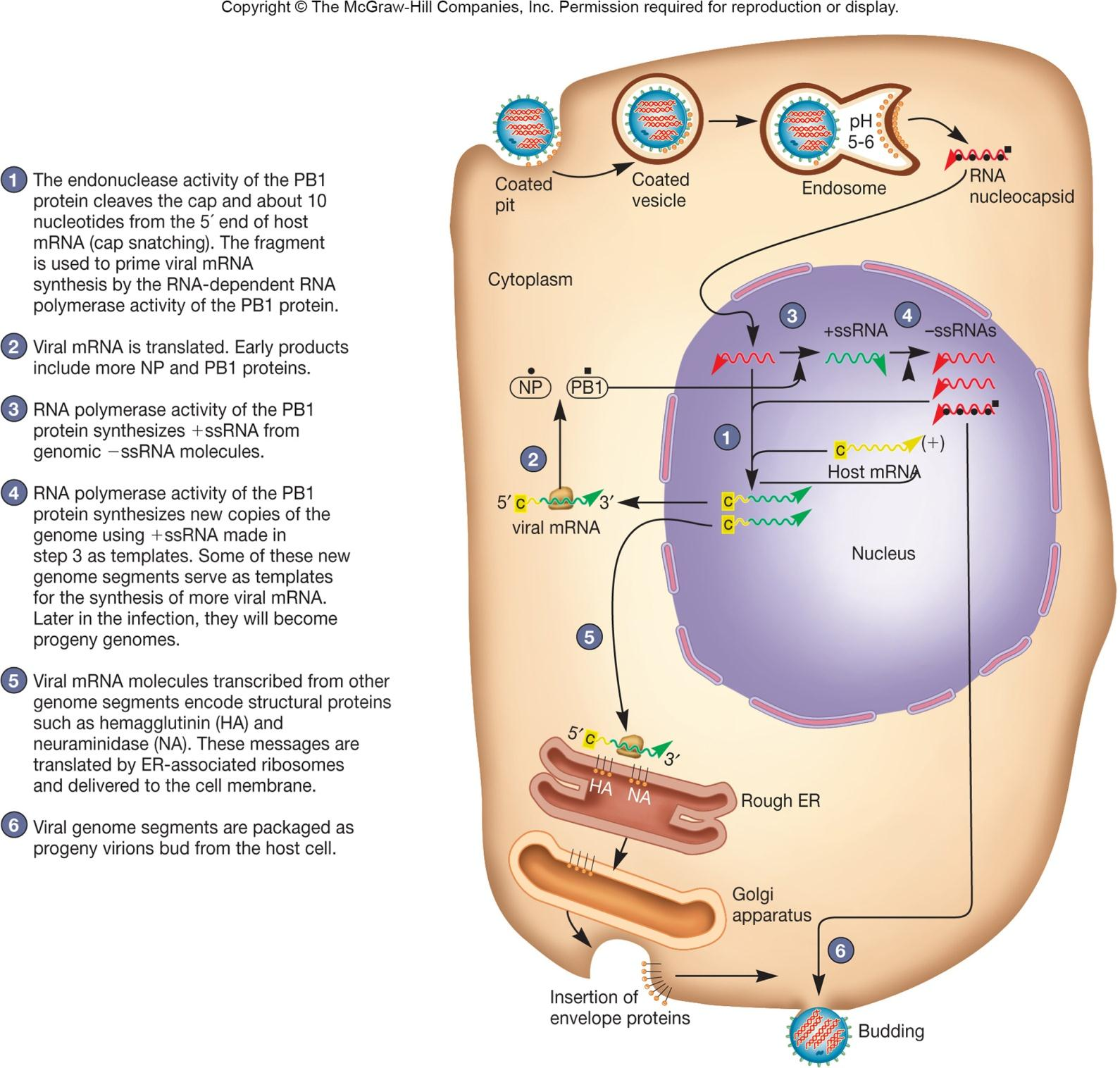
Reverse Transcribing DNA Viruses
1. Hepatitis B Virus
Circular, dsDNA genome (3.2 kb, 4 genes)
one complete, nicked strand
complementary strand has large gap (incomplete)
Viral infection
gapped DNA released into the nucleus
host repair enzymes repair gap
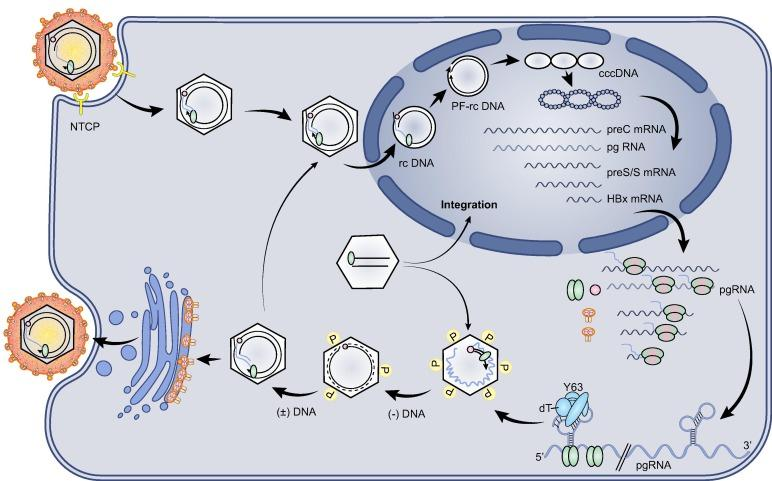
rcDNA: relaxed circular DNA
cccDNA: covalently closed circular DNA
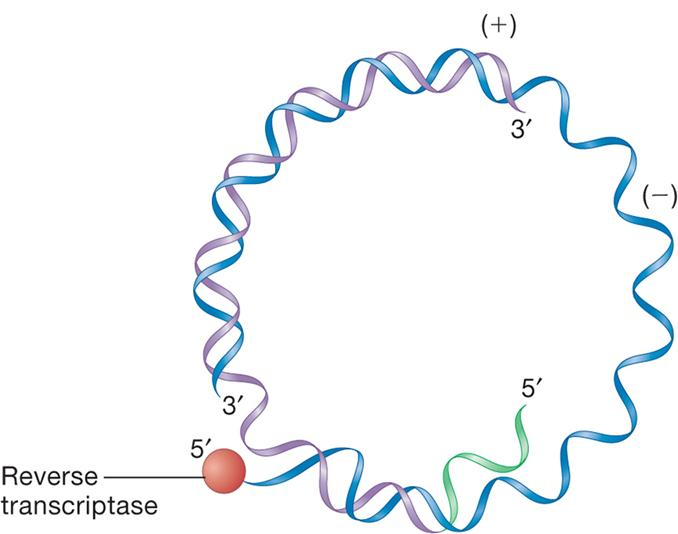
Retroviruses
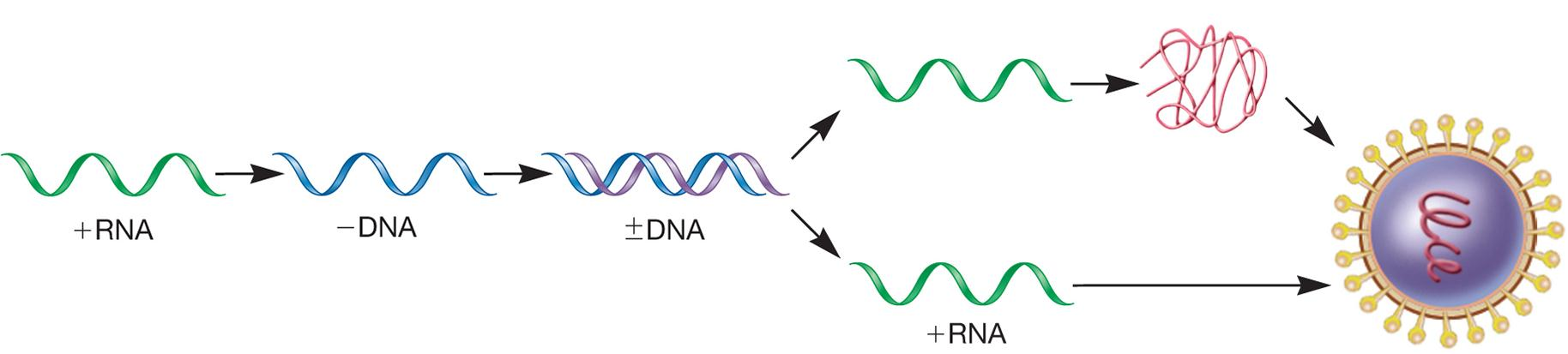
Convert ssRNA into dsDNA using reverse transcriptase
dsDNA integrates into host cell genome and serves as template for mRNA synthesis and genome synthesis
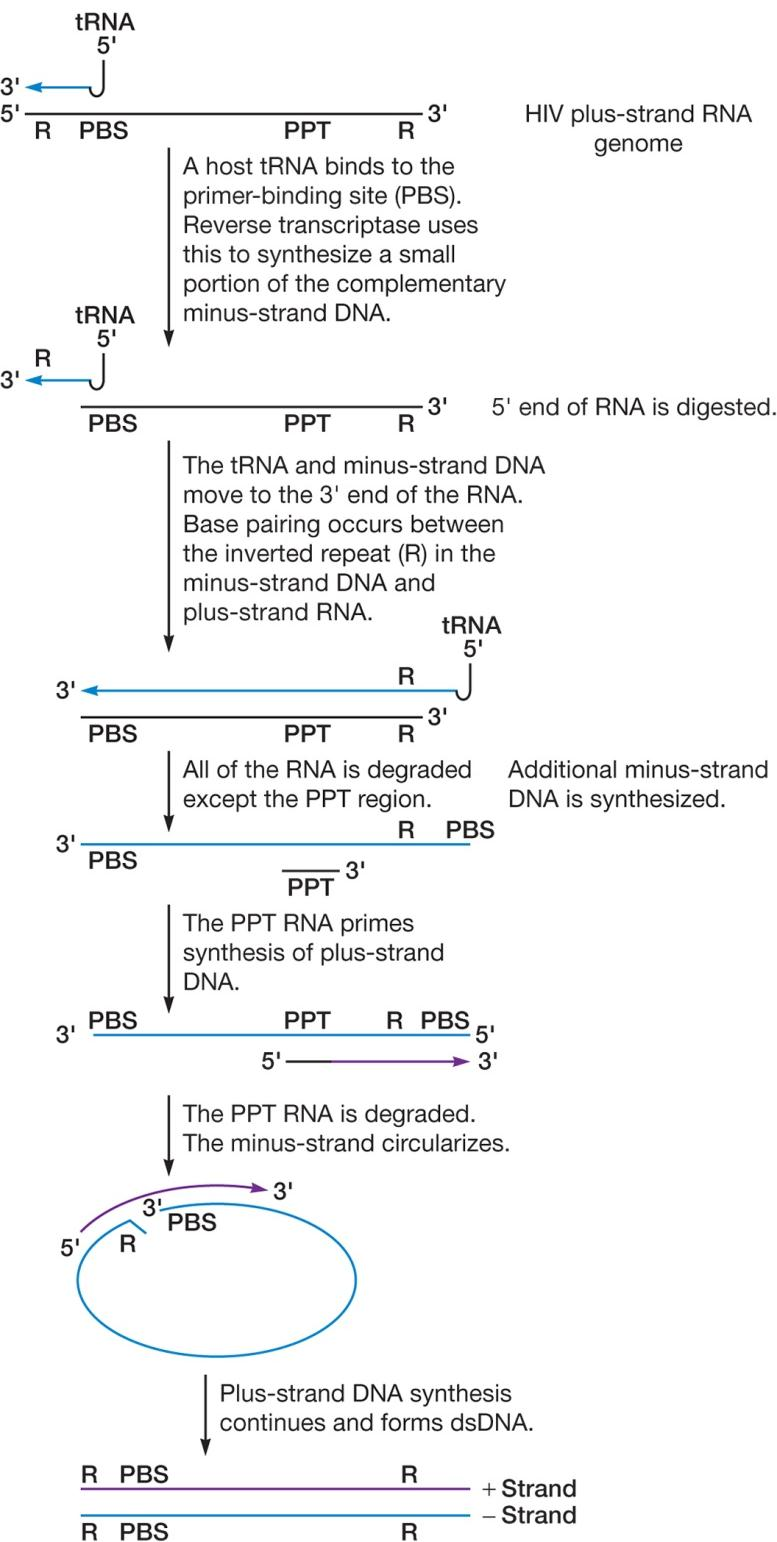
1. HIV-1 life cycle
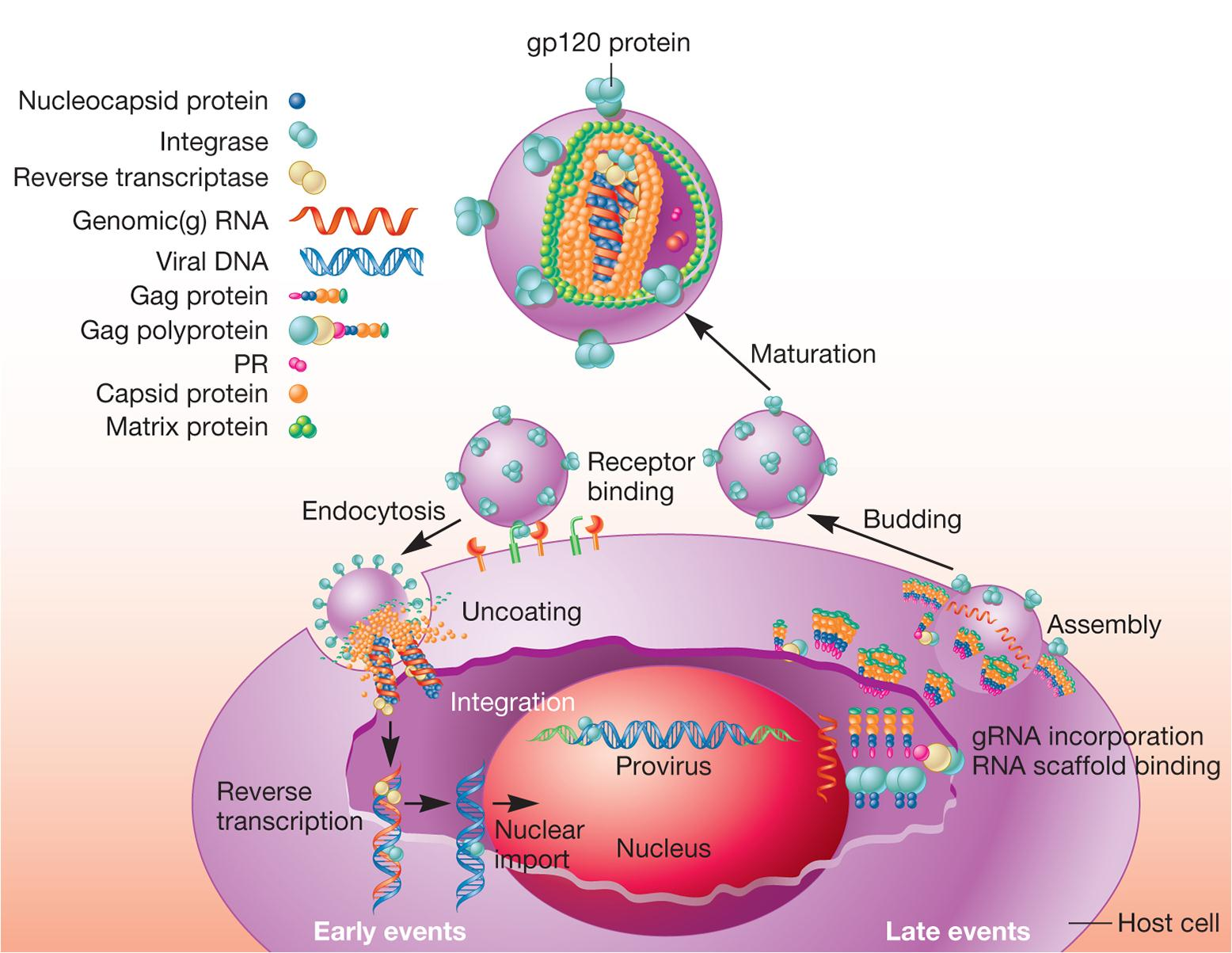
Reverse transcriptase
- RNA dependent DNA polymerase
- ribonuclease RNase H
- DNA dependent DNA polymerase
- error prone (容易出错), has no proofreading capability