L12 Innate Host Resistance
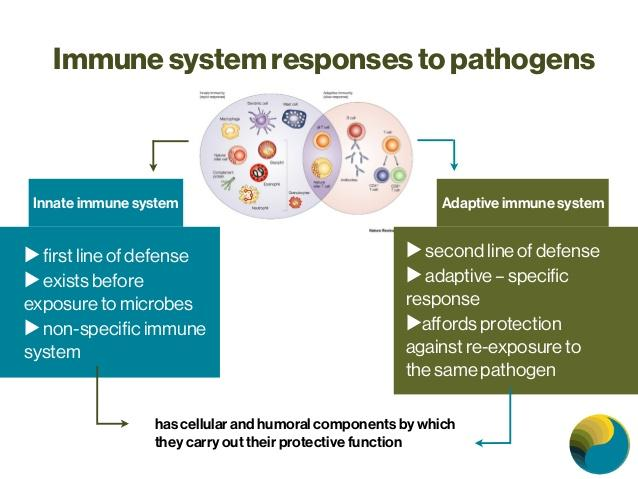
一、Host Resistance Overview
1. Pathogens
Pathogens are disease causing microbes
Must overcome surface barriers and reach underlying
overcome resistance by host
- nonspecific resistance
- specific immune response
2. Immune system
composed of widely distributed cells, tissues, and organs
recognizes foreign substances or microbes and acts to neutralize or destroy them
3. Immunity
ability of host to resist a particular disease or infection
4. Immunology
science concerned with immune responses
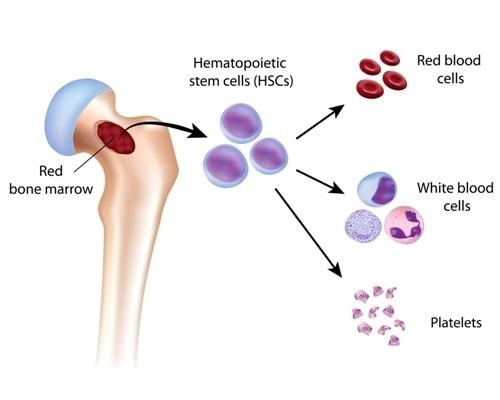
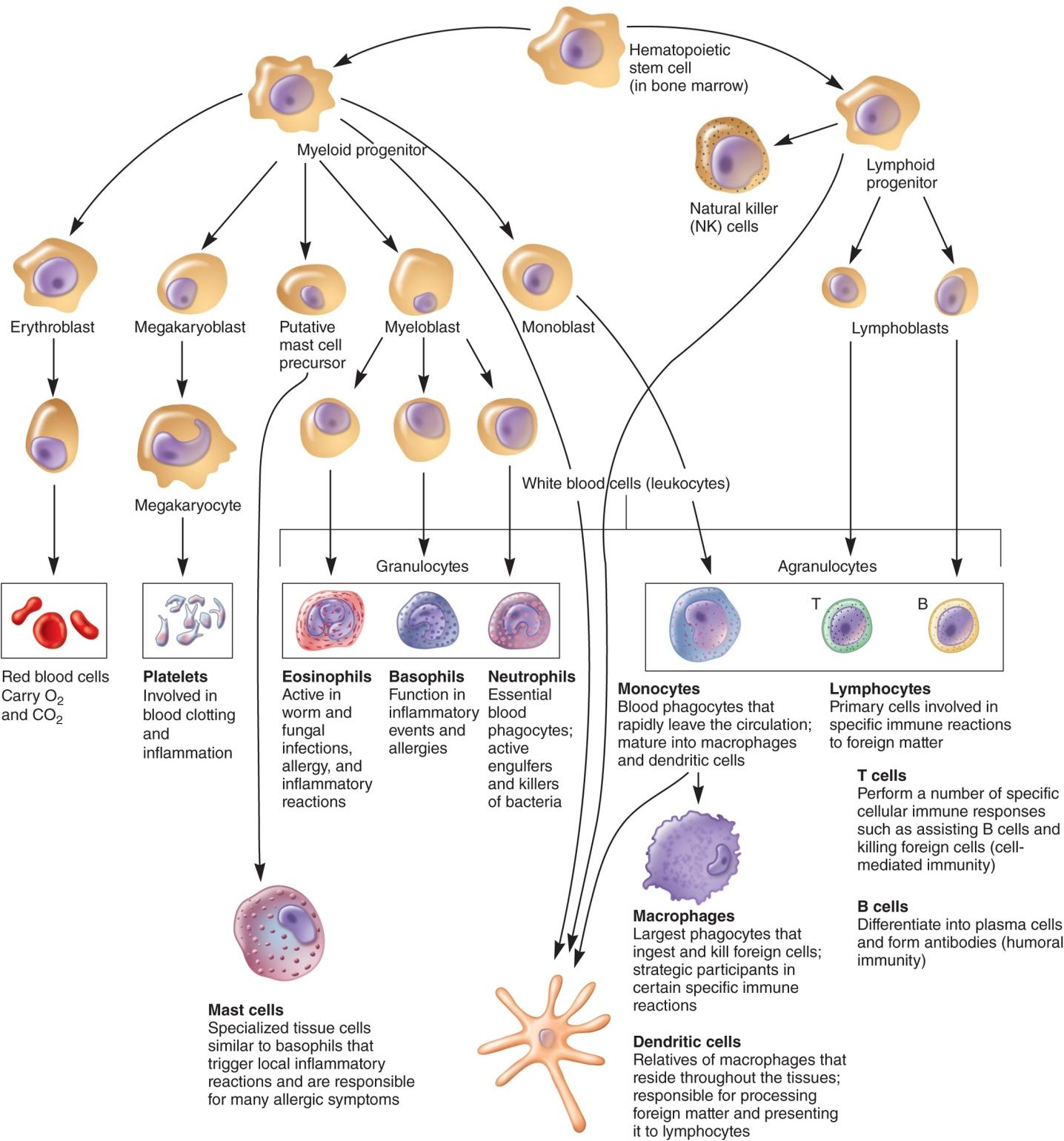
Hematopoiesis 造血作用
二、Physical and Mechanical Barrier Defenses of Innate Resistance
Physical Barriers in Nonspecific (Innate) Resistance
This is the first line of defense against microbe
1. Skin
Inhospitable(不宜居的) environment for microbes
attached organisms removed by shedding of outer skin cells
pH is slightly acidic
high NaCl concentration
subject to periodic drying (受制于周期性的干燥)
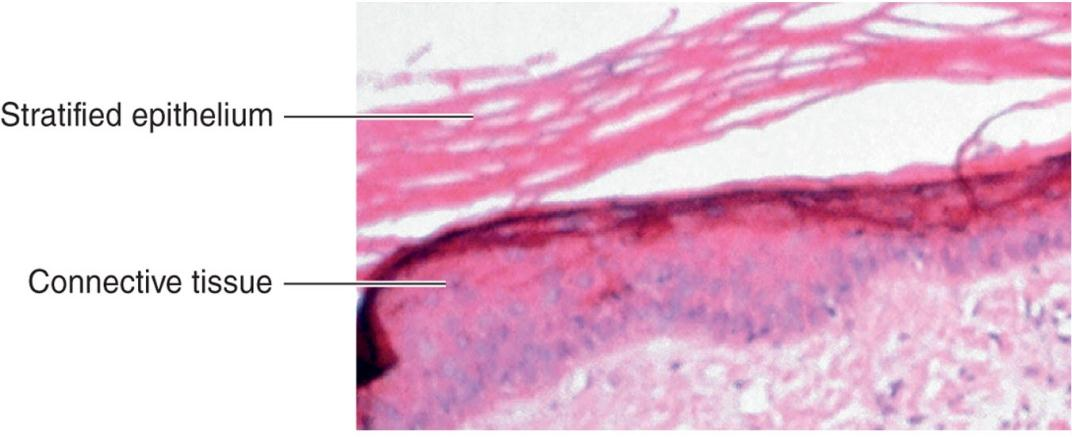
2. Mucous Membranes
Form protective covering that resists penetration and traps many microbes
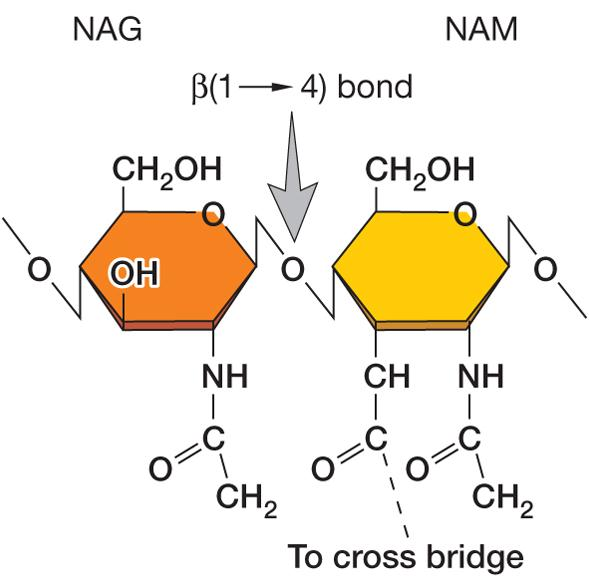
- lysozyme 溶菌酶
hydrolyzes bond connecting sugars in peptidoglycan
- lactoferrin 乳铁蛋白
乳铁蛋白是人体免疫系统的组分之一,它具有抗菌活性(抗细菌剂,抗真菌剂),是先天防御的一部分,主要存在于粘膜中。乳铁蛋白保护婴儿使其免受细菌等病原侵害。 乳铁蛋白还相互DNA和RNA、 多糖和肝素之间相互作用 ,并在这些这些受体-配体复合物中表现出一定的生理功能。
sequesters iron from plasma
- lactoperoxidase 乳过氧化物酶
Lactoperoxidase is a peroxidase enzyme secreted from mammary, salivary, and other mucosal glands that functions as a natural antibacterial agent.
produces superoxide radicals (超氧自由基)
3. Respiratory System
Mucociliary blanket
mucous secretions trap microbes
once trapped, microbes transported away from the lungs
- expelled by coughing(咳嗽) or sneezing(喷嚏)
- salivation washes microbes to stomach
4. Gastrointestinal Tract 胃肠道
- Stomach: gastric acid (胃酸)
- Intestines
- pancreatic enzymes 胰酶 (消化酶(英语:Digestive enzymes)是将聚合的高分子降解为他们的构建单元的酶类,以促进他们被身体吸收。)
- bile: 胆汁, 由大多数脊椎动物的肝细胞分泌出的一种绿黄色、带有苦涩味的碱性液体。肝脏持续分泌出胆汁,存放于胆囊内,然后在进食时把胆汁经胆总管释放入小肠帮助消化。胆汁的主要作用是乳化脂质(其中不含酵素)。
- intestinal enzymes: 肠内酶
- shedding of columnar epithelial cells: 柱状上皮细胞脱落
- peristalsis: 蠕动
- secretory IgA: 免疫球蛋白
- normal microbiota: 正常微生物群
- Paneth cells :潘氏细胞(或称帕内特细胞,Paneth cell)是小肠内一种少见的细胞,提供宿主防卫微生物的侵犯。其功能的类似于中性粒细胞。在细菌或细菌抗原侵犯机体时,潘氏细胞分泌一些抗菌分子如防御素到小肠管腔的绒毛,以助于维持胃肠道屏障。
- produce lysozyme
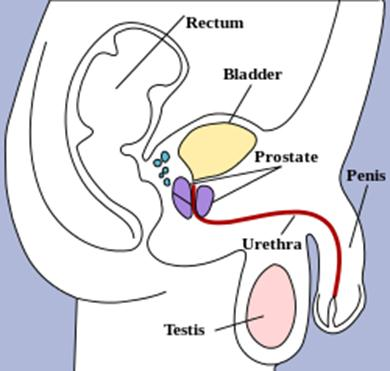
5. Genitourinary Tract 泌尿生殖道
Unfavorable environment for foreign microbes
vagina(阴道) has lactobacilli(乳杆菌)
low pH of urine and vagina
urea(尿素) and other toxic metabolic end products in urine
Flushing with urine and mucus
Distance barrier of male urethra(男性尿道距离障碍)
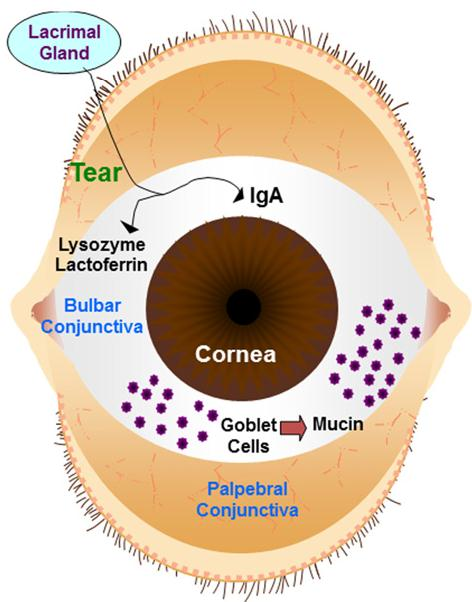
6. The Eye
Mucus secreting epithelial membrane 粘液分泌上皮膜
Flushing action of tears
Lysozyme, lactoferrin, and secretory IgA in tears
三、 Chemical Mediators in Nonspecific (Innate) Resistance
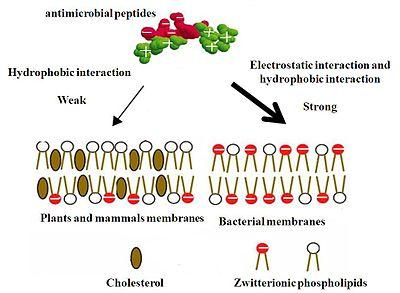
Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) 抗微生物肽
Cationic peptides 阳离子肽,正电性肽
- highly conserved through evolution
- e.g., cathelicidin(抗菌肽), histatin(组氨素)
抗菌肽:抗菌肽(Cathelicidin),系一系列可在巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞的溶酶体中找到的具有抗菌作用的多肽。
组氨素:组氨素(Histatin)是一类存在于唾液中的蛋白质。这种蛋白质能够抗真菌和细菌,也有促进伤口闭合的作用。
Bacteriocins 细菌素
Peptides produced by normal microbiota 微生物群
Lethal to related species
The Complement System 补体系统
Augments(增加) (or “complements”) the antibacterial activity of antibody
Composed of >30 serum(血清;免疫血清) proteins
Three major activities:
defending against bacterial infections
bridging(架桥) innate and adaptive immunity
disposing of wastes
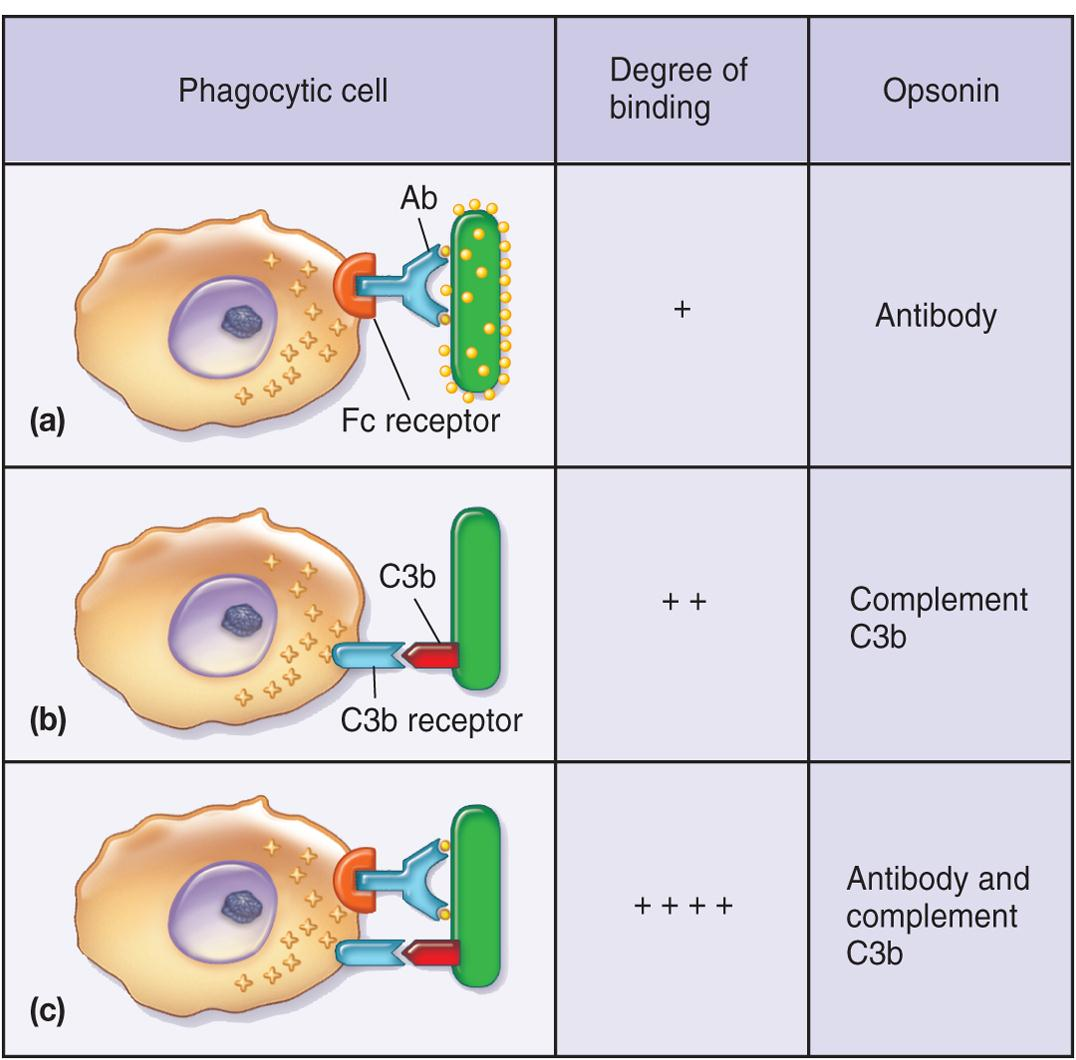
1. Opsonization 条理(作用)
An opsonin (from the Greek opsōneîn, to prepare for eating) is any molecule that enhances phagocytosis by marking an antigen for an immune response or marking dead cells for recycling (i.e., causes the phagocyte to “relish” the marked cell).
例如条理素与细菌表面颗粒抗原结合而促进吞噬作用
Process in which microbes are coated by serum components(血清成分) (opsonins) in preparation for recognition/ingestion by phagocytic cells
Some complement proteins are opsonins(调理素)
2. Other Functions of Complement Proteins
Function as chemotactic signals(趋化现象的信号) that recruit phagocytes to their activation site
Puncture(穿刺) cell membranes causing cell lysis
Unite the nonspecific and specific arms of the immune system
3. Complement Activation
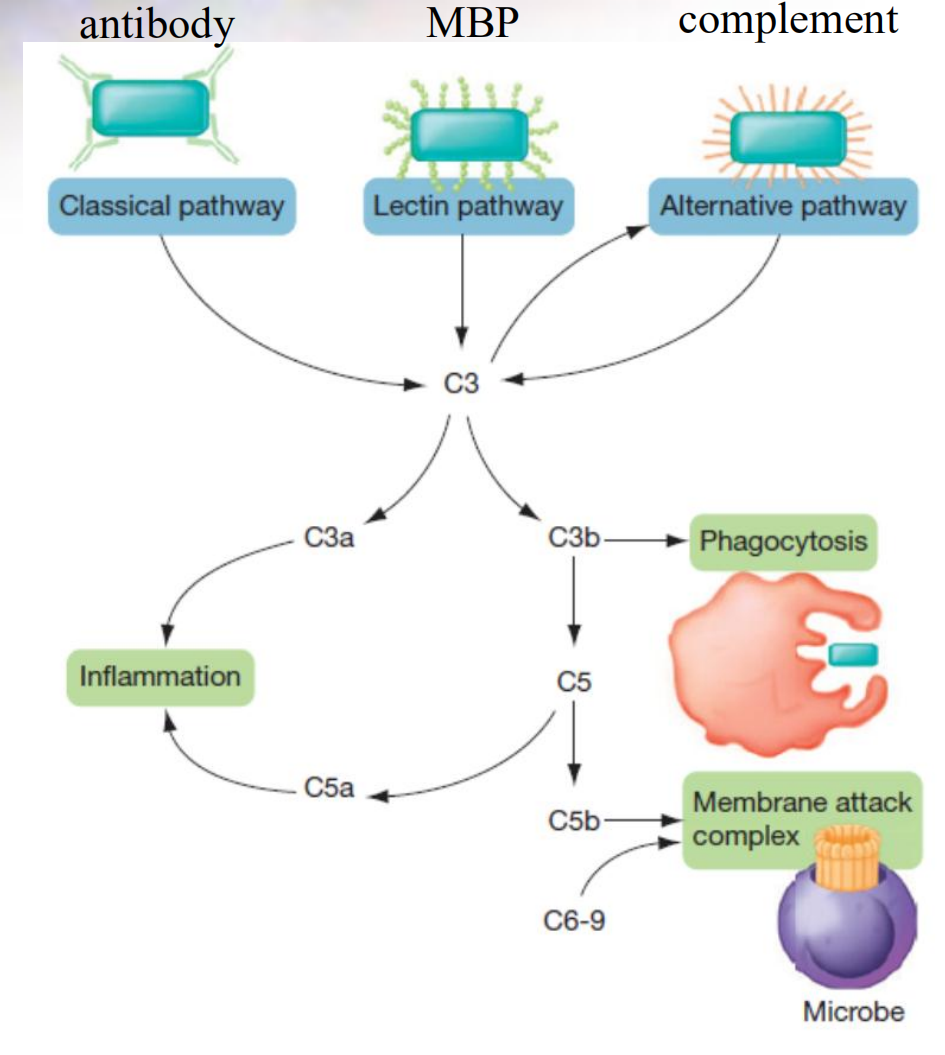
Produced in inactive forms
Activated following enzymatic cleavage
Three pathways of activation
- classical
- lectin 外源凝集素
- alternative
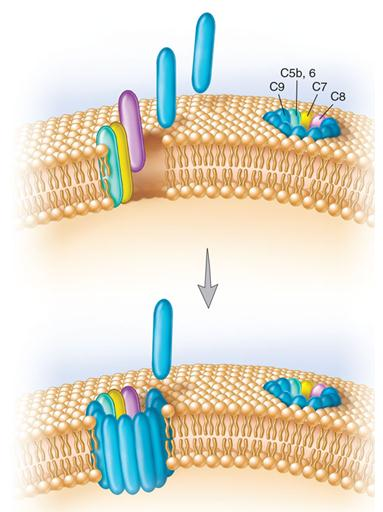
Alternative Complement Pathway
Dependent on interaction of complement with repetitive structures on pathogens
Begins with activation of C3
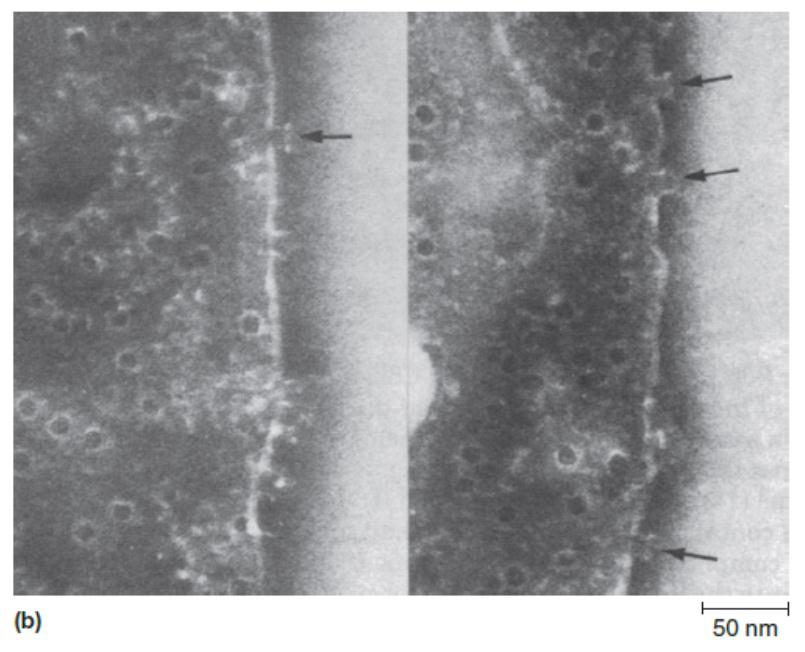
Results in formation of membrane attack complex
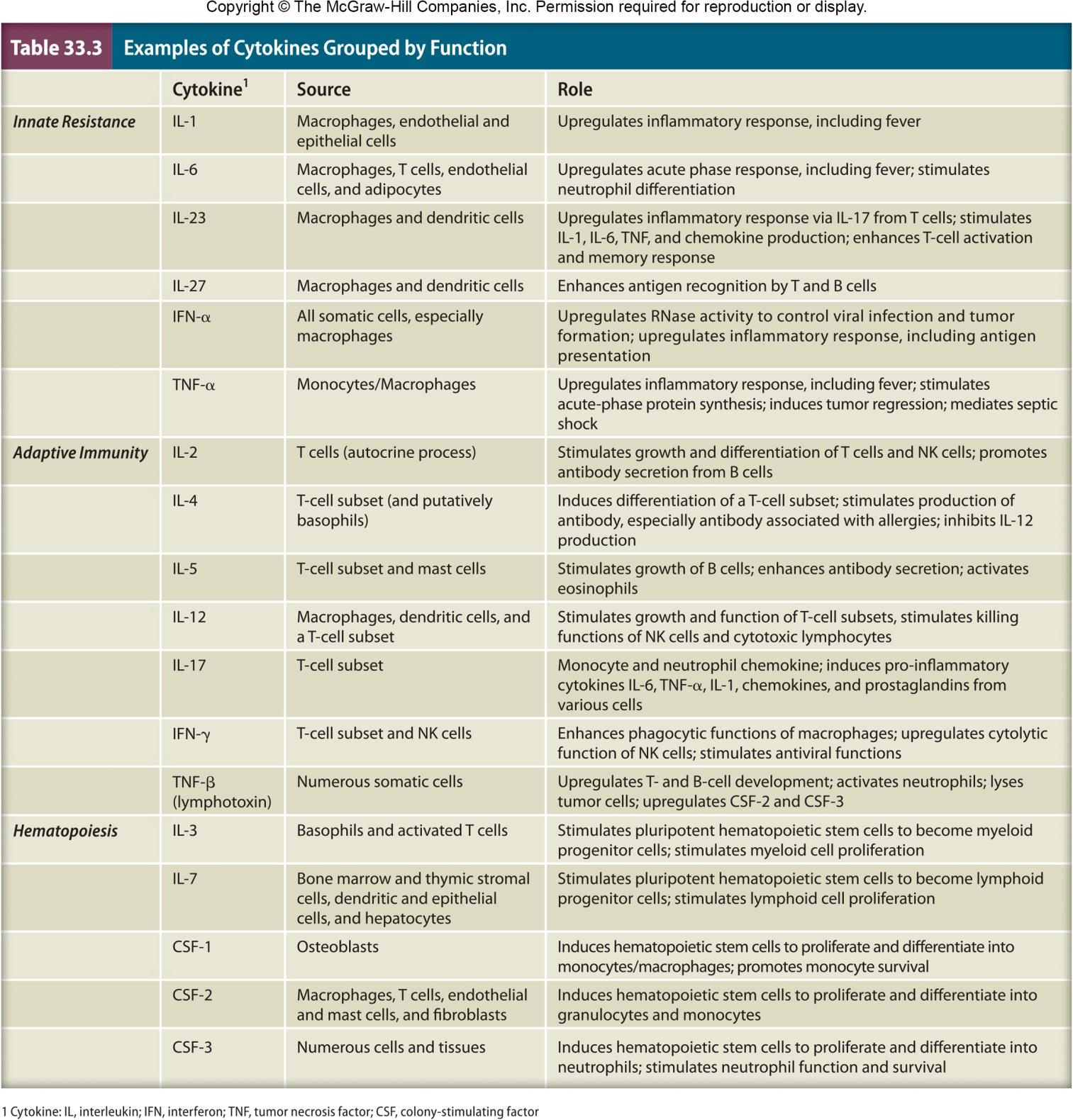
Cytokines 细胞因子
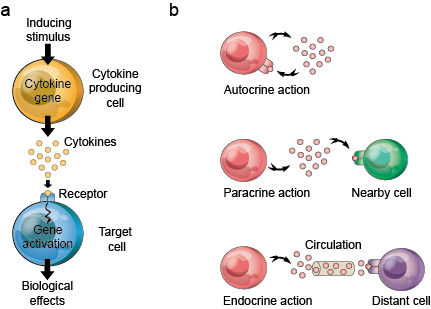
Soluble proteins or glycoproteins that are released by one cell population that act as intercellular mediators or signaling molecules
Three proposed groups based on function
regulators of innate resistance mechanisms
regulators of adaptive immunity
stimulators of hematopoiesis
(1) Interleukins 白细胞介素,白介素
released from one leukocyte(白细胞) and act on another leukocyte
白细胞介素或介白素(interleukin)是一组细胞因子(分泌的信号分子)。最早发现在白细胞中表达作为细胞间信号传递的手段。实际上,白细胞介素可以由多种细胞产生。免疫系统的功能,在很大程度上依赖于白细胞介素。一些罕见的白细胞介素缺陷不足都常出现自身免疫性疾病或免疫缺陷。
(2) Chemokines 趋化因子
mediate chemoattraction (chemotaxis, 化学引诱) between cells
趋化因子,也称做趋化激素、趋化素或是化学激素。是一小分子细胞因子家族蛋白。
有的趋化因子被认为促进炎症反应,而有些趋化因子被认为在正常的修复过程或发育中控制细胞的迁徙。在所有脊椎动物和一些病毒和一些细菌中有趋化因子存在,但不存在于其他无脊椎动物。这些蛋白质结合到趋化因子受体而起作用,趋化因子受体是G蛋白偶联受体,选择性地表达在靶细胞表面。
(3) Monokines 单核因子
released from mononuclear phagocytes
单核因子(英语:monokine)是指一大类主要由单核细胞和巨噬细胞产生的细胞因子。
(4) Lymphokines 淋巴因子
released from T lymphocytes
淋巴因子(Lymphokine)是细胞因子的一亚类,指由免疫细胞细胞产生的细胞因子。通常是由T细胞产生的通过影响其他免疫细胞的功能而改变免疫系统的反应。这一分类方法已经过时。现常统称为细胞因子。
(5) Interferons 干扰素
involved in antiviral responses
干扰素(Interferon,IFN)是动物细胞在受到某些病毒感染后分泌的具有抗病毒功能的宿主特异性糖蛋白。细胞感染病毒后分泌的干扰素能够与周围未感染的细胞上的相关受体作用,促使这些细胞合成抗病毒蛋白防止进一步的感染,从而起到抗病毒的作用,但干扰素对已被感染的细胞没有帮助。
四、Cells, Tissues, and Organs of the Immune System
Cells of The Immune System
Mast Cells 肥大细胞
Bone marrow-derived cells 骨髓干细胞
Contain granules containing histamine and other pharmacologically(药理学的) active chemicals
Play important role in development of allergies(变态反应,过敏) and hypersensitivities(超敏(反应),过敏性)
超敏反应(hypersensitivity),也叫变态反应,是免疫反应产生作用分子移除外来抗原的过程,这些作用分子诱导产生轻微、无临床症状或局部性的发炎反应,并不会对宿主造成组织伤害。
特殊的状况下,发炎反应可能导致明显的组织伤害甚至死亡,这类免疫反应称为超敏反应hypersensitivity或allergy。 大部分的超敏反应是个体因无害性抗原或过敏原的刺激而产生IgE抗体所导致。
过敏症状可由体液性或细胞媒介免疫反应中发展出来。
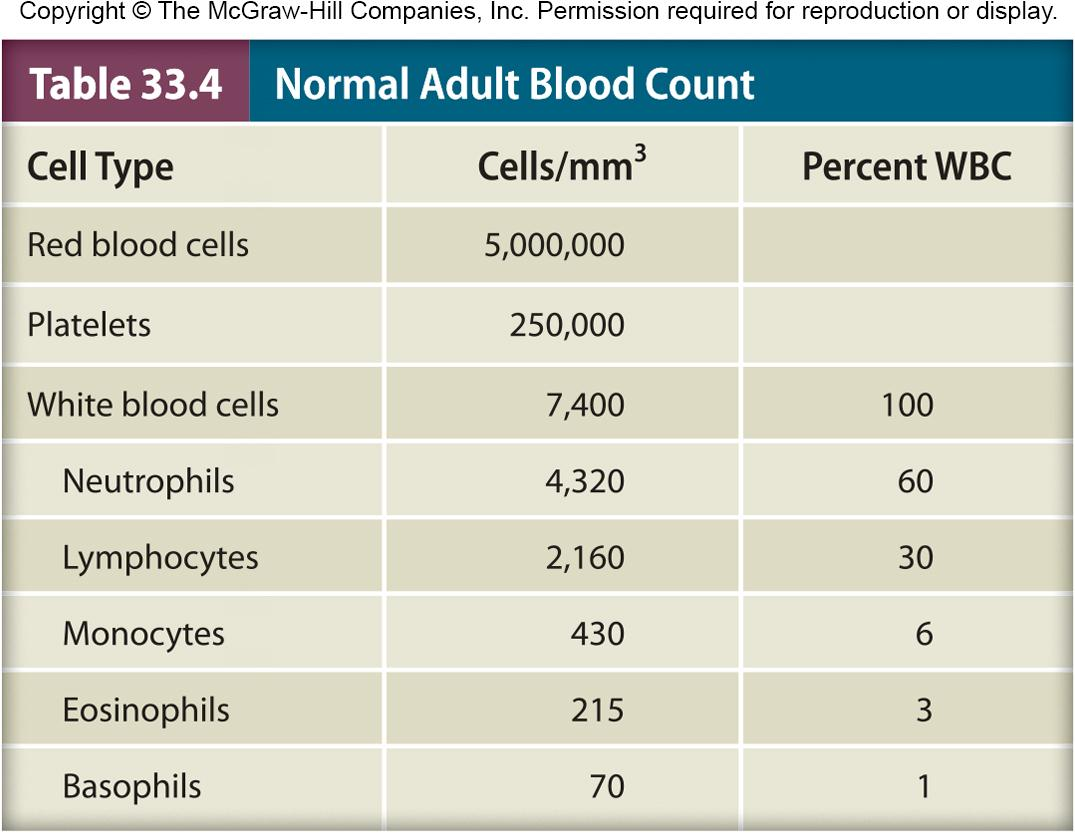
Granulocytes 粒细胞
Irregularly-shaped nuclei with two to five lobes
Cytoplasm has granules with reactive substances
- kill microbes, enhance inflammation
Three types
- basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils
粒细胞是一类细胞质中包含颗粒体的白细胞,又因其细胞核形态多样而称多形核白细胞,(PMN或PML)。术语多形核白细胞通常特指最常见的中性粒细胞。粒细胞由补体调节蛋白调控从骨髓中产生。
1. Basophils 嗜碱性球、嗜碱性粒细胞
Stain bluish-black (蓝黑色) with basic dyes
Nonphagocytic 非吞噬
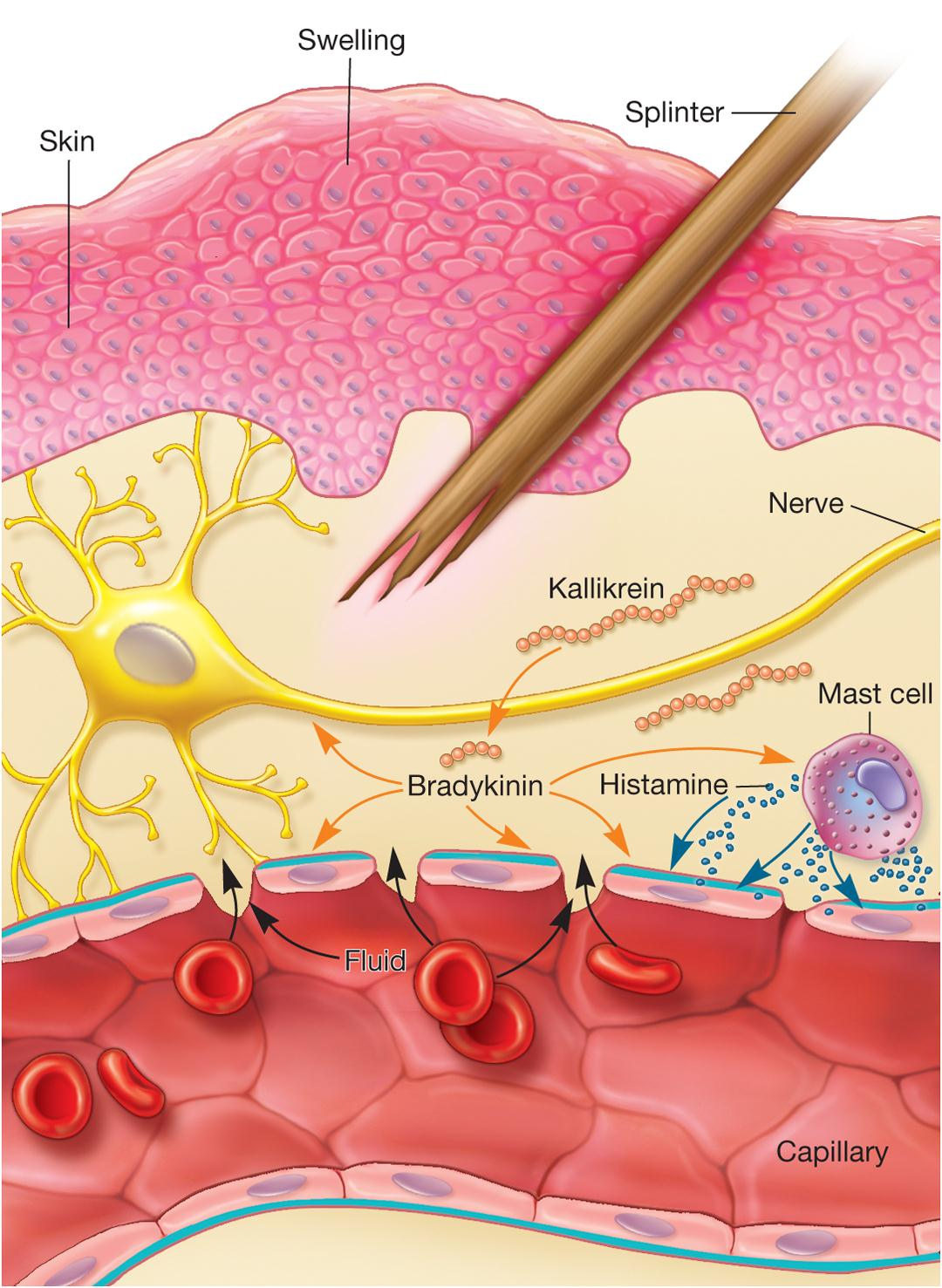
Release vasoactive mediators (血管活性介质)
- e.g., histamine (组织胺), prostaglandins (前列腺素), serotonin (5-羟色胺,血清紧张素,血清素), and leukotrienes (白三烯) from granules
Play important role in development of allergies(过敏症) and hypersensitivities(超敏(反应),过敏性)
histamine
组织胺(Histamine)也称组胺,是一种有机含氮化合物,它参与局部免疫反应,在肠道调节生理功能并被用作神经递质。它也参与炎症反应,并具有作为瘙痒介体中心的作用。作为对外部的病原体免疫反应的一部分,组织胺由嗜碱细胞和由附近结缔组织肥大细胞产生。另外,它也增加毛细血管对白血球和某些蛋白质的通透性,以允许其啮合感染组织中的病原体。广泛存在于动植物组织中,可人工合成。
prostaglandins
前列腺素(Prostaglandin,简称:PG)是一类具有五元脂肪环、带有两个侧链(上侧链7个碳原子、下侧链8个碳原子)的20个碳的酸。是一类激素。
serotonin
血清素(血清张力素,英语:Serotonin,又称5-羟色胺和血清胺,简称为5-HT)为单胺型神经递质,由色氨酸经色氨酸羟化酶转化为5-羟色氨酸,再经5-羟色氨酸脱羧酶合成于中枢神经元及动物(包含人类)消化道之肠嗜铬细胞。血清素在大脑中的含量为总量的2%,有九成位于粘膜肠嗜珞细胞和肌间神经丛,参与肠蠕动的调节。与肠粘膜进入血液的5-HT主要被血小板摄取。8%-9%的位于血小板中。因为5-HT不能透过血脑屏障,故中枢和外周可视为两个独立的系统。
许多真菌与植物中皆含有血清素,而人类必须通过食物获取色氨酸。
leukotrienes
白三烯(Leukotriene, LTs)是一类含三个共轭双键的20碳直链羟基酸的总称,是与过敏性反应有关的生物活性物质,其他与过敏性反应有关的生物活性物质包括组胺、缓激肽、血小板活化因子等。白三烯由于最早是在白细胞中发现故而得名。它们在体内的主要作用是引起气管平滑肌的收缩,同时也增加微血管通透性。白三烯的过多释放是引起哮喘和过敏性鼻炎的主要原因之一。白三烯拮抗剂(Leukotriene antagonist)可通过抑制白三烯的产生和活动达到治疗哮喘和过敏性鼻炎的效果。
2. Eosinophils 嗜酸性粒细胞
嗜酸性粒细胞(英语:Eosinophil granulocyte)是粒细胞中含有嗜酸性颗粒的一种,其他两种是中性粒细胞和嗜碱性粒细胞。
正常人体中的嗜酸性粒细胞一般占白细胞总数的1~6%,超过此数则为嗜酸性粒细胞增多症,通常意味着机体功能异常或是疾病。
Stain red with acidic dyes
Defend against protozoan(原虫) and helminth parasites(蠕虫寄生虫)
Release cationic proteins and reactive oxygen metabolites
May play a role in allergic reactions
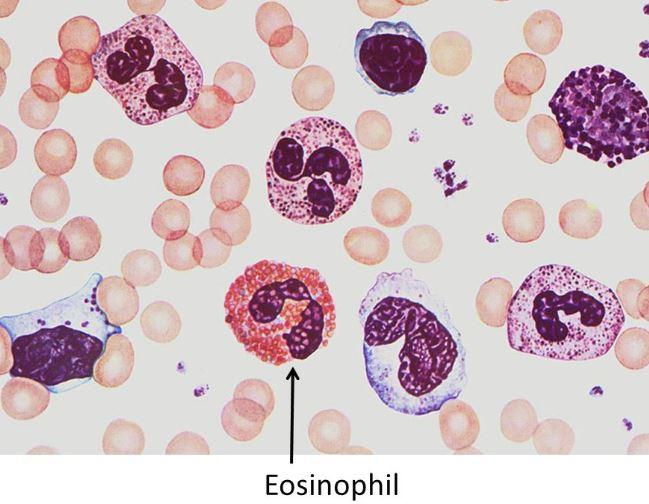
3. Neutrophils 中性粒细胞
Stain at neutral pH
Highly phagocytic
Circulate in blood then migrate(移动) to sites of tissue damage
Kill ingested microbes(摄入的微生物) with lytic enzymes and reactive oxygen metabolites contained in primary and secondary granules
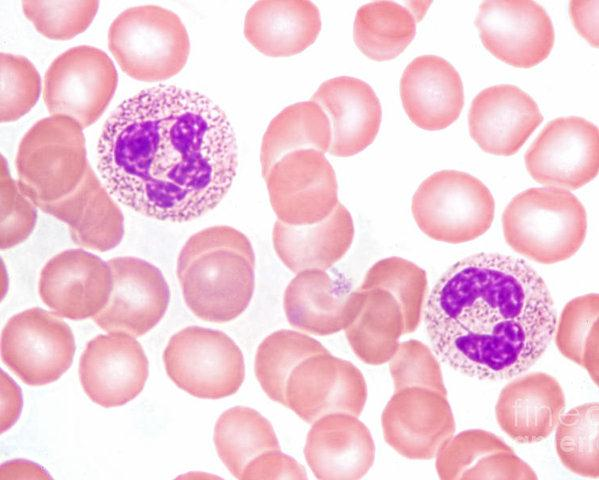
Monocytes 单核细胞
单核细胞(英语:Monocyte)是人体免疫系统中的一种白细胞。其在人体免疫系统内有两种作用:
一,补充正常状态下的巨噬细胞和树状细胞;
二,在有炎症信号下,单核细胞会在8到12小时快速聚集到感染组织,并分化出巨噬细胞和树状细胞产生免疫反应。
Highly phagocytic cells
• Monocytes
are mononuclear phagocytic leukocytes
after circulating for ~8 hours, mature into macrophages
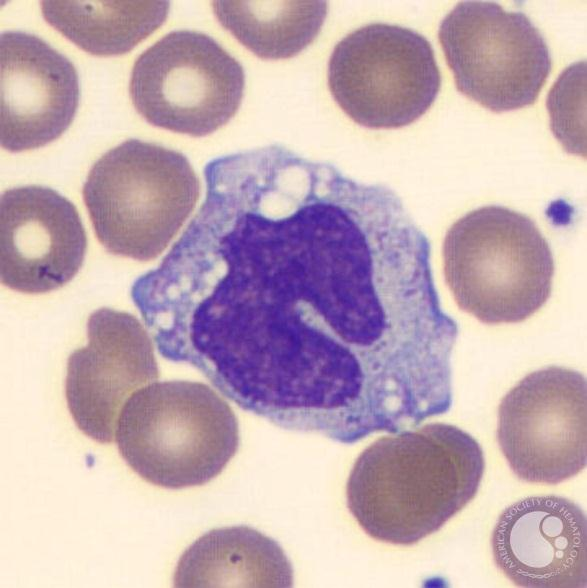
Macrophages 巨噬细胞
Highly phagocytic cells
• Macrophages
larger than monocytes, reside in specific tissues
named according to tissue in which they reside
have a variety of surface receptors (including pattern recognition receptors)
- bind pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
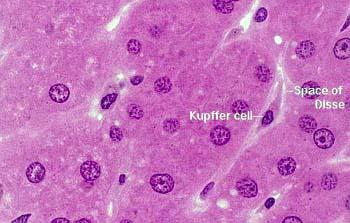
巨噬细胞(英语:macrophages,缩写为mø)是一种位于组织内的白血球,源自单核细胞,而单核细胞又来源于骨髓中的前体细胞。巨噬细胞和单核细胞皆为吞噬细胞,在脊椎动物体内参与非特异性防卫(先天性免疫)和特异性防卫(细胞免疫)。它们的主要功能是以固定细胞或游离细胞的形式对细胞残片及病原体进行噬菌作用(即吞噬以及消化),并激活淋巴球或其他免疫细胞,令其对病原体作出反应。
Dendritic Cells 树突状细胞、树状细胞
树突状细胞(英语:dendritic cell)是一种存在于哺乳动物的一种白血球。它存在于血液和暴露于环境中的组织中,如皮肤和鼻子、肺、胃和小肠的上皮组织。它们的作用是调节对当前环境刺激的先天和后天免疫反应。它的其中一个最重要的功能就是将抗原处理后展示给免疫系统的其他白细胞,故是一种抗原呈递细胞。
树状细胞是一种哺乳类的免疫细胞。简而言之,主要功能为施加抗原物质在免疫系统中其他的细胞上。
它们通常少量分布于与外界接触的皮膜(黏膜)部位,主要为皮肤(在皮肤上的,称为郎格罕细胞,和内层的鼻子、肺、胃与肠的内层。血液中也可发现他们的未成熟型式。他们被活化时,会移至淋巴组织中与T细胞与B细胞互相作用,以刺激与控制适当的免疫反应。
Heterogeneous group of cells with neuron-like appendages(肢)
- from lymphoid(淋巴的) and myeloid(骨髓的) lines
Present in small numbers in blood, skin, and mucous membranes of nose, lungs, and intestines
express pattern recognition receptors
antigen presentation
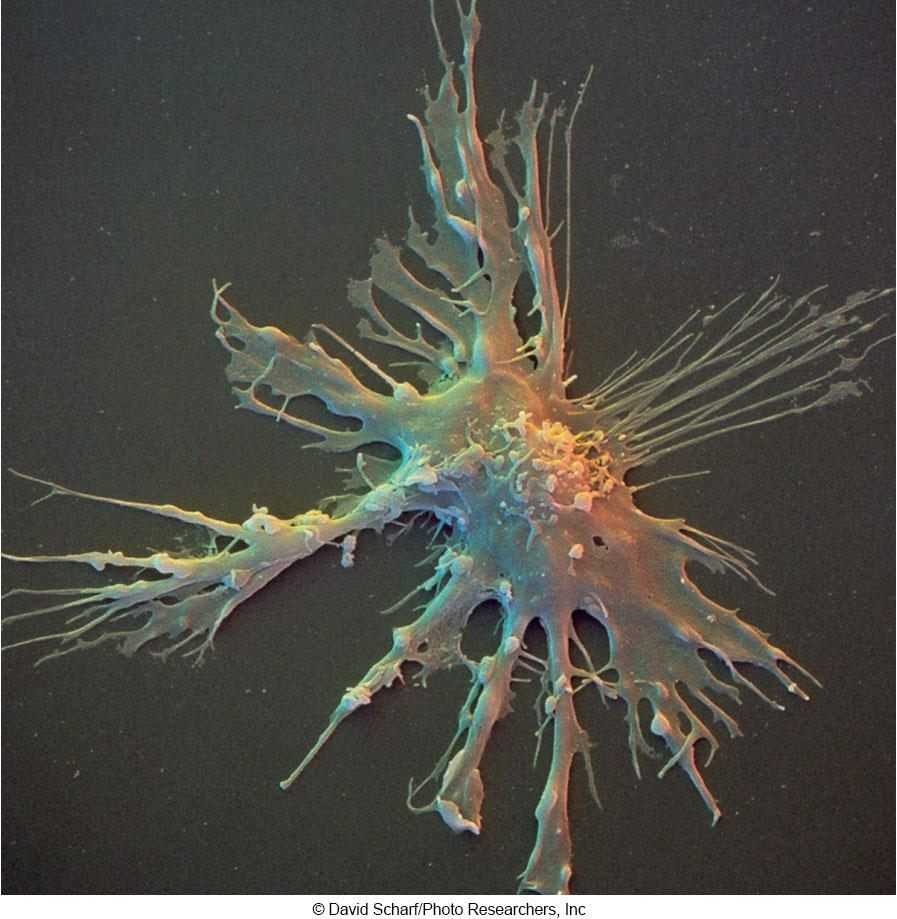
Lymphocytes 淋巴细胞
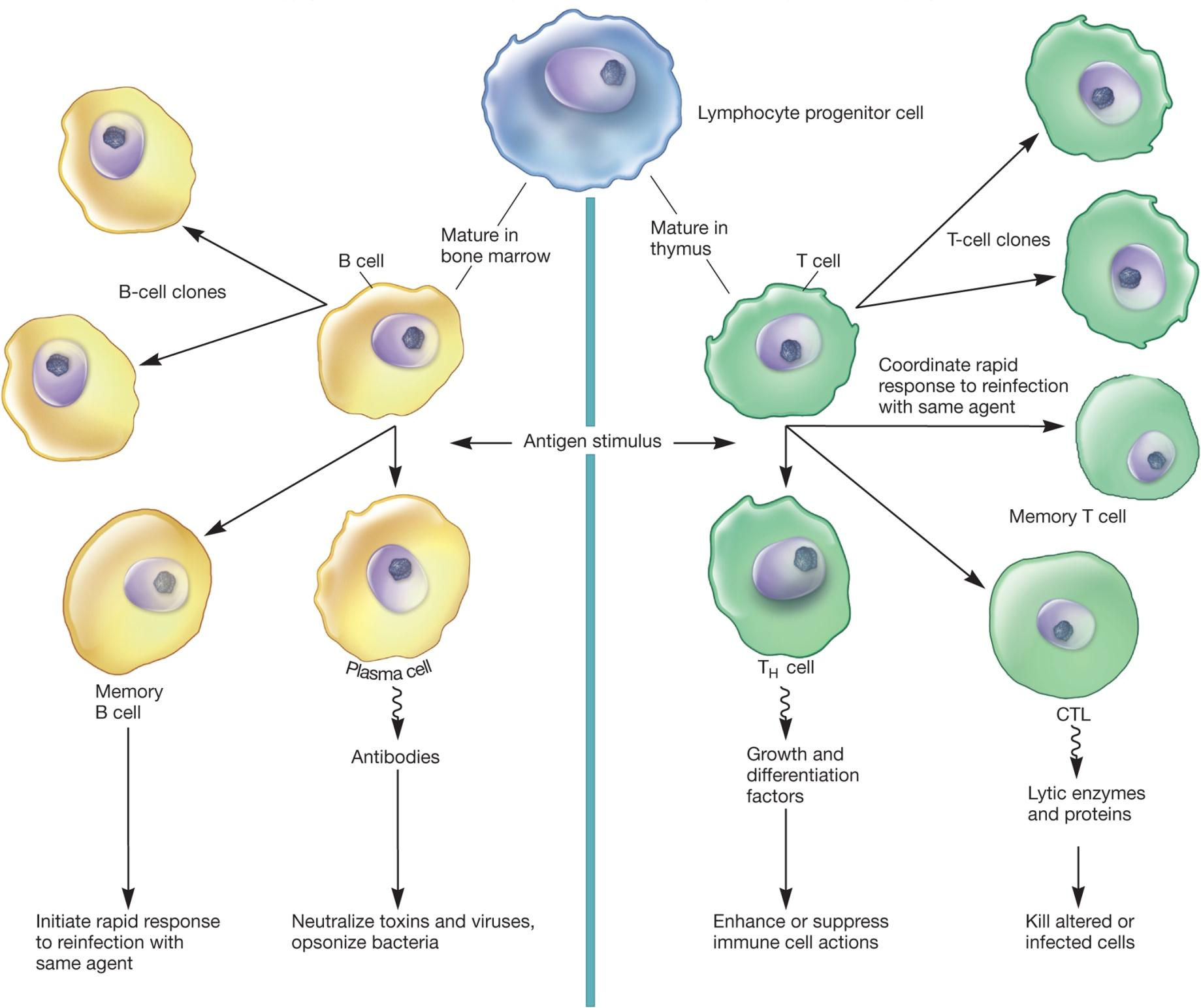
Major cells of the immune system
T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells
B and T lymphocytes differentiate in bone marrow from stem cells
BCR or TCR
memory cells
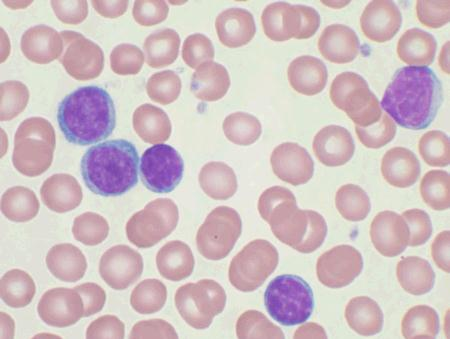
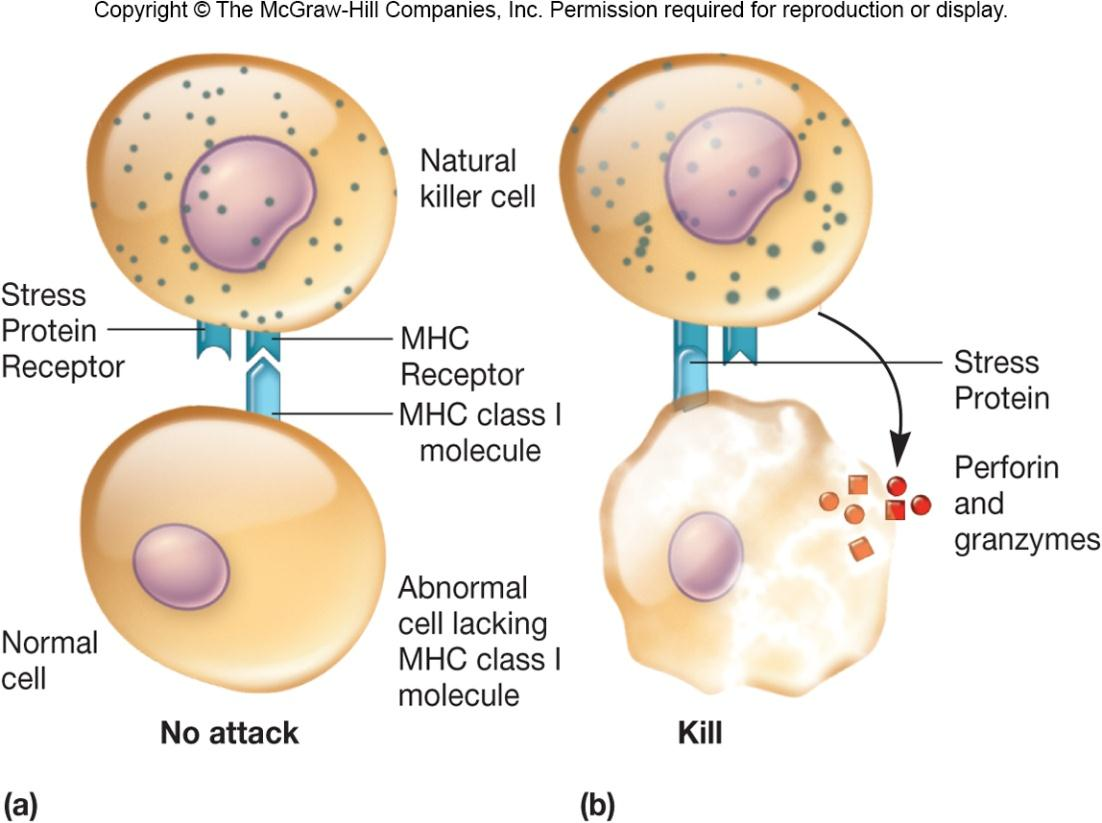
1. Natural Killer (NK) Cells 自然杀伤细胞
自然杀手细胞(英语:natural killer cell)是一种细胞质中具有大颗粒的细胞,也称NK细胞(NK cell)。由骨髓淋巴样干细胞发育而成,其分化、发育依赖于骨髓或胸腺微环境,主要分布于外周血和脾脏,在淋巴结和其他组织中也有少量存在。
因为其非专一性的细胞毒杀作用而被命名。没有T细胞与B细胞所具的受体,不会进行受体的基因重组。但仍具有一些特殊受体,称为“杀伤细胞免疫球蛋白样受体”,可以活化或抑制其作用在血液中循环,但也在骨髓,脾脏、淋巴结中出现,约占所有淋巴球的细胞的5~10%,但它可以消灭许多种病源体及多种肿瘤细胞。
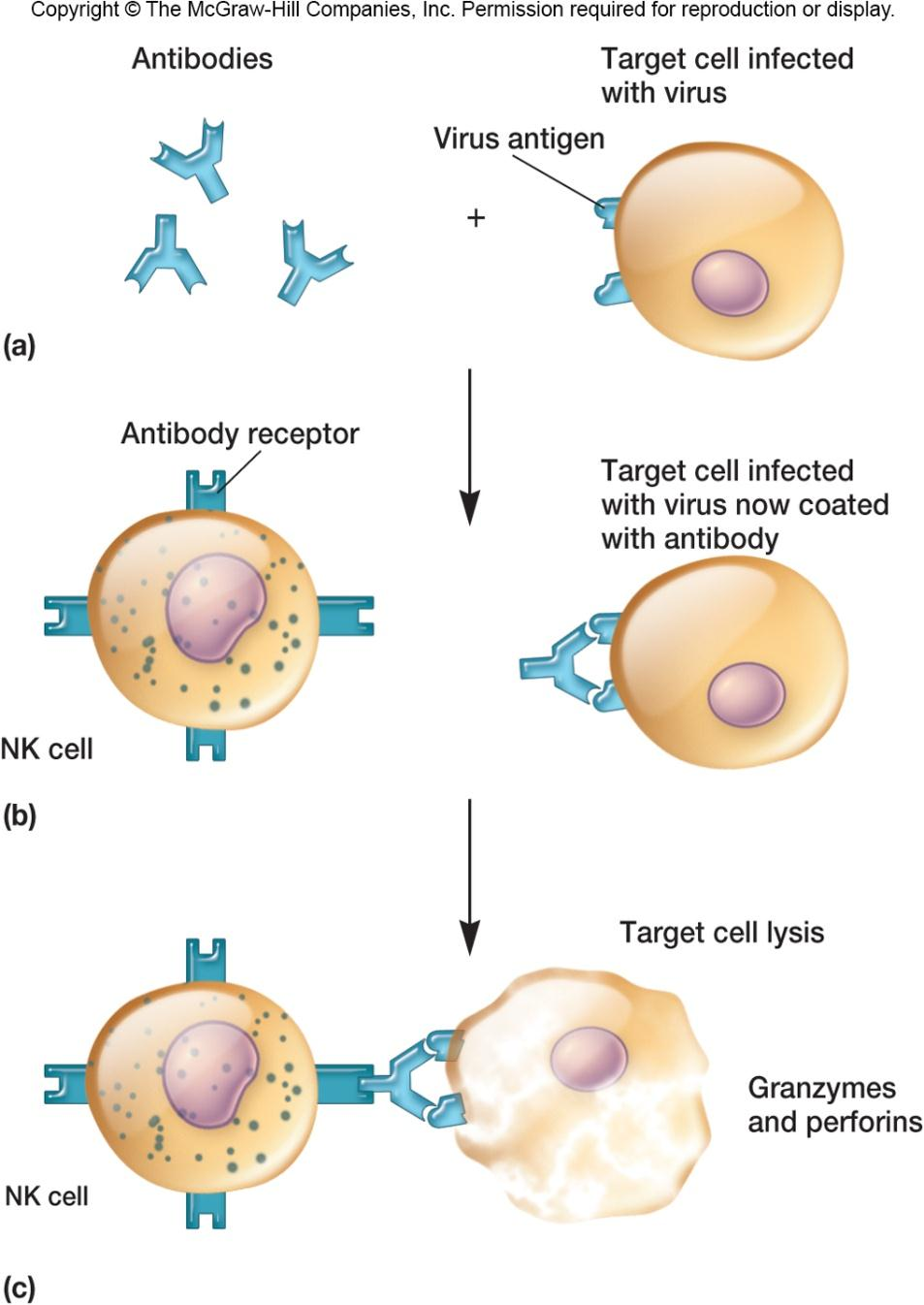
自然杀手细胞会直接和陌生细胞接触,并以细胞膜破裂之方式杀死此细胞,可利用分泌穿孔素及肿瘤坏死因子,摧毁目标细胞
Large non-phagocytic granular lymphocytes
important role in innate immunity
kill malignant cells and cells infected with pathogens by releasing granzymes (颗粒酶,cytotoxic enzymes)
Two ways of recognizing target cells
ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
recognizes cells that have lost their class I major histocompatibility(组织兼容性) (MHC-I) antigen
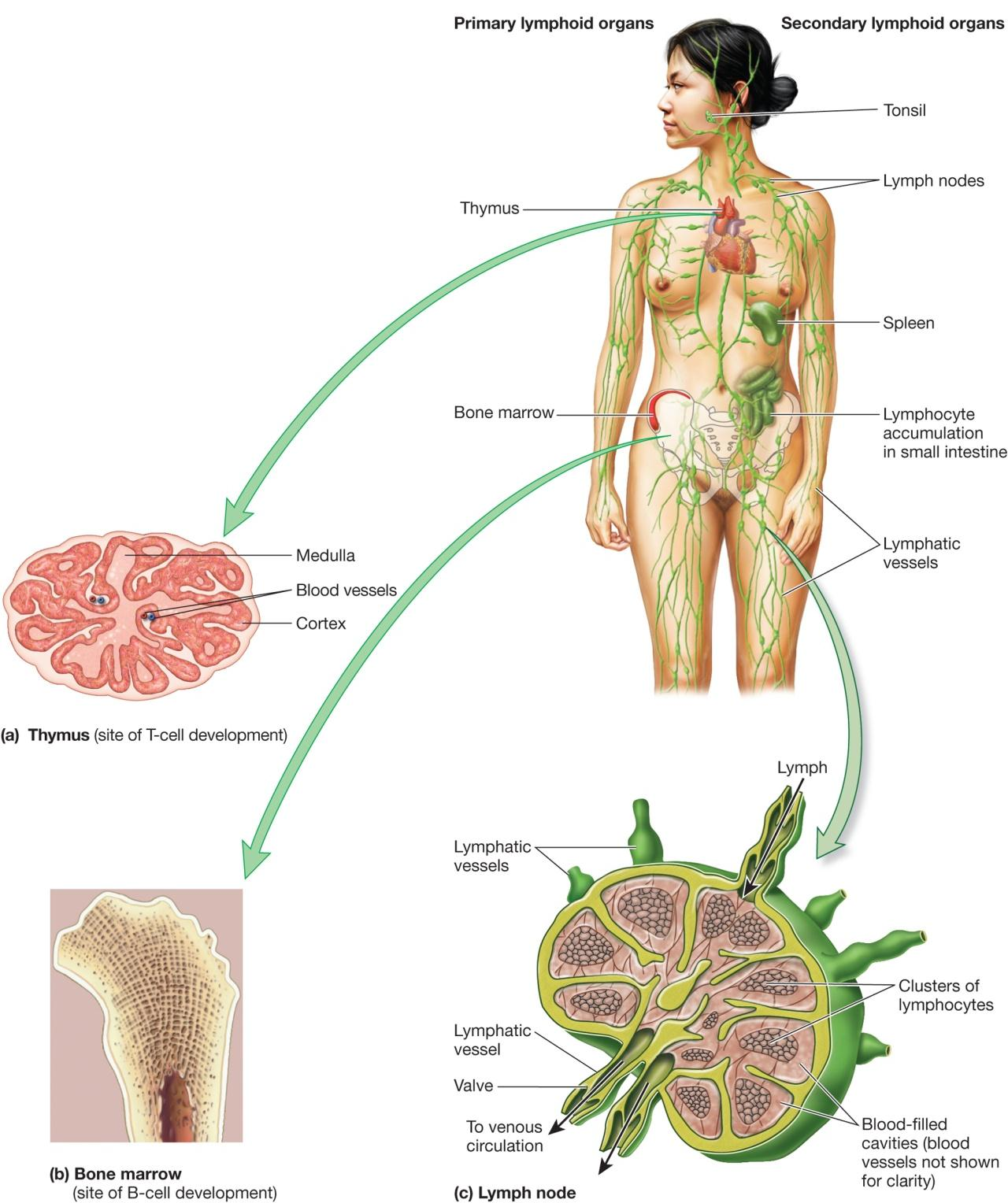
五、Organs and Tissues of the Immune System
Primary organs and tissues 主要器官和组织
- sites where lymphocytes mature and differentiate into antigen-sensitive mature B and T cells
Secondary organs and tissues 次生器官和组织
areas where lymphocytes may encounter and bind antigen
- followed by proliferation(增殖,分芽繁殖) and differentiation into fully mature effector cells
1. Anatomy of the lymphoid system
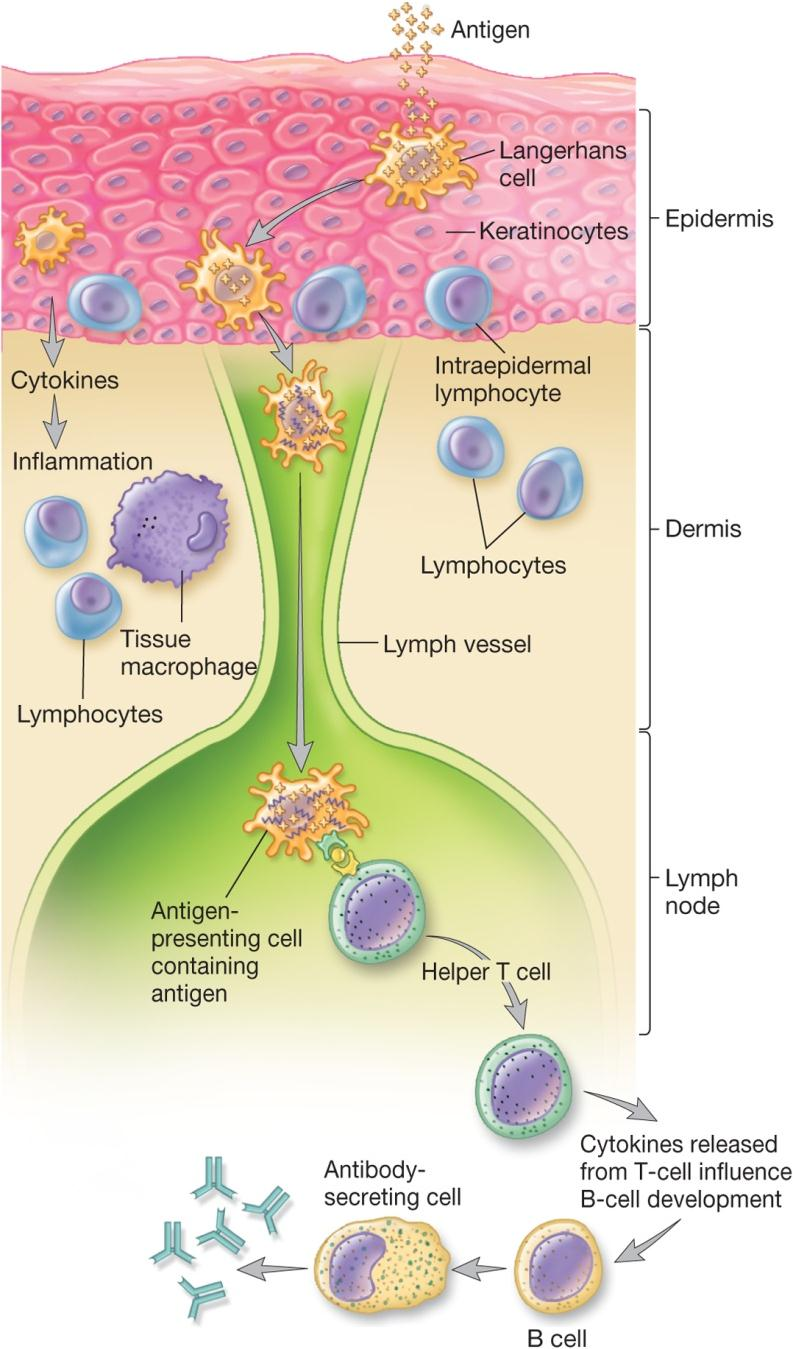
Skin Associated Lymphoid Tissue (SALT)
Contains specialized cells
Langerhans cell 朗氏细胞[见于皮肤和淋巴器官]
- dendritic cell that can phagocytose antigens
- presents antigen to and activates T cells
intraepidermal lymphocyte 表皮内的淋巴细胞
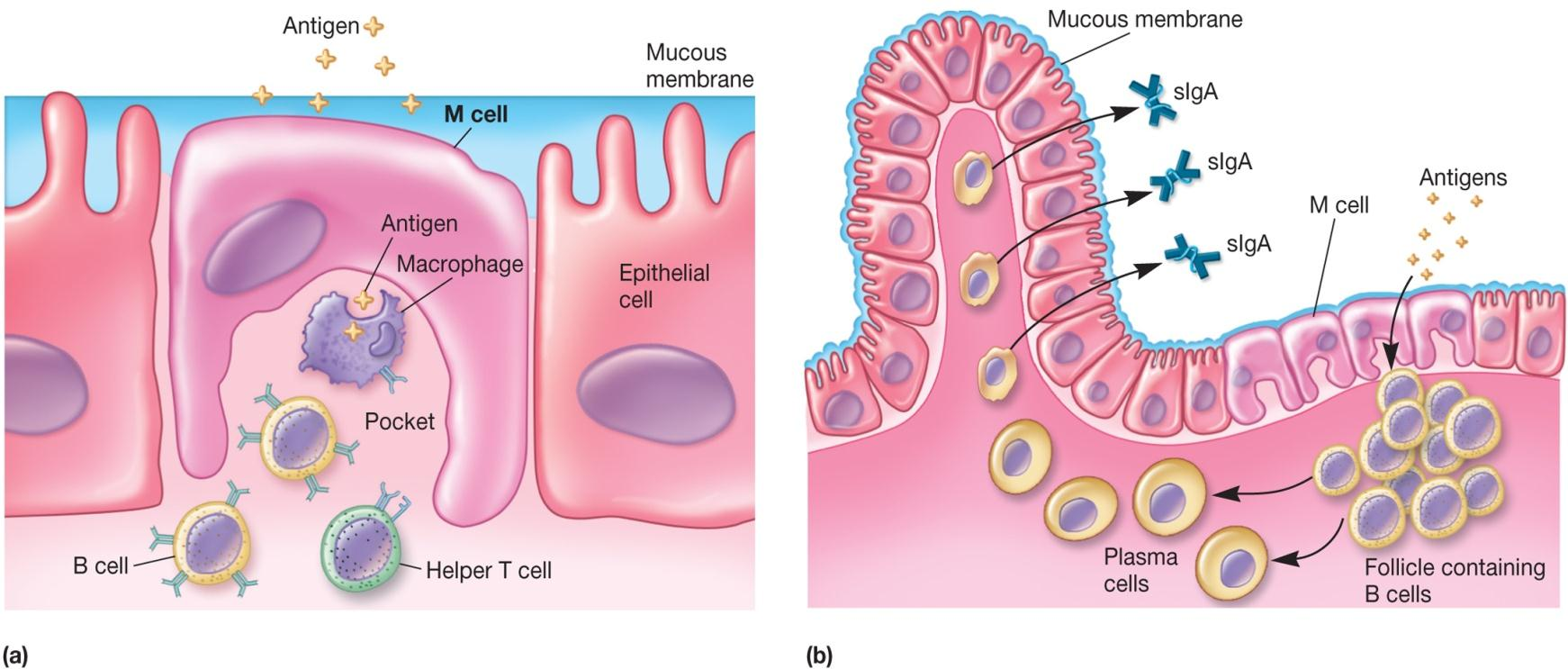
Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)
Specialized immune barrier
gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
bronchial-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT)
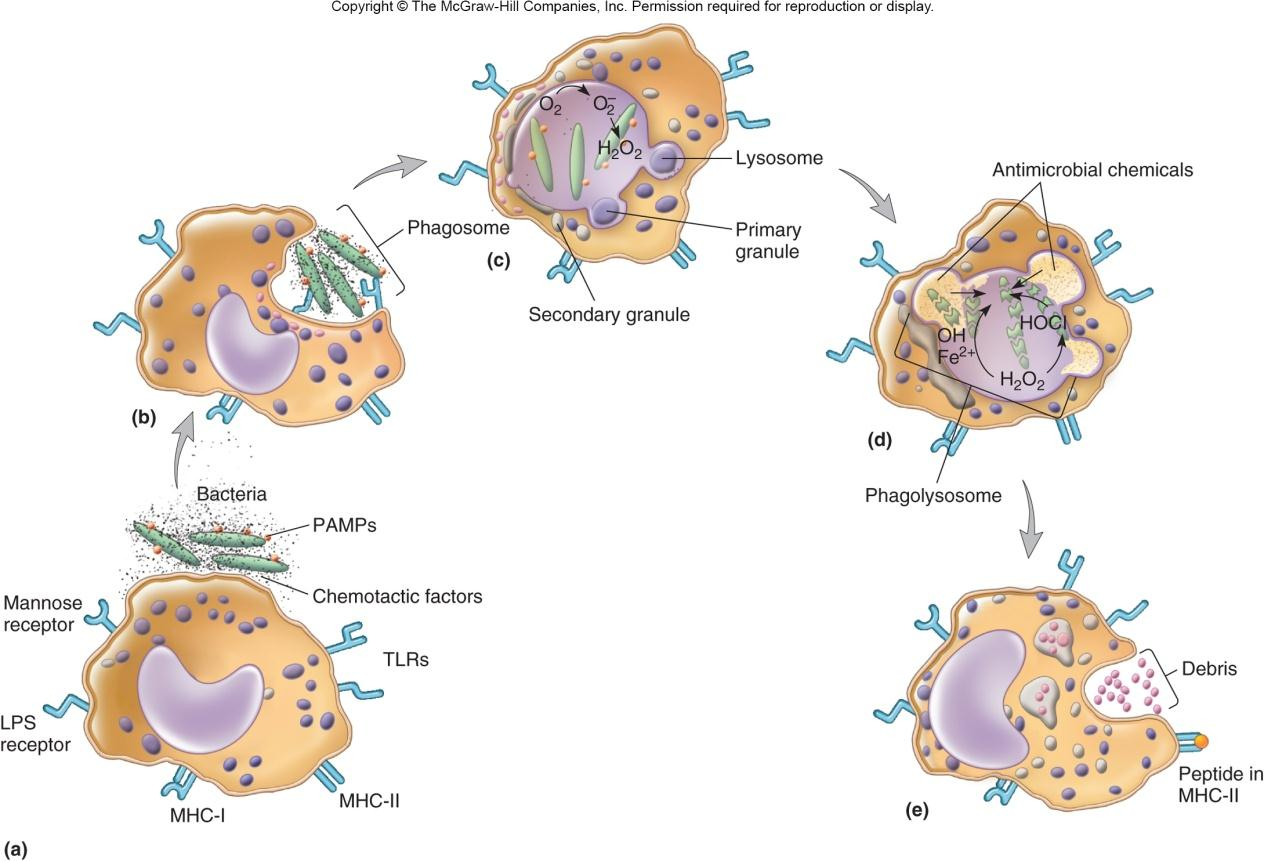
六、 Phagocytosis
Process by which phagocytic cells (monocytes, tissue macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils) recognize, ingest, and kill extracellular microbes
Two mechanisms for recognition of microbe by phagocyte
opsonin-dependent (opsonic) recognition
opsonin-independent (nonopsonic) recognition
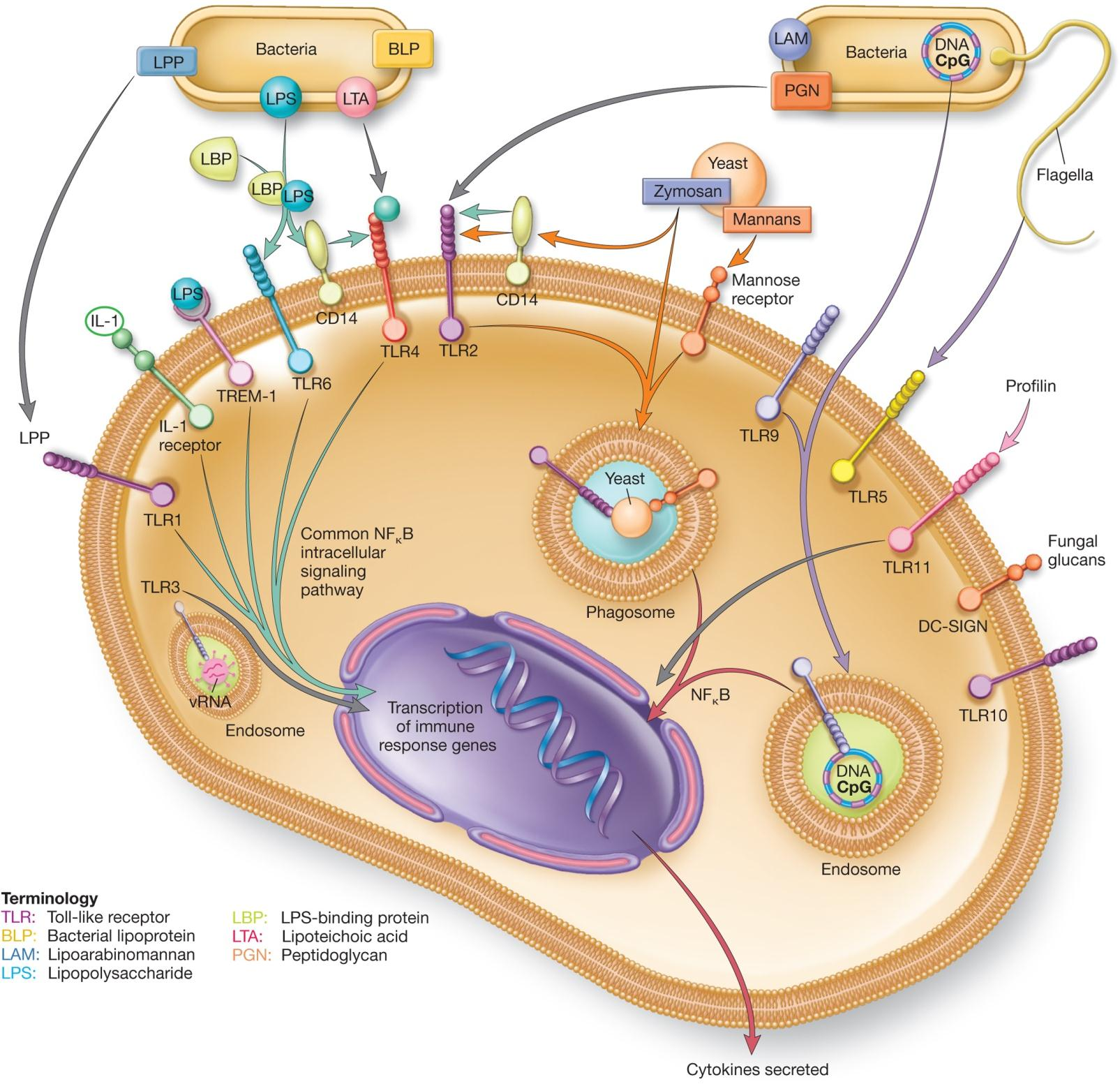
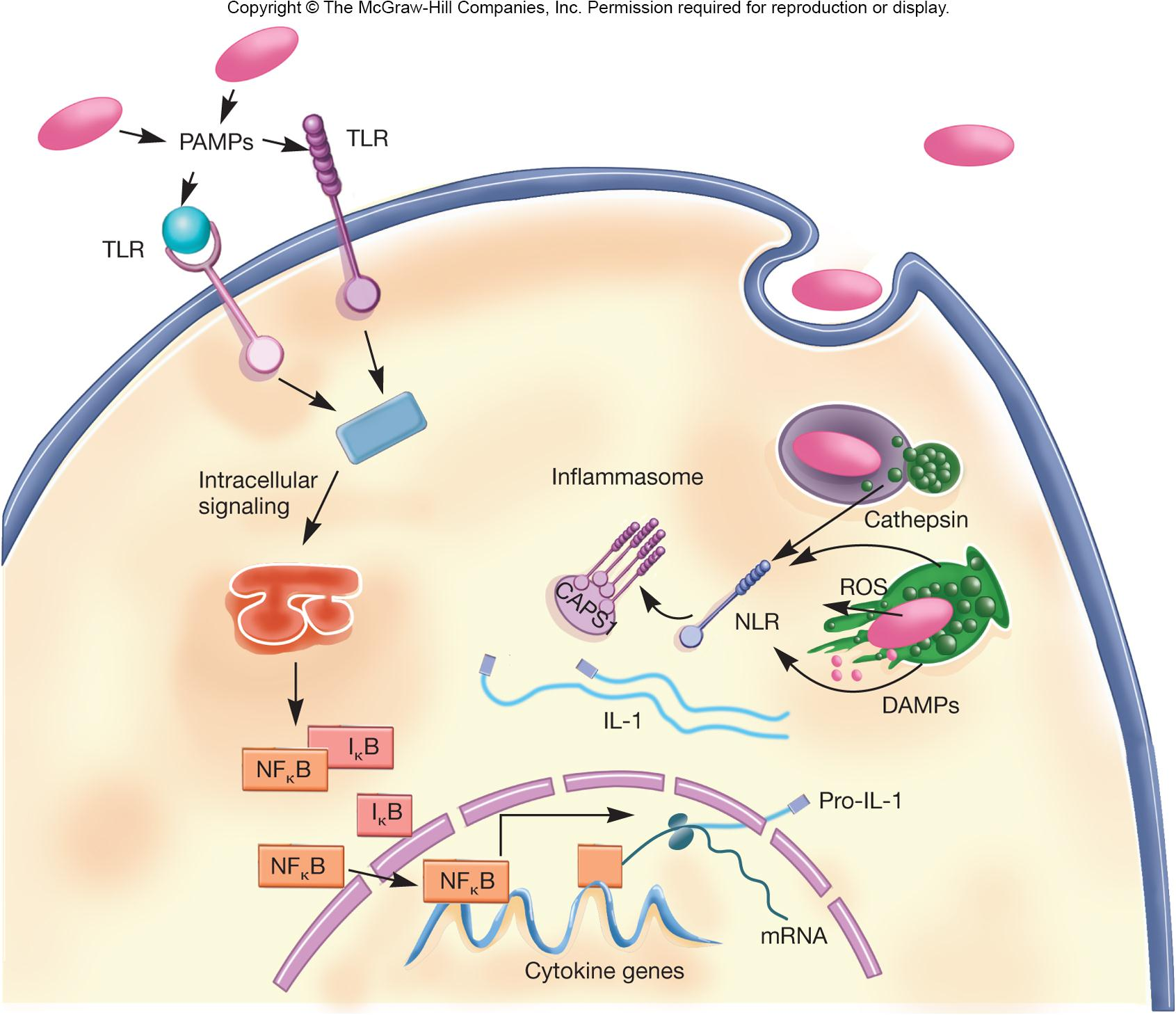
Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
conserved microbial molecular structures
PAMPs are unique to microbes, not present in host
e.g., LPS of Gram-negative bacteria
e.g., peptidoglycan of Gram-positive bacteria
PAMPs recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on/in phagocytic cells
1. TLR
The Process of Phagocytosis
七、 Inflammation
1. Nonspecific response to tissue injury
can be caused by pathogen or physical trauma (外伤;创伤)
acute and chronic inflammation
2. Cardinal signs
- redness
- warmth
- pain
- swelling
- altered function
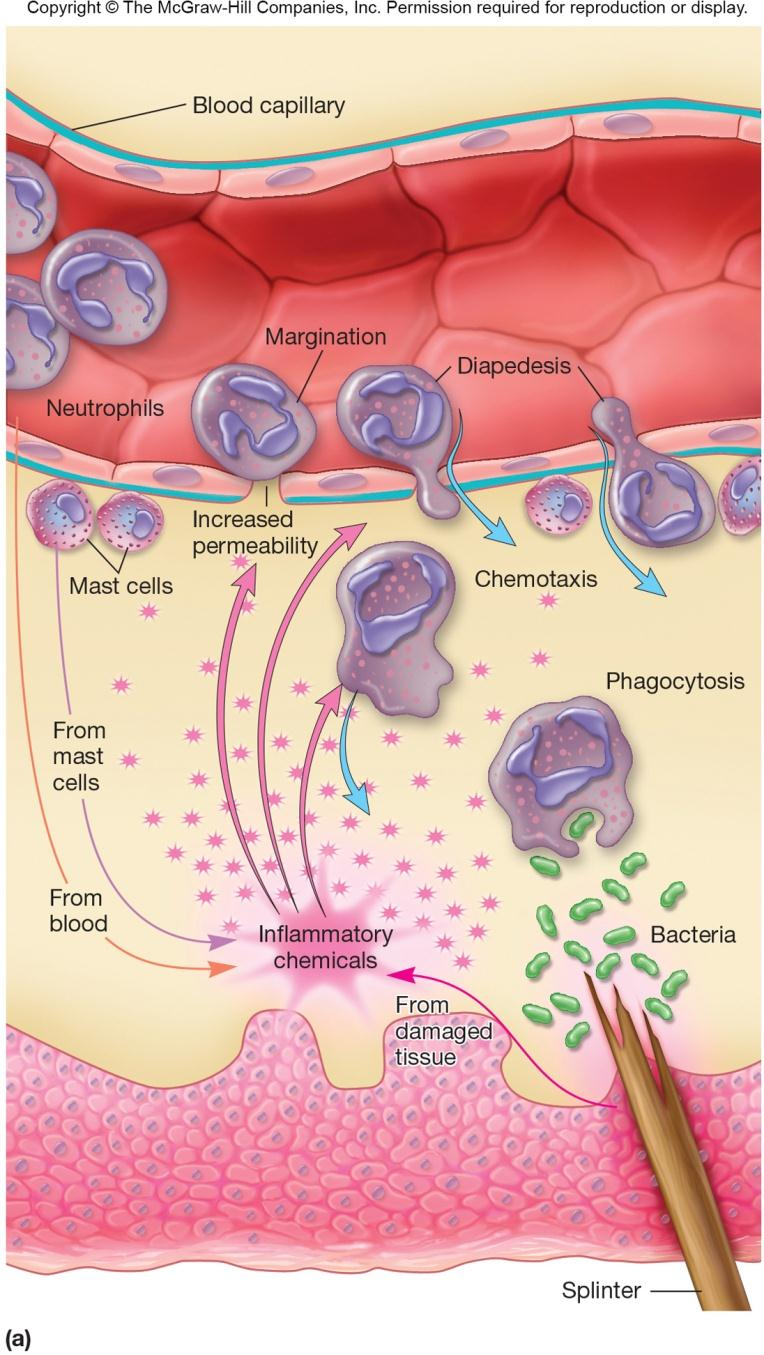
Acute Inflammatory Response
A cascade of events
Involves chemical mediators:
(1) selectins 选择素
cell adhesion molecules on activated capillary endothelial cells
选择素(英语:selectins,又译为选择蛋白,或称为表面抗原分化簇-62,即CD62)是一个细胞粘附分子CAM家族。所有的选择素都是单链跨膜糖蛋白,与C-型凝集素属性类似,有着相似的N-末端和钙依赖性。选择素能与糖链基团结合而被视为一种凝集素。
(2) integrins 集成素、整合素
adhesion receptors on neutrophils
集成素(英语:Integrin,又译为整联蛋白)是一种介导细胞和其外环境(如细胞外基质,ECM)之间的连接的跨膜受体。在信号转导中,集成素将ECM的化学成分与力学状态等有关信息传入细胞。 因此,集成素除了穿过膜的机械作用,也参与了细胞消息、细胞周期之调节、细胞型态以及细胞的运动。
通常,受体的作用是将外环境的变化通知细胞并引起细胞反应。但集成素不仅介导由外到内的信号,也介导由内到外的细胞信号。因此集成素不但将ECM的信息传递给细胞,也将细胞的状态表达给外界,从而可以迅速和灵活地响应环境中的变化,比如血液的凝固作用。
(3) chemotaxins 化学毒素、趋化因子类
chemotactic factors released by injured cells
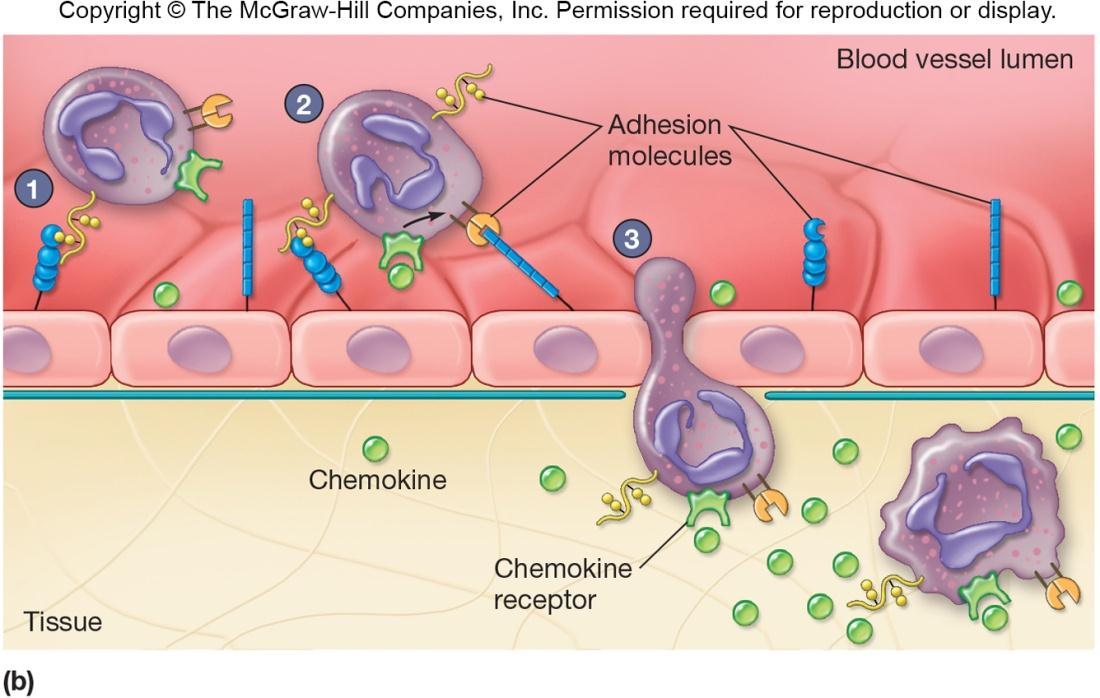
(4) margination 着边
着边(炎症初期白细胞附集于血管壁)
(5) diapedesis 血细胞渗出
血细胞渗出[血细胞从血管内渗出]
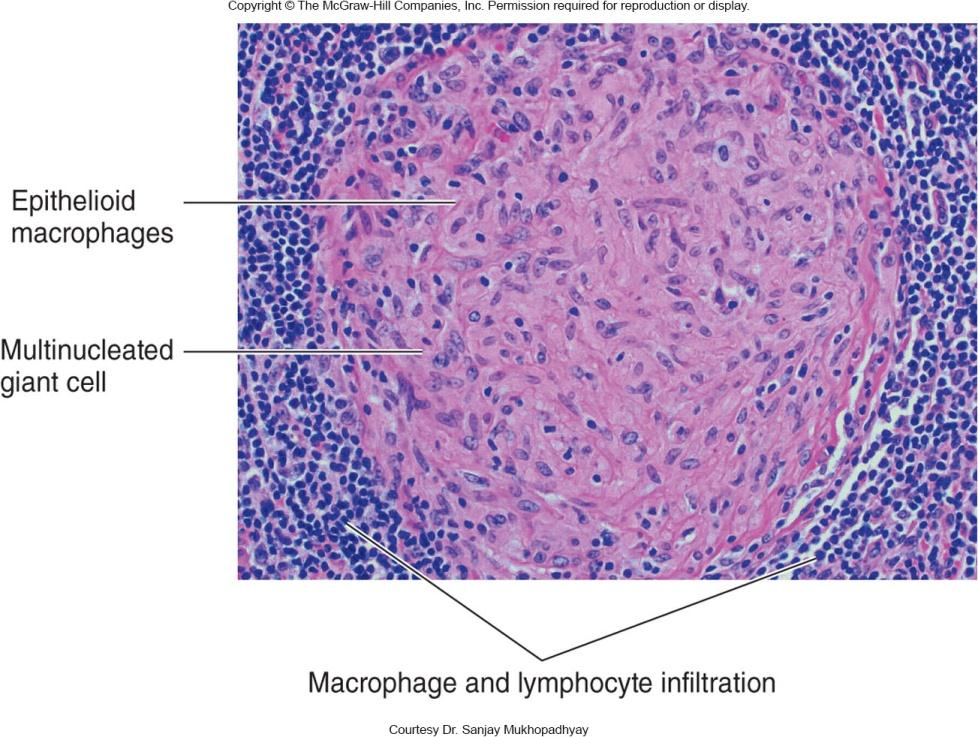
Chronic Inflammation
Slow process
Involves formation of new connective tissue
Usually causes permanent tissue damage
Dense infiltration of lymphocytes and macrophages at site of inflammation
- granuloma 肉芽肿,肉芽瘤
- formed when phagocytic cells can’t destroy pathogen